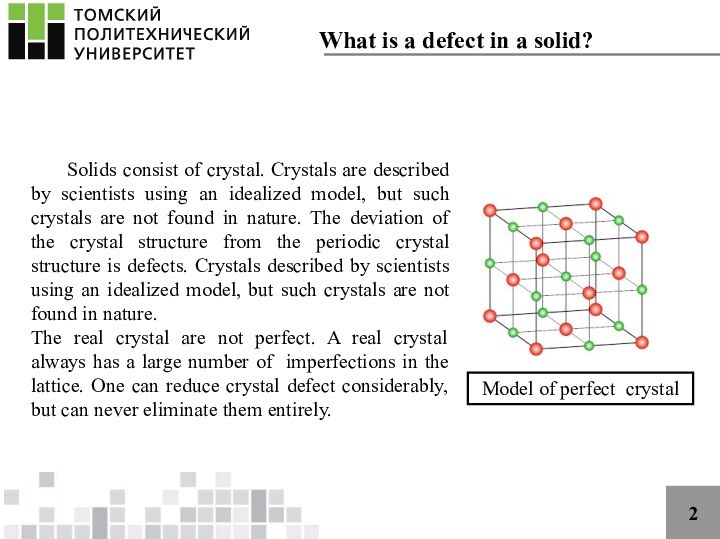
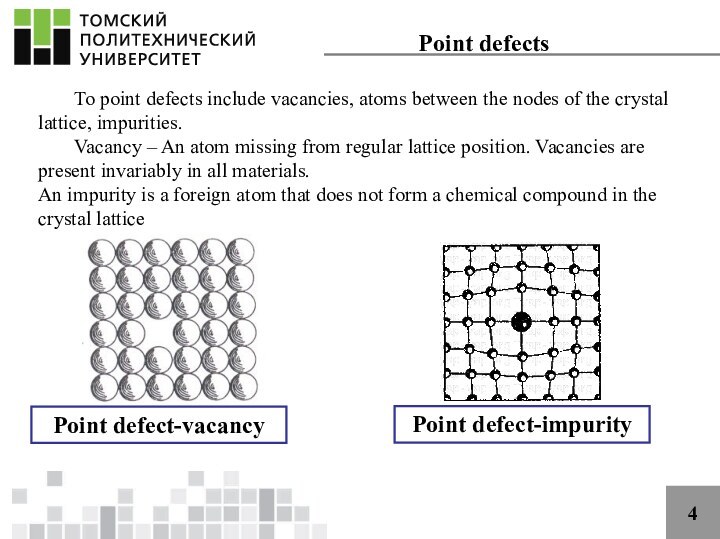
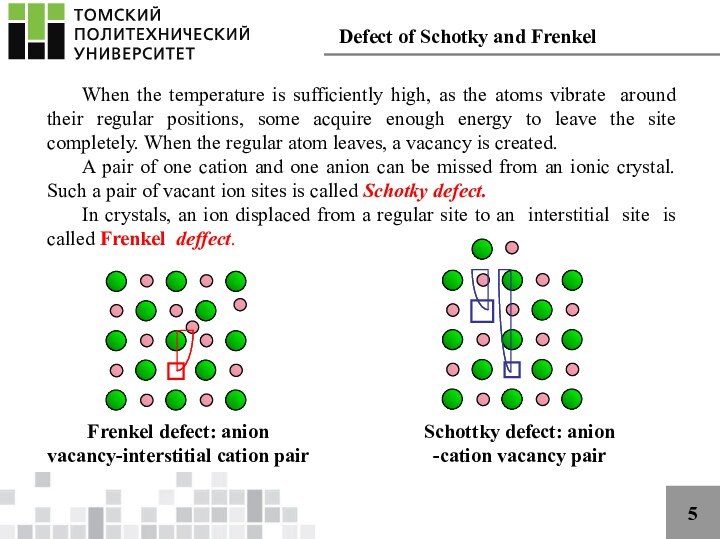
scientists using an idealized model, but such crystals are
not found in nature. The deviation of the crystal structure from the periodic crystal structure is defects. Crystals described by scientists using an idealized model, but such crystals are not found in nature.The real crystal are not perfect. A real crystal always has a large number of imperfections in the lattice. One can reduce crystal defect considerably, but can never eliminate them entirely.
Model of perfect crystal
What is a defect in a solid?