Слайд 2
Overview
Definitions
Cognition
Expert Knowledge
Human Thinking and Learning
Implications for Management
Слайд 3
Definitions
Knowledge: Understanding gained through experience or study “know-how”
Intelligence:
Capacity to acquire and apply knowledge; thinking and reasoning;
ability to understand and use language
Memory: Ability to store and retrieve relevant experience at will; part of intelligence
Слайд 4
Definitions
Learning: Knowledge acquired by instruction or study; consequence
of intelligent problem solving
Experience: Relates to what we’ve done
and to knowledge; experience leads to expertise
Common Sense: Unreflective opinions of ordinary people
Heuristic: A rule of thumb based on years of experience
Слайд 5
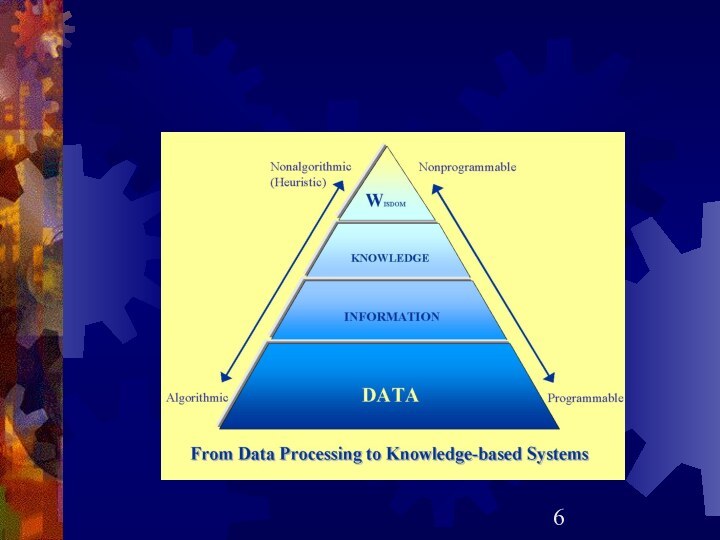
Data, Information, and Knowledge
Data: Unorganized and unprocessed facts;
static; a set of discrete facts about events
Information: Aggregation
of data that makes decision making easier
Knowledge is derived from information in the same way information is derived from data; it is a person’s range of information
Слайд 7
Data, Information, and Knowledge
Data is a set of
discrete facts about events
Information becomes knowledge with questions like
“what implications does this information have for my final decision?”
Knowledge is understanding of information based on its perceived importance
Knowledge, not information, can lead to a competitive advantage in business
Слайд 8
Types of Knowledge
Shallow (readily recalled) and deep (acquired
through years of experience)
Explicit (codified) and tacit (embedded in
the mind)
Procedural (psychomotor skills) versus episodical (chunked by episodes; autobiographical)
Chunking knowledge
Слайд 9
Knowledge as Know-How
Know-how distinguishes an expert from a
novice
Experts represent their know-how in terms of heuristics, based
on experience
Know-how is not book knowledge; it is practical experience
Слайд 10
Reasoning and Heuristics
Humans reason in a variety of
ways:
Reasoning by analogy: relating one concept to another
Formal reasoning:
using deductive or inductive methods
Case-based reasoning: reasoning from relevant past cases
Слайд 11
Deductive and inductive reasoning
Deductive reasoning: exact reasoning. It
deals with exact facts and exact conclusions
Inductive reasoning: reasoning
from a set of facts or individual cases to a general conclusion
FROM PROCEDURAL TO EPISODIC KNOWLEDGE
Shallow
Procedural Knowledge
Knowledge
Knowledge of how to do a task that is essentially motor in
nature; the same knowledge is used over and over again.
_______________________________________________
Declarative Knowledge
Surface-type information that is available in short-term
memory and easily verbalized; useful in early stages
of knowledge capture but less so in later stages.
_______________________________________________
Semantic Knowledge
Hierarchically organized knowledge of concepts, facts,
and relationships among facts.
_______________________________________________
Episodic Knowledge
Knowledge that is organized by temporal spatial means,
not by concepts or relations; experiential information that
is chunked by episodes. This knowledge is highly compiled
Deep and autobiographical and is not easy to extract or capture.
Knowledge
Слайд 13
EXPLICIT AND TACIT KNOWLEDGE
Explicit knowledge: knowledge codified and
digitized in books, documents, reports, memos, etc.
Tacit knowledge: knowledge
embedded in the human mind through experience and jobs
Tacit and explicit knowledge have been expressed in terms of knowing-how and knowing-that, respectively
Understanding what knowledge is makes it easier to understand that knowledge hoarding is basic to human nature.
Слайд 14
Knowledge As An Attribute of Expertise
An expert in
a specialized area masters the requisite knowledge
The unique performance
of a knowledgeable expert is clearly noticeable in decision-making quality
Knowledgeable experts are more selective in the information they acquire
Experts are beneficiaries of the knowledge that comes from experience
See Figure 2.5 next: academic knowledge contributes to conceptual knowledge—a prerequisite for practical knowledge