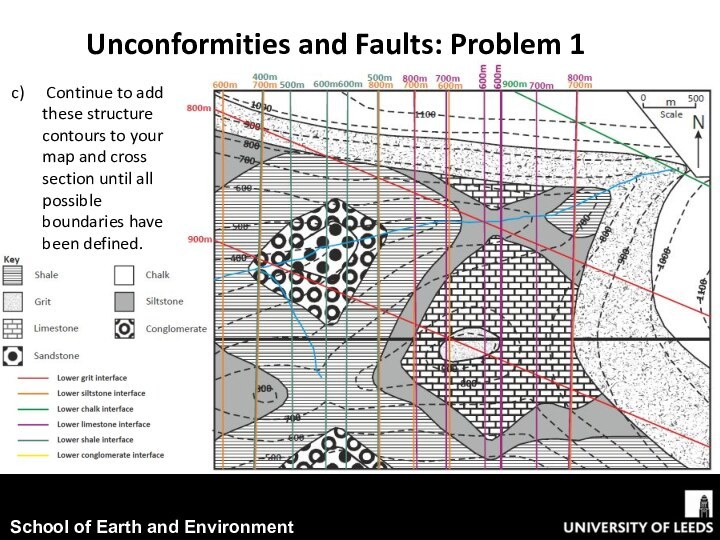
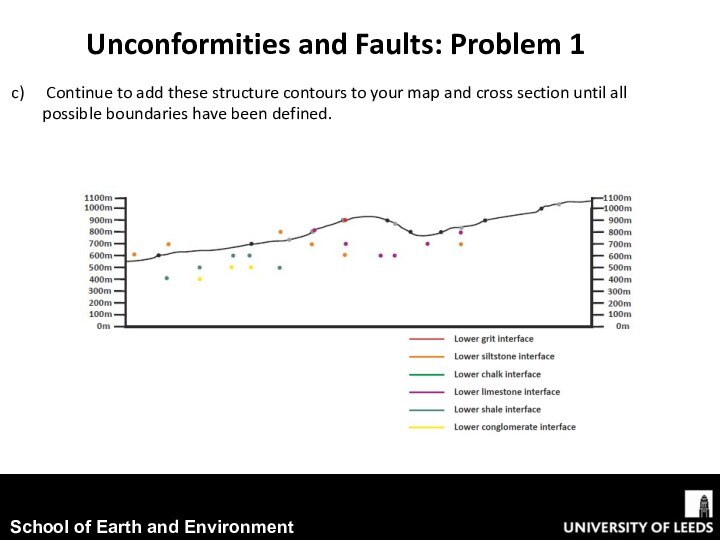
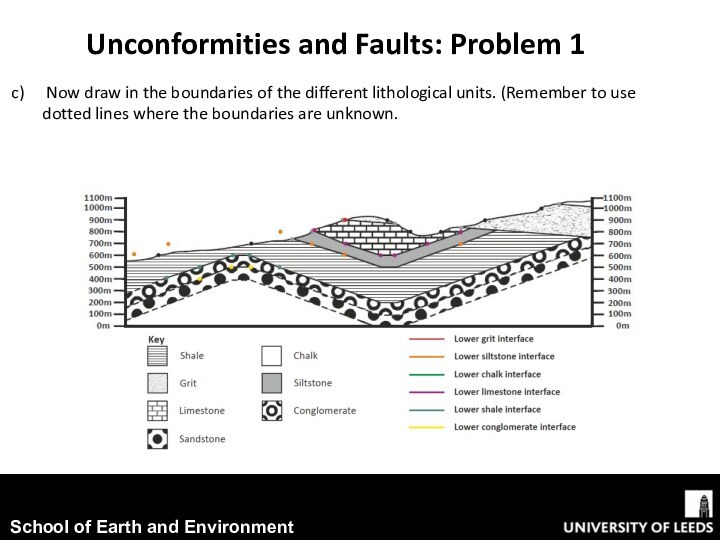
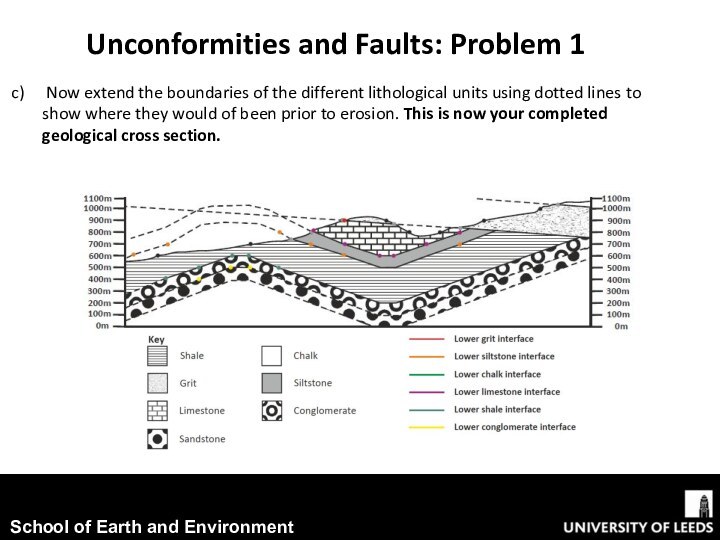
conjunction with exercise worksheet 5.
Objectives:
By the end of
this exercise you should:Be able to construct cross sections of unconformities.
Be able to calculate the throw and type of a fault.
Unconformities and Faults
This exercise will build on many of the concepts you have learnt so far, utilising:
Folded structures.
Fault terminology
Drawing cross sections.
Calculating true thickness.