Слайд 2
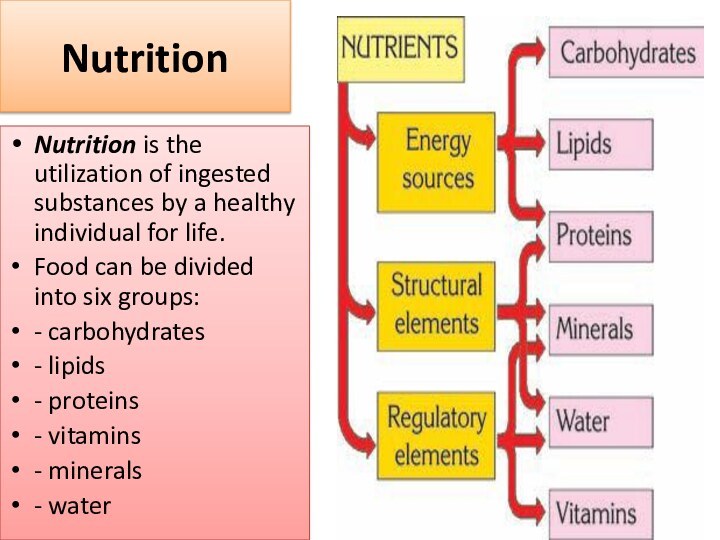
Nutrition
Nutrition is the utilization of ingested substances by
a healthy individual for life.
Food can be divided into
six groups:
- carbohydrates
- lipids
- proteins
- vitamins
- minerals
- water
Слайд 3
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy.
Carbohydrates are
abundant in cereals and their products, vegetables, fruits and
legumes.
Слайд 4
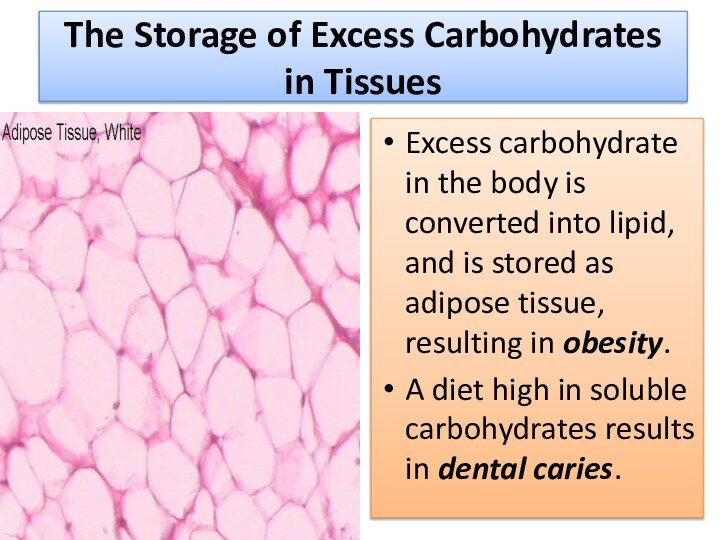
The Storage of Excess Carbohydrates in Tissues
Excess carbohydrate
in the body is converted into lipid, and is
stored as adipose tissue, resulting in obesity.
A diet high in soluble carbohydrates results in dental caries.
Слайд 5
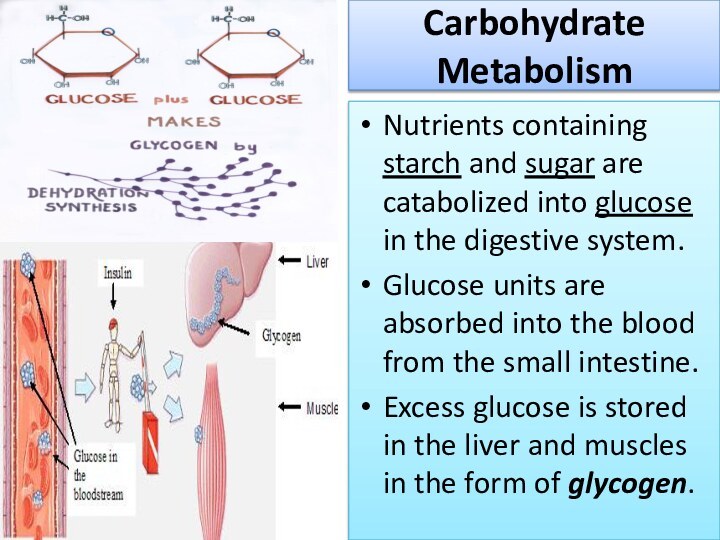
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Nutrients containing starch and sugar are catabolized
into glucose in the digestive system.
Glucose units are absorbed
into the blood from the small intestine.
Excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscles in the form of glycogen.
Слайд 6
Lipids
Gives the most energy
Excess lipid is stored in
adipose tissue.
Lipid sources are olives, nuts and egg, milk,
meat
Слайд 7
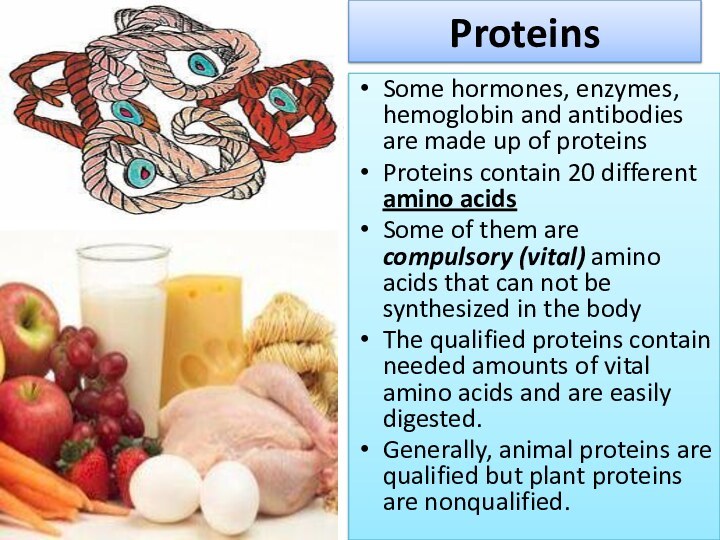
Proteins
Some hormones, enzymes, hemoglobin and antibodies are made
up of proteins
Proteins contain 20 different amino acids
Some of
them are compulsory (vital) amino acids that can not be synthesized in the body
The qualified proteins contain needed amounts of vital amino acids and are easily digested.
Generally, animal proteins are qualified but plant proteins are nonqualified.
Слайд 8
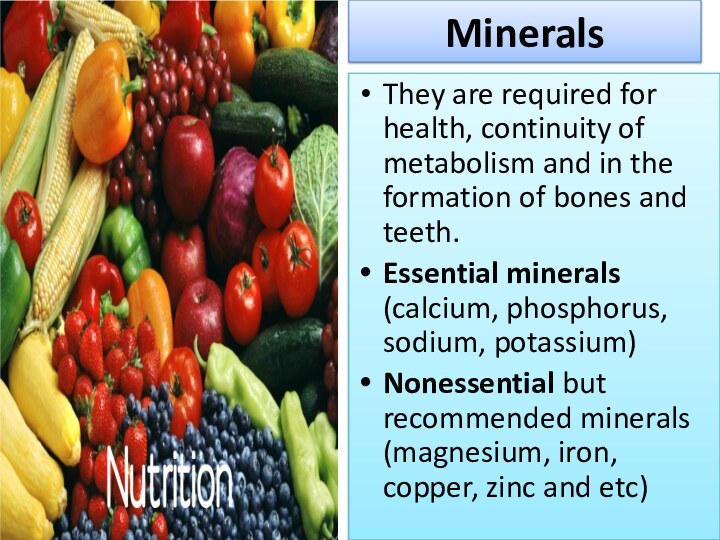
Minerals
They are required for health, continuity of metabolism
and in the formation of bones and teeth.
Essential minerals
(calcium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium)
Nonessential but recommended minerals (magnesium, iron, copper, zinc and etc)
Слайд 9
Water constitutes 60-70% of the body of an
adult.
Functions of water
--Absorption, transport and digestion of food
--Excretion of
metabolic wastes
--Regulation of body temperature
--In the absence of water, enzymes can not perform function
Water
Слайд 10
Vitamins
Vitamins were first discovered in 1890 when the
disease beriberi was found to be due to a
lack of vitamin B.
A small amount of vitamins is ingested in food and play important roles in regulation of the metabolism of the body.
The main source of vitamins is plants. However, animal tissues, especially liver, contain a rich supply of vitamins.
Слайд 11
Vitamins
Overheating of food, therefore, may cause destruction of
vitamins.
Functions of vitamins
--to give the body resistance to infection.
--to
prevent against bleeding and blood deficiency.
--to assist in formation, development and rigidity of bone tissue.
--to regulate growth, development and reproduction.
--to provide a regular program of nutrition.
Слайд 12
Capacity of energy in food. Daily energy requirement.
Diet
Слайд 13
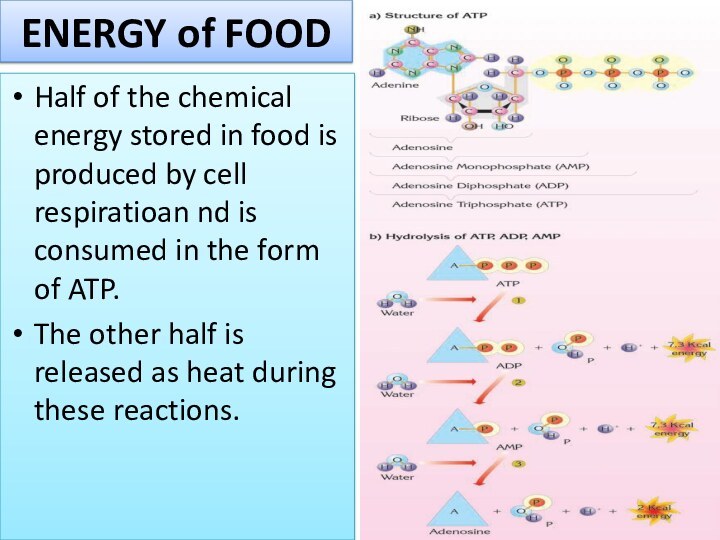
ENERGY of FOOD
Half of the chemical energy stored
in food is produced by cell respiratioan nd is
consumed in the form of ATP.
The other half is released as heat during these reactions.
Слайд 14
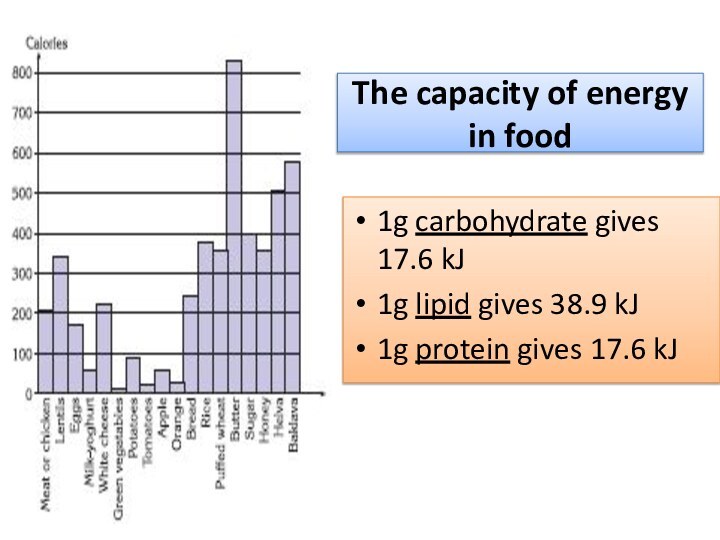
The capacity of energy in food
1g carbohydrate gives
17.6 kJ
1g lipid gives 38.9 kJ
1g protein gives 17.6
kJ
Слайд 15
Daily energy requirement of an organism
Basal metabolism, the
energy requirements of an individual at rest, is determined
at room temperature.
The basal metabolism is approximately 1700 kcal for males and 1600 kcal for females
Слайд 16
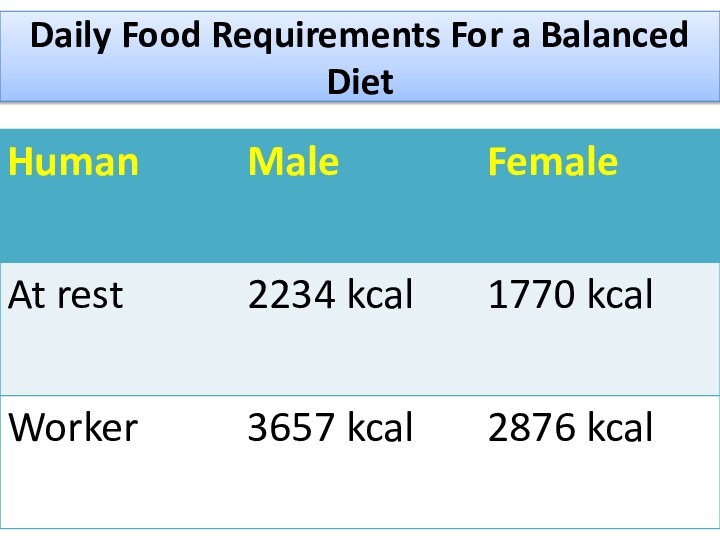
Daily Food Requirements For a Balanced Diet
The recommended
daily intake is 500 g of carbohydrate, 70 g
of lipid and 70 g of protein.
The energy requirements of organisms with heavy bodies are obviously greater than organisms with light bodies.
Слайд 17
Daily Food Requirements For a Balanced Diet