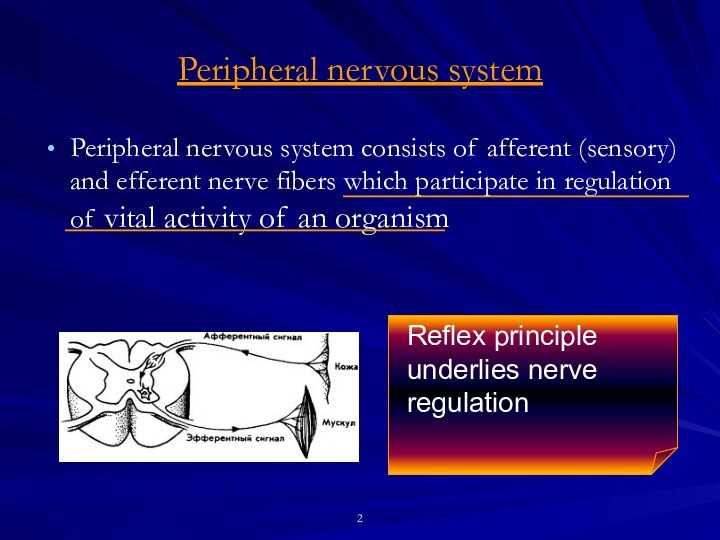
(sensory) and efferent nerve fibers which participate in regulation
of vital activity of an organismReflex principle underlies nerve regulation
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть

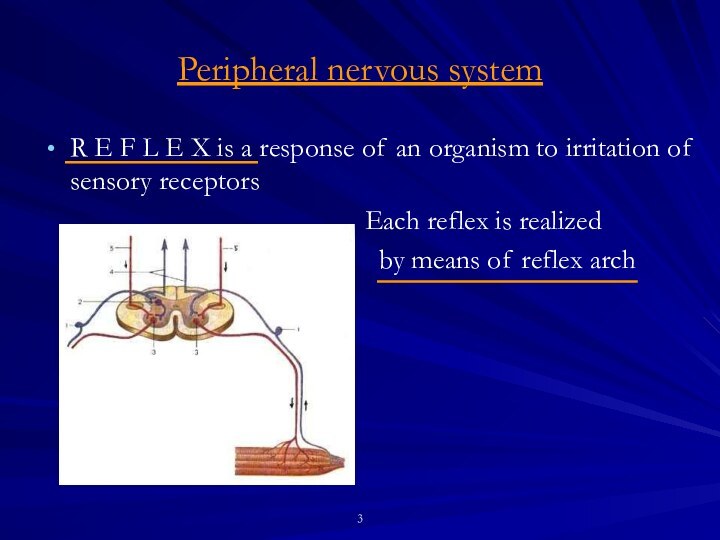






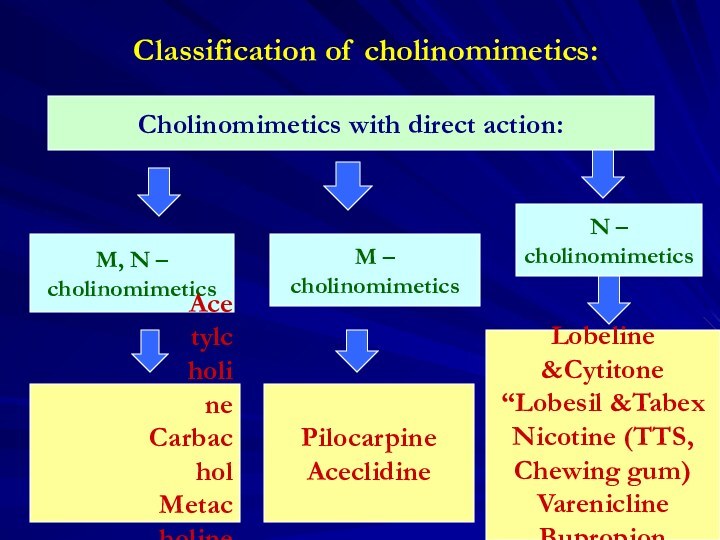
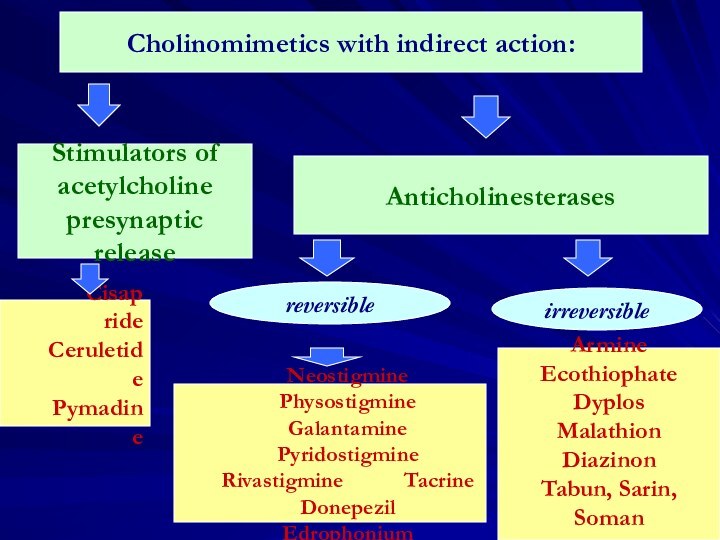














Reflex principle underlies nerve regulation
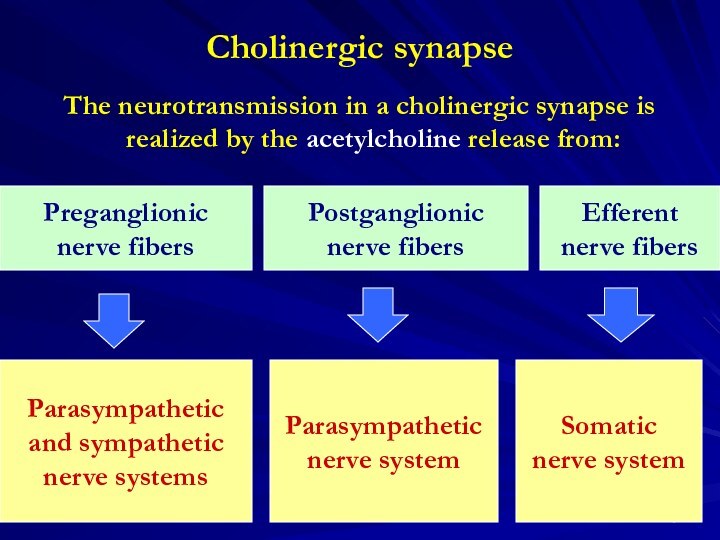
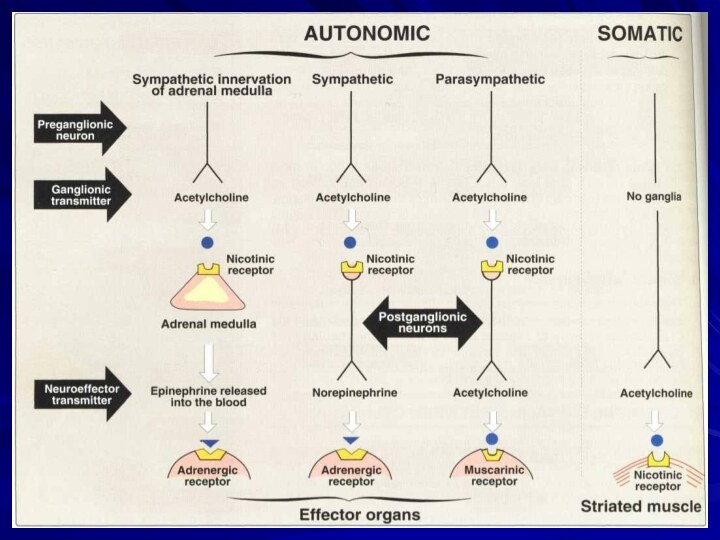
Efferent
nerve fibers
Parasympathetic
and sympathetic
nerve systems
Parasympathetic
nerve system
Somatic
nerve system
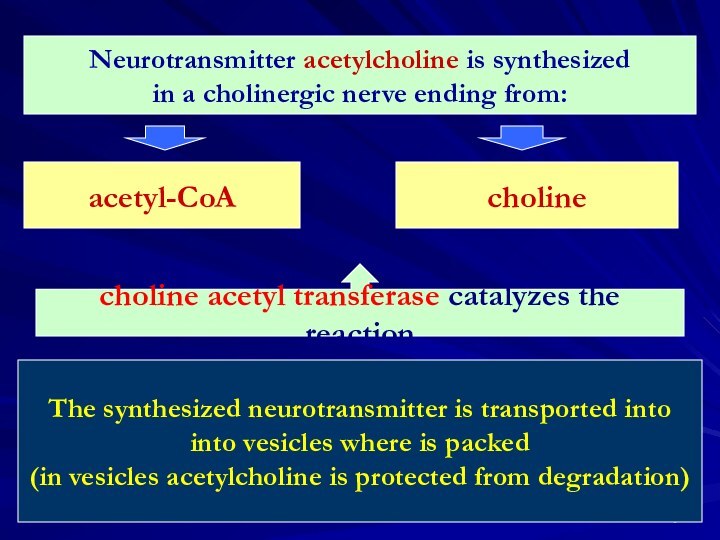
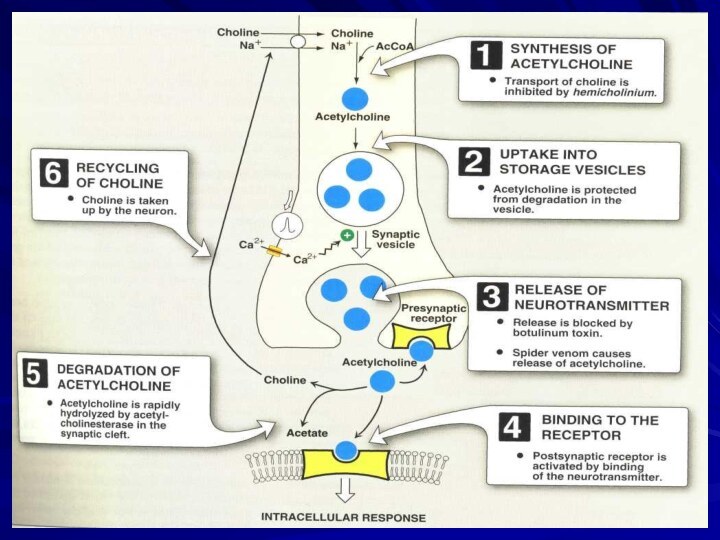
The synthesized neurotransmitter is transported into
into vesicles where is packed
(in vesicles acetylcholine is protected from degradation)
It happens when an action potential arrives
at a nerve ending
Increase in endocellular concentration of calcium occurs
and in turn, it causes the fusion of vesicles with
membrane surface and release of their content
(Ach, co-transmitters- ATP) into the synaptic cleft
by exocytosis.
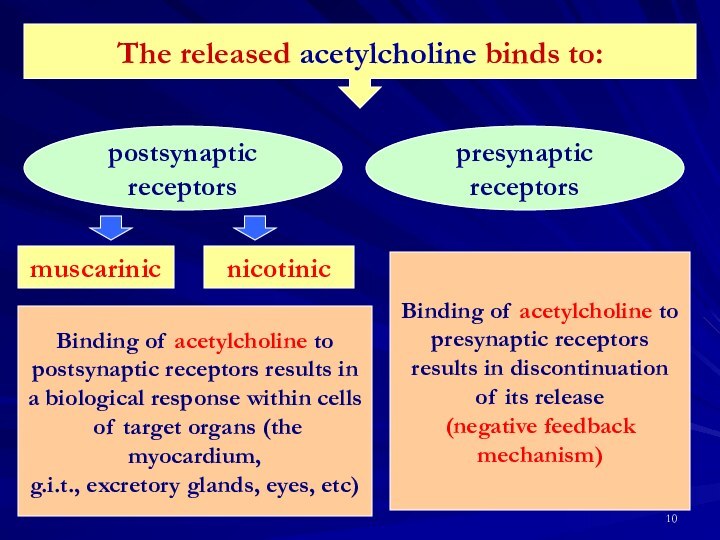
Binding of acetylcholine to
presynaptic receptors
results in discontinuation
of its release
(negative feedback
mechanism)
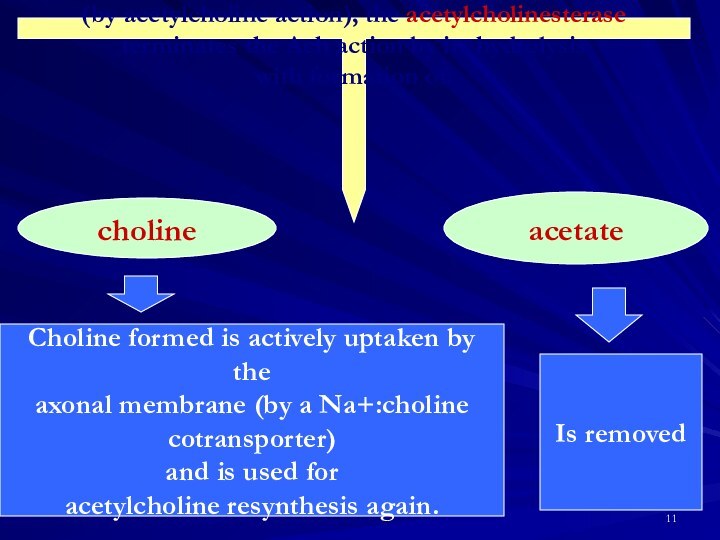
choline
acetate
Choline formed is actively uptaken by the
axonal membrane (by a Na+:choline
cotransporter)
and is used for
acetylcholine resynthesis again.
Is removed
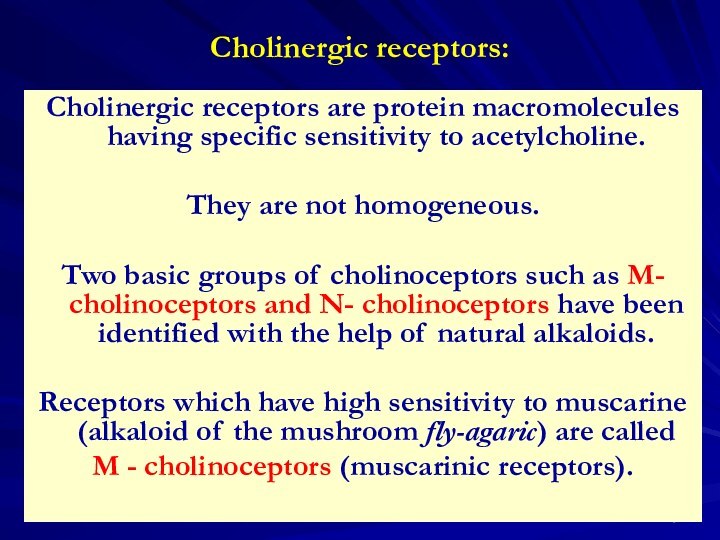
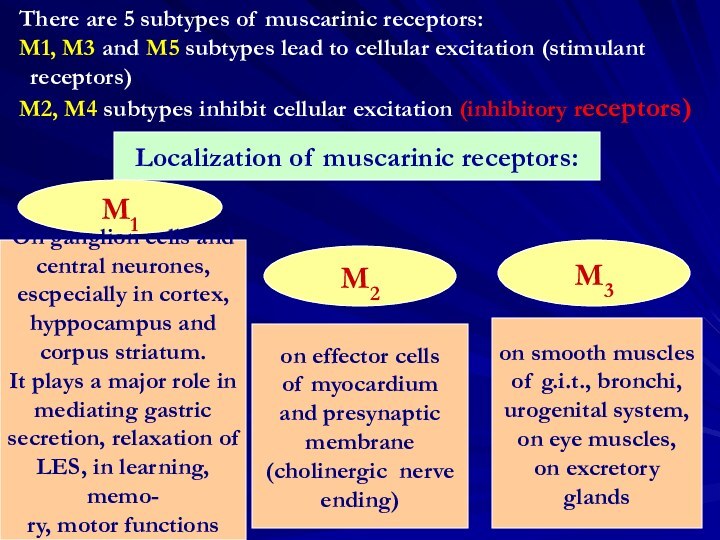
Localization of muscarinic receptors:
M1
M2
M3
On ganglion cells and
central neurones,
escpecially in cortex,
hyppocampus and
corpus striatum.
It plays a major role in
mediating gastric
secretion, relaxation of
LES, in learning, memo-
ry, motor functions
on effector cells
of myocardium
and presynaptic
membrane
(cholinergic nerve
ending)
on smooth muscles
of g.i.t., bronchi,
urogenital system,
on eye muscles,
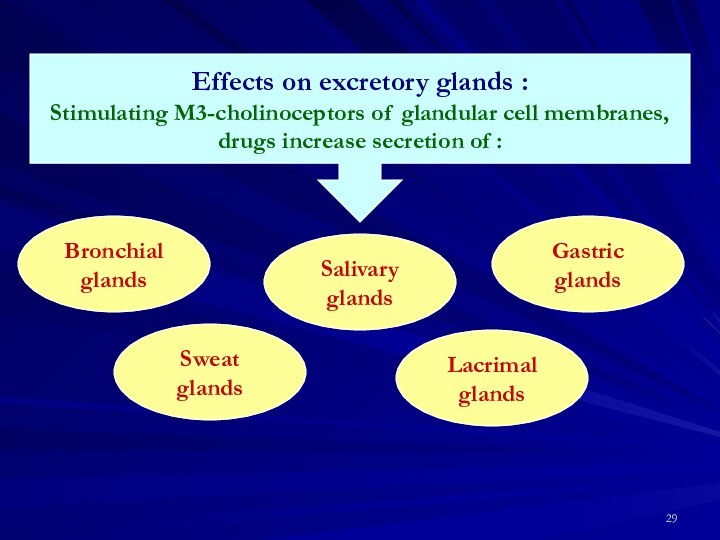
on excretory glands
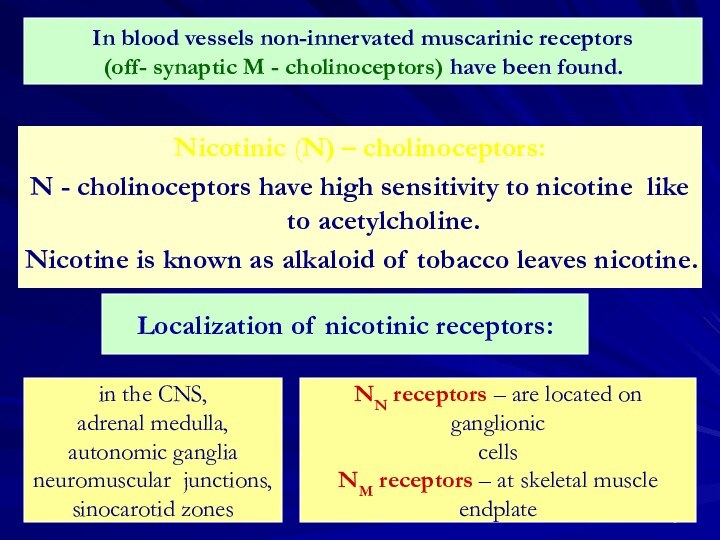
Localization of nicotinic receptors:
in the CNS,
adrenal medulla,
autonomic ganglia
neuromuscular junctions,
sinocarotid zones
In blood vessels non-innervated muscarinic receptors
(off- synaptic M - cholinoceptors) have been found.
NN receptors – are located on ganglionic
cells
NM receptors – at skeletal muscle
endplate
reversible
irreversible
Armine
Ecothiophate
Dyplos
Malathion
Diazinon
Tabun, Sarin, Soman
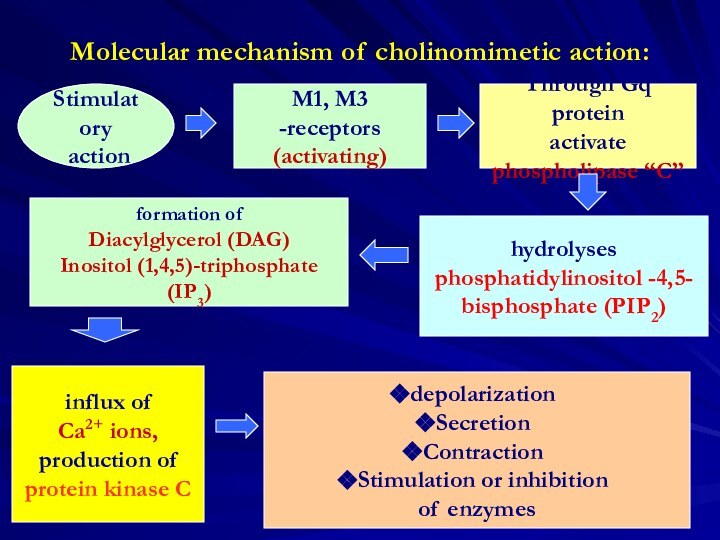
depolarization
Secretion
Contraction
Stimulation or inhibition
of enzymes
influx of
Ca2+ ions,
production of
protein kinase C
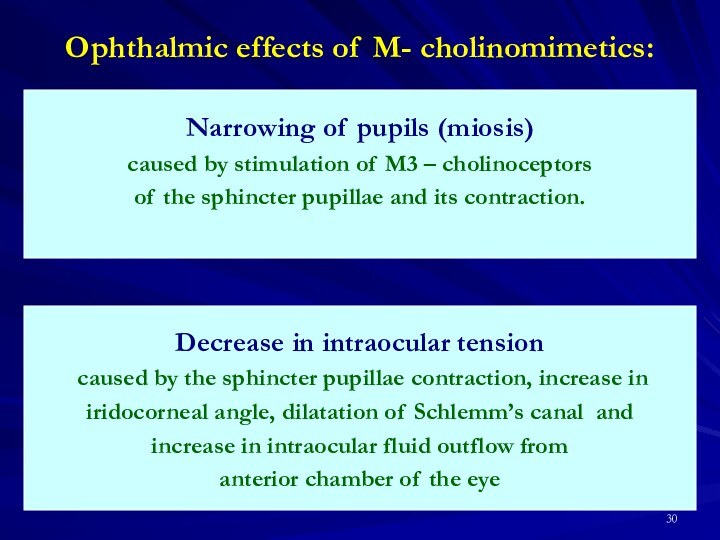
Ophthalmic effects:
narrowing of pupils,
decrease in intraocular pressure,
spasm of accommodation.
urinary bladder
(stimulate detrusor
and relax the trigon)
uterus
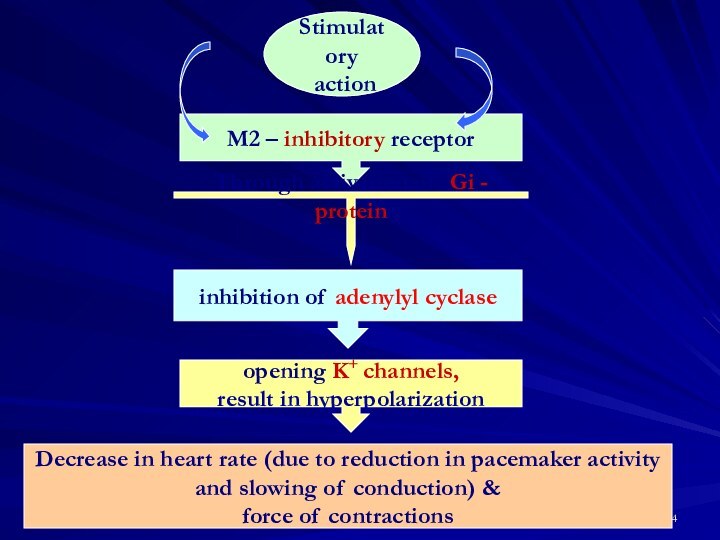
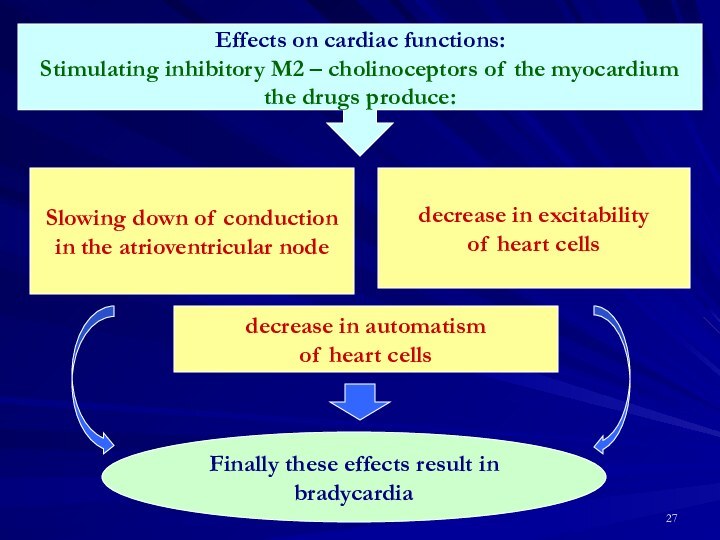
decrease in excitability
of heart cells
decrease in automatism
of heart cells
Finally these effects result in bradycardia
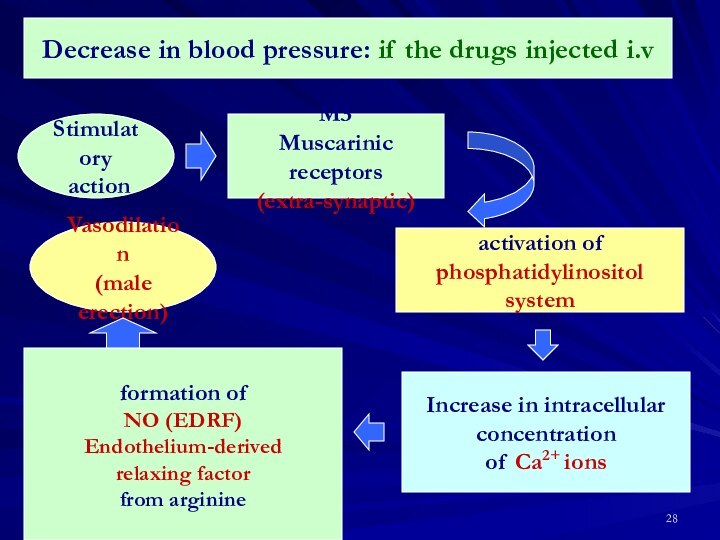
formation of
NO (EDRF)
Endothelium-derived
relaxing factor
from arginine
Vasodilation
(male erection)
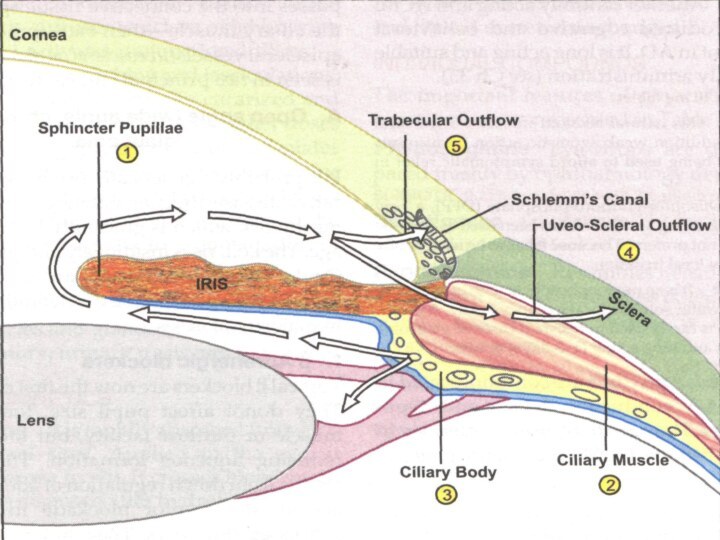
Decrease in intraocular tension
caused by the sphincter pupillae contraction, increase in
iridocorneal angle, dilatation of Sсhlemm’s canal and
increase in intraocular fluid outflow from
anterior chamber of the eye
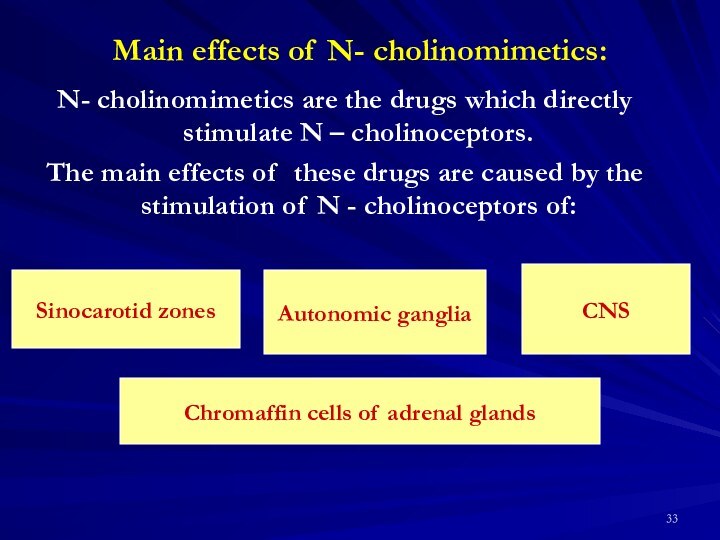
Sinocarotid zones
Autonomic ganglia
CNS
Chromaffin cells of adrenal glands
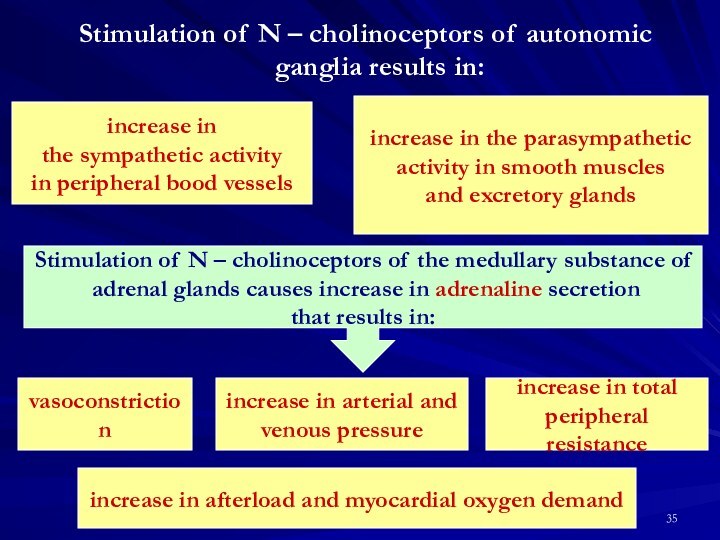
increase in the parasympathetic
activity in smooth muscles
and excretory glands
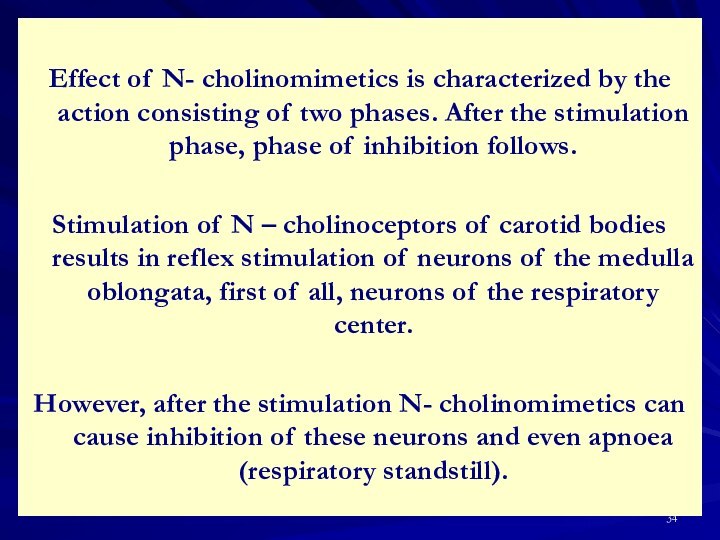
Stimulation of N – cholinoceptors of the medullary substance of
adrenal glands causes increase in adrenaline secretion
that results in:
vasoconstriction
increase in arterial and
venous pressure
increase in total
peripheral resistance
increase in afterload and myocardial oxygen demand
Their main pharmacological effects are:
The mechanism of acetylcholinesterase inhibition is reversible.
After inhibition, enzymatic activity of the enzyme
is restored and it continues to control
acetylcholine level in synapses.
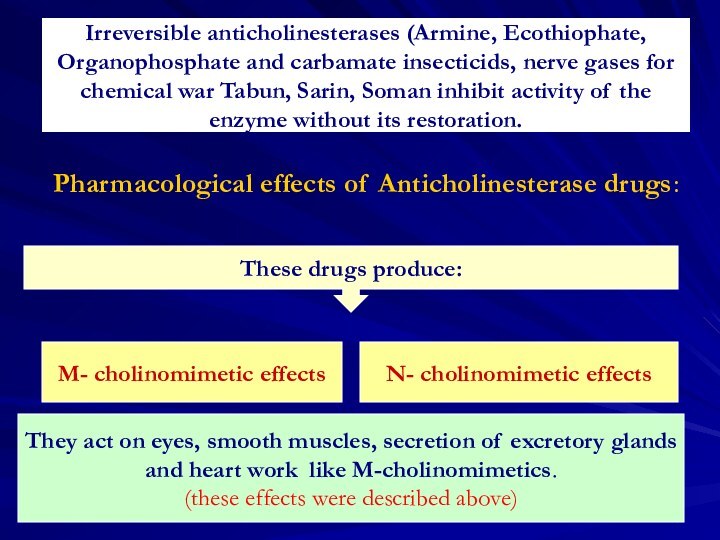
Pharmacological effects of Anticholinesterase drugs:
These drugs produce:
М- cholinomimetic effects
N- cholinomimetic effects
They act on eyes, smooth muscles, secretion of excretory glands
and heart work like M-cholinomimetics.
(these effects were described above)
Influence on the CNS:
At small doses, anticholinesterase drugs take stimulatory effect,
whereas at high doses they produce inhibitory effect on the CNS.
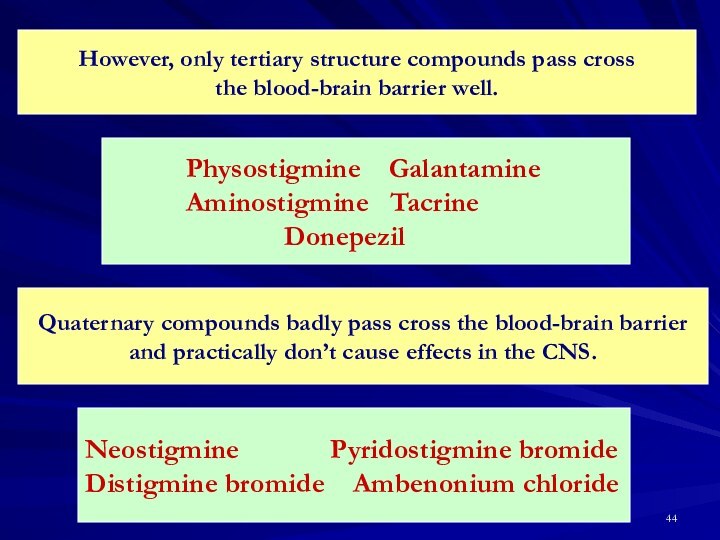
Quaternary compounds badly pass cross the blood-brain barrier
and practically don’t cause effects in the CNS.
Neostigmine Pyridostigmine bromide
Distigmine bromide Ambenonium chloride
Adverse effects of anticholinesterase drugs:
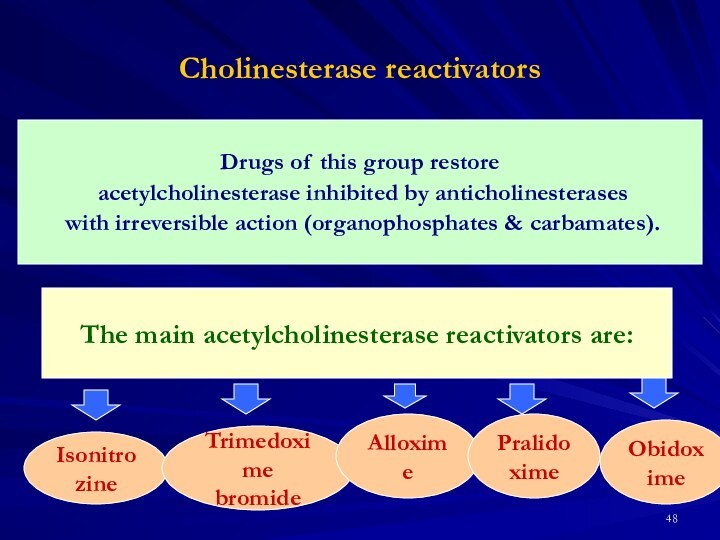
Isonitrozine
Trimedoxime
bromide
Alloxime
Pralidoxime
Obidoxime
Mechanism of acetylcholinesterase reactivator action: