- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Allergy. (Subject 3)
Содержание
- 2. Immune system disordersWeakened immune response:Primary immunodeficiencySecondary immunodeficiencyExcessive immune response:Allergic reactionsAutoimmune reactions
- 3. Antigen - any substance that can stimulate
- 4. Allergy classification by P. G. H.
- 5. Pathogenesis of allergyAbsence of antibodiesPresence of antibodies to hen’s fluff (75 -90%)Allergy manifestation 10-15%
- 6. Immune and Allergic reactionsSimilar features: protection of
- 7. Hereditary Predisposition to Allergyincreased permeability of barriers↑
- 8. Immunological Stage of Allergic Reaction revealing
- 9. Biochemical Stage of Allergic Reactionallergen interaction
- 10. The stage of allergy clinical manifestation (type
- 11. Type 1 Allergic Reactions (anaphylactic,
- 12. Immunological StageTransformation to blastcytokinesPhagocytehelpersuppressorIgE and IgGAllergen
- 13. Immunological Stage ResultMast Cell Fixation of antibodies
- 14. Biochemical StageMast CellMediators of Allergy
- 15. Classification of Allergy MediatorsPrimary(pre-stored) HistamineHeparineSerotonineSecondary(new synthesis)ProstaglandinsLeukotrienesCytokines
- 16. Primary Mediators EffectsHistamine & Serotonin – vasodilation,
- 17. Secondary Mediators Leukotrienes - ↑ vessels permeability,
- 18. Type 2 allergic reactions (antibody-dependent cytotoxicity)Transfusion
- 19. Antibody-dependent mechanisms of cell damage Target cellM A CopsonizationMAC - membrane attack complex
- 20. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity enzymesmacrophagesneutrophils, eosinophils, natural killers
- 21. Type 5 allergic reactions (stimulating reactions)Autoimmune thyroiditis
- 22. Type 3 allergic reactions (immune complexes)Immune complex
- 23. Features of type 3 hypersensitivityCirculation of immune
- 24. Phases of the systemic immune-complex diseaseformation of
- 25. Serum SicknessBlood plasma amountT I M ESerumAntibodies to serumClinical signs and symptoms
- 26. Pathogenic properties of immune complexesThe amount
- 27. Mechanism of tissue injury by immune complexesVessel wallEnzymesActive O2 radicals
- 28. Local Manifestation of Immunocomplex ReactionArthus reaction -
- 29. Type 4 allergic reactions (cell-mediated, delayed)
- 30. Type 4 hypersensitivityImmunological stage - production of
- 31. Mechanisms of tissue injury T-killers (perforins, granzymes) phagocytes (active oxygen radicals)lysosomal enzymesgranulomatous (specific) inflammation
- 32. Pseudoallergy distinctive featuresSensitization (immunologic) phase is absentSymptoms
- 33. Pseudo-allergy mechanismsNon-immune degranulation of mast cells (histamine
- 34. The mechanisms of self reactivity prevention
- 35. Mechanisms of autoimmune diseasesDamage of physiological isolation
- 36. General mechanisms of autoimmune pathology Direct
- 37. Hyposensitization The patient is gradually vaccinated with
- 38. Скачать презентацию
- 39. Похожие презентации
Immune system disordersWeakened immune response:Primary immunodeficiencySecondary immunodeficiencyExcessive immune response:Allergic reactionsAutoimmune reactions

































Слайд 2
Immune system disorders
Weakened immune response:
Primary immunodeficiency
Secondary immunodeficiency
Excessive immune
response:
Слайд 3 Antigen - any substance that can stimulate immune
system
Allergen – any substance that can induce allergy
Allergy –
excessive reaction of immune system to normally harmless substance House Dust Mite
Pollen
Слайд 4 Allergy classification by P. G. H. Gell and
R. R. A. Coombs
Type I hypersensitivity - Anaphylactic
reactions.Type II hypersensitivity - Cytotoxic reactions.
Type III hypersensitivity - Reactions mediated by immune complexes.
Type IV hypersensitivity - Cell mediated reactions.
Type V hypersensitivity - Stimulating allergic reactions.
Слайд 5
Pathogenesis of allergy
Absence of antibodies
Presence of antibodies to
hen’s fluff (75 -90%)
Allergy manifestation 10-15%
Слайд 6
Immune and Allergic reactions
Similar features:
protection of the
organism from genetically foreign ones
similar mechanisms of reactions
mediated
with immune cellsDistinctive features of allergic reactions:
increased reactivity
transformed character of immune answer
tissue injury
Слайд 7
Hereditary Predisposition to Allergy
increased permeability of barriers
↑ activity
of T-helpers, ↑ synthesis of IgE
↑ synthesis of allergic
mediators↓ inactivation of allergic mediators
hyperreactivity of bronchi, skin.
Allergic diseases with hereditary predisposition – atopic diseases – type 1 hypersensitivity
Слайд 8
Immunological Stage
of Allergic Reaction
revealing the allergen
presentation of the allergen to lymphocytes
Ig synthesis
immune memory
cells formationfixation of the antibodies or T-killers in the site of allergen localization
Слайд 9
Biochemical Stage
of Allergic Reaction
allergen interaction with specific
antibodies or sensitized lymphocytes;
release or synthesis of biologically active
substances – mediators of allergy.
Слайд 10
The stage of allergy clinical manifestation (type 1)
Local
signs:
Itching, pain, rashes
Nasal congestion
? Mucus secretion.
Systemic Signs
of AllergySmooth muscles constriction
bronchi (problems with breathing)
GIT (abdominal cramps)
Swelling of tongue, mouth
Vessels dilation, hypotension, shock
Слайд 11
Type 1 Allergic Reactions
(anaphylactic, reaginic)
Allergic asthma
Conjunctivitis
Allergic rhinitis ("hay fever")
Anaphylactic shock
Angionevrotic edema (Quincke's disease)
Urticaria
(hives).
Слайд 12
Immunological Stage
Transformation to blast
cytokines
Phagocyte
helper
suppressor
IgE and IgG
Allergen
Слайд 13
Immunological Stage Result
Mast Cell
Fixation of antibodies on
the mast cells and basophils
Its possible to detect
IgE in blood serum (diagnosis of type 1 hypersensitivity)
Слайд 15
Classification of Allergy Mediators
Primary
(pre-stored)
Histamine
Heparine
Serotonine
Secondary
(new synthesis)
Prostaglandins
Leukotrienes
Cytokines
Слайд 16
Primary Mediators Effects
Histamine & Serotonin – vasodilation, ?
vascular permeability, ? tone of smooth muscle cells
Histamine +
pain, itchingSerotonin + ? secretion of mucus.
Heparin decreases blood clotting
Chemotaxins for neutrophils and eosinophils – provide the movement of the neutrophils and eosinophils
Слайд 17
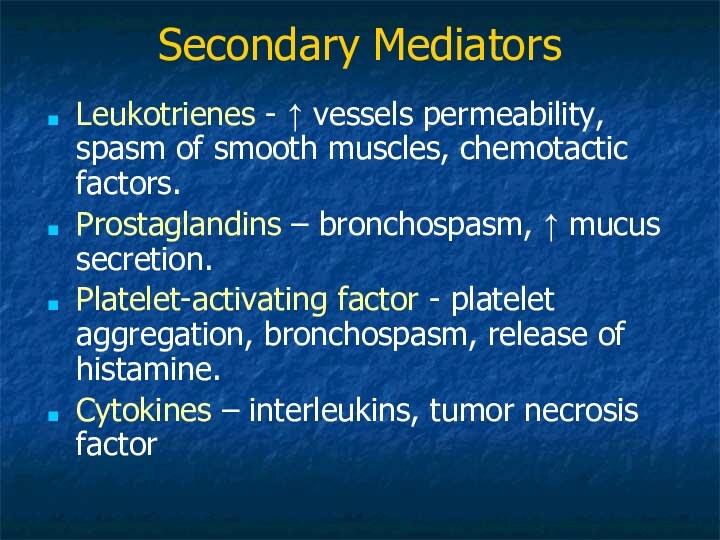
Secondary Mediators
Leukotrienes - ↑ vessels permeability, spasm
of smooth muscles, chemotactic factors.
Prostaglandins – bronchospasm, ↑ mucus
secretion. Platelet-activating factor - platelet aggregation, bronchospasm, release of histamine.
Cytokines – interleukins, tumor necrosis factor
Слайд 18
Type 2 allergic reactions
(antibody-dependent cytotoxicity)
Transfusion reactions, autoimmune
anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, thyroiditis.
Transformation of own antigens to
“non-self” antigens by chemicals, viruses.The cell with transformed antigen – target cell
Synthesis of IgG and IgM against target cell antigens
Слайд 19
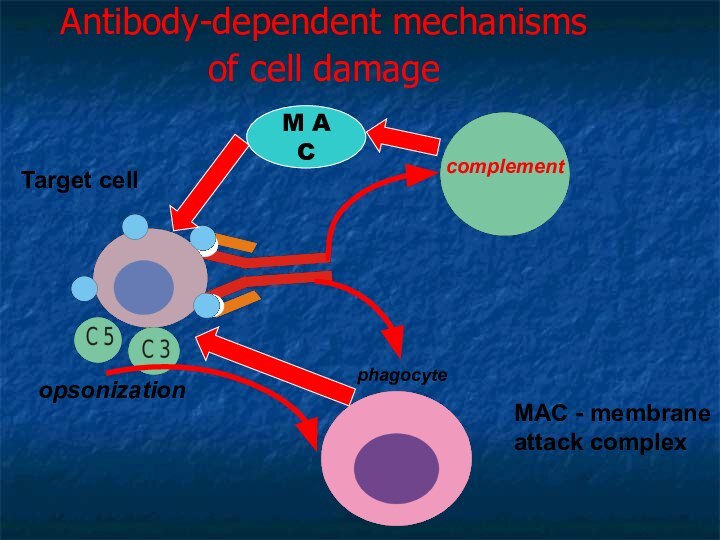
Antibody-dependent mechanisms
of cell damage
Target cell
M A
C
opsonization
MAC - membrane attack complex
Слайд 20
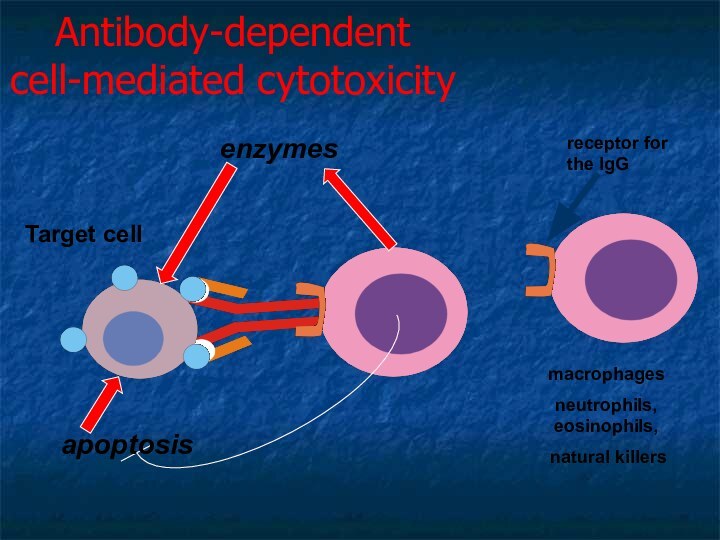
Antibody-dependent
cell-mediated cytotoxicity
enzymes
macrophages
neutrophils, eosinophils,
natural killers
Слайд 21
Type 5 allergic reactions (stimulating reactions)
Autoimmune thyroiditis
Antibodies
bind to TSH receptor on thyroid epithelial cells and
STIMULATE themThyroid gland hyperplasia
Excessive secretion of thyroid hormones.
Слайд 22
Type 3 allergic reactions
(immune complexes)
Immune complex glomerulonephritis
Serum sickness
Arthus
reaction (local reaction)
Antigens – antibiotics, Ig (serum as
medicine), bacteria, viruses
Слайд 23
Features of type 3 hypersensitivity
Circulation of immune complexes
in blood (systemic diseases)
IgG and IgM
Involvement of complement and
phagocytes in tissue injuryLow blood complement level
Слайд 24
Phases of the systemic immune-complex disease
formation of antigen-antibody
complexes in circulation;
deposition of the immune complexes in various
tissues;inflammatory reaction in the site of immune complexes deposition.
Слайд 25
Serum Sickness
Blood plasma amount
T I M E
Serum
Antibodies to
serum
Clinical signs and symptoms
Слайд 26
Pathogenic properties
of immune complexes
The amount of antigen
- large enough to form immune complexes.
The size of
the complexes - intermediate or small.The dysfunction or overloading of phagocyte system.
Deposition of immune complexes: kidneys, joints, skin, heart, lungs, arterioles.
Слайд 28
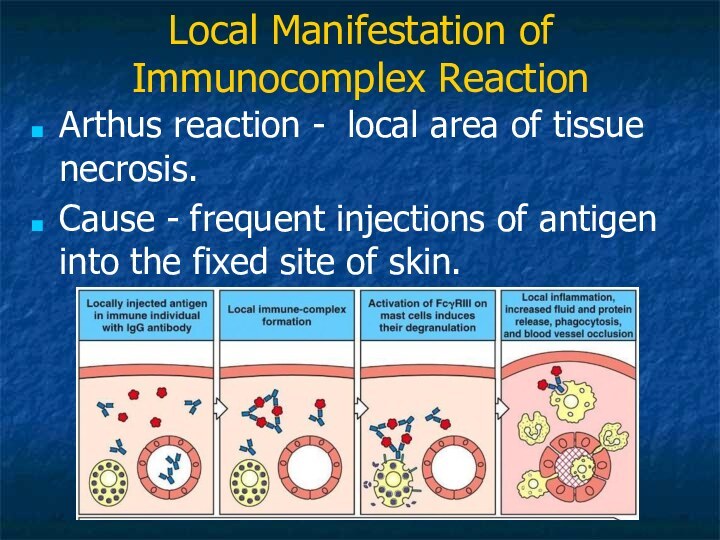
Local Manifestation of Immunocomplex Reaction
Arthus reaction - local
area of tissue necrosis.
Cause - frequent injections of
antigen into the fixed site of skin.
Слайд 29
Type 4 allergic reactions
(cell-mediated, delayed)
Tuberculin test
(Mantoux reaction )
Tuberculosis and leprosy
Transplant rejection
Viral infection
Tumor cells
Слайд 30
Type 4 hypersensitivity
Immunological stage - production of sensitized
T-lymphocytes
Cell injury is mediated by phagocytes and cytokines.
Cytokines function:
Organization
and regulation of immune response and inflammationCell injury (perforation of membranes, induction of apoptosis)
Слайд 31
Mechanisms of tissue injury
T-killers (perforins, granzymes)
phagocytes
(active oxygen radicals)
lysosomal enzymes
granulomatous (specific) inflammation
Слайд 32
Pseudoallergy distinctive features
Sensitization (immunologic) phase is absent
Symptoms can
occur at the first exposure.
The symptoms are directly
depend on the dose of the substance
Слайд 33
Pseudo-allergy mechanisms
Non-immune degranulation of mast cells (histamine –
liberating substances).
The alternative pathway of complement activation (without action
of specific IgG and M antibodies).Disturbances of arachidonic acid metabolism – aspirin asthma
Слайд 34
The mechanisms
of self reactivity prevention
Selection and
deletion of self-reactive T-cells and B-cells.
Peripheral suppression by
T-suppressor
cells.
Слайд 35
Mechanisms of autoimmune diseases
Damage of physiological isolation (nervous
system, a crystalline lens, thyroid gland).
Altering of self-antigens (burns,
medicines, chemicals).Similarity of exogenous antigen to self antigen:
(streptococci antigens are similar to myocardial and kidneys antigens).
Primary changes of immune system.
Слайд 36
General mechanisms
of autoimmune pathology
Direct antibody mediated
effects (diabetes mellitus, autoimmune hemolytic anemia)
T cell mediated effects
(psoriasis)Immune complex mediated effects (lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid artritis)