- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Medication Safety Standard. Medication management processes, partnering with patients and carers
Содержание
- 2. Medication management processes The clinical workforce is supported
- 3. Medication management processes4.9: Ensuring that current and
- 4. 4.9: Ensuring that current and accurate medicines
- 5. Medication management processesClinical decision support for electronic
- 6. Medication management processes4.9: Ensuring that current and
- 7. Medication management processes4.10: Ensuring that medicines are
- 8. Medication management processes4.10: Ensuring that medicines are
- 9. Medication management processes4.10: Ensuring that medicines are
- 10. Medication management processes4.10: Ensuring that medicines are
- 11. Medication management processes4.10: Ensuring that medicines are
- 12. Medication management processes4.10. 5 System for disposal
- 13. Medication management processes4.11: Identifying high risk medicines
- 14. Medication management processes4.11: Identifying high risk medicines
- 15. Audits of compliance3. Medication management processes
- 16. Medication management processes4.11: Identifying high risk medicines
- 17. Medication management processes4.11: Identifying high risk medicines
- 18. Communicating with patients and carersThe clinical workforce
- 19. Communicating with patients and carers4.13: The clinical
- 20. Communicating with patients and carers4.14: Developing a
- 21. Communicating with patients and carers4.14: Developing a
- 22. Communicating with patients and carers4.14 Developing a
- 23. Communicating with patients and carers4.15: Providing current
- 24. Communicating with patients and carers
- 25. Скачать презентацию
- 26. Похожие презентации
Medication management processes The clinical workforce is supported for the prescribing, administering, storing, manufacturing, compounding and monitoring of medicines






















Слайд 3
Medication management processes
4.9: Ensuring that current and accurate
medicines information and decision support tools are readily available
to clinical workforceWhat?
Implement and maintain up-to-date medicines information resources and decision support tools (manual or electronic) that are accessible to staff in clinical areas (at point of care) (4.9.1)
formulary information, prescribing requirements, approval systems
reference texts
policies, protocols and guidelines
drug interaction database
guidelines for safe administration of medicines (eg administering medicines via enteral tubes, intravenous injection)
antibiotic approval systems
Слайд 4 4.9: Ensuring that current and accurate medicines information
and decision support tools are readily available to clinical
workforceHospital protocols, guidelines
3. Medication management processes
SHPA Australian Injectable Drugs Handbook
SHPA Don’t Rush to Crush Handbook
Слайд 5
Medication management processes
Clinical decision support for electronic medication
management systems (EMMS)
As a minimum the EMMS should reflect
the core functional and technical features outlined in the Electronic Medication Management Systems - A Guide to Safe Implementation Guide 2nd edition and be working towards the desirable features. Guide available fromhttp://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/our-work/medication-safety/electronic-medication-management-systems/
Слайд 6
Medication management processes
4.9: Ensuring that current and accurate
medicines information and decision support tools are readily available
to clinical workforceWhat?
Regular review of the use and content of clinical information and decision support tools, to ensure that resources are current, and are endorsed for use within the organisation (4.9.2)
Drug & Therapeutics Committee minutes/documentation
Risk assessment of drug information domain in MSSA
Q. These services are largely outsourced through the Clinical Information Access Portal (CIAP). We rely on the service provider to maintain up to date and relevant references. Is this sufficient?
A. Yes for CIAP. However the facility needs to review other resources used, hard and soft copy.
Слайд 7
Medication management processes
4.10: Ensuring that medicines are distributed
and stored securely, safely (cont’d)
What?
Regular review and risk assessment
of medicines storage and distribution across the organisation.(4.10.1)Do as part of overall self assessment
Audit against policies, procedures
Observation audits and “walk arounds”
Review medication incidents
Слайд 8
Medication management processes
4.10: Ensuring that medicines are distributed
and stored securely, safely (Cont’d)
What?
4.10.2. Actions taken to reduce
risks associated with storage and distribution of medicinesPolicies and procedures
Safe handling and disposal of S8 medicines, cytotoxic products and hazardous substances
Purchasing for safety
Identifying risks and putting in place mitigation strategies
Safer distribution systems
Individual patient supply
Bedside lockers
Automated systems with patient profiling
Staff communication, alerts, bulletins
Слайд 9
Medication management processes
4.10: Ensuring that medicines are distributed
and stored securely, safely
What?
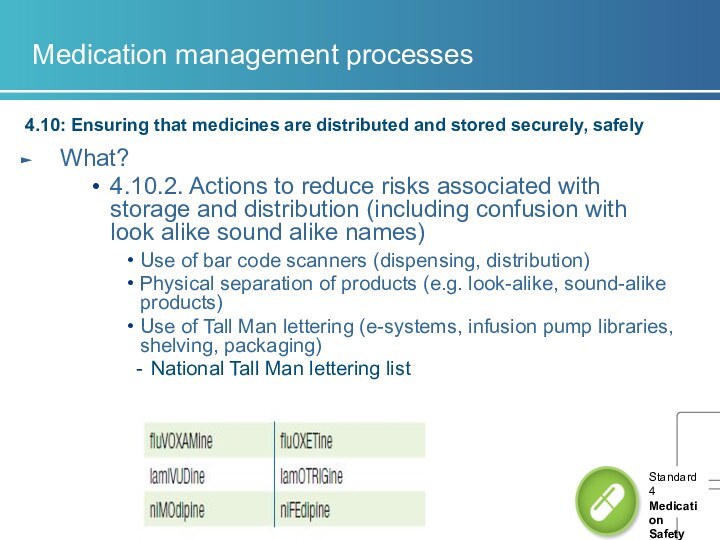
4.10.2. Actions to reduce risks associated
with storage and distribution (including confusion with look alike sound alike names) Use of bar code scanners (dispensing, distribution)
Physical separation of products (e.g. look-alike, sound-alike products)
Use of Tall Man lettering (e-systems, infusion pump libraries, shelving, packaging)
National Tall Man lettering list
Слайд 10
Medication management processes
4.10: Ensuring that medicines are distributed
and stored securely, safely
What?
Temperature sensitive medicines are monitored and
integrity of temperature-sensitive medicines maintained (4.10.3)Temperatures measured, recorded, reviewed
Q. We have installed electronic fridges that alarm when fridge is outside of set parameters. Do we have to document daily Min/Max temps for these fridges ? Are we required to have documented evidence of daily checking?
A. Need to have regular testing, scheduled maintenance of alarms. Temperature recording device in the fridge – a record that the refrigerator is operating within the required temperature range. Monitor the record. This replaces the need to check and record the temperature daily.
Health service needs to have policy for responding to the alarm.
Слайд 11
Medication management processes
4.10: Ensuring that medicines are distributed
and stored securely, safely
What?
Workforce disposes of unused, unwanted
or expired medicines, in accordance with legislative and jurisdictional requirements (4.10.4)S8 medicines audits
Disposal of cytotoxic products and hazardous substances (Work Health and Safetyissues)
Monitoring disposal of unused, unwanted or expired medicines (4.10.5)
Compliance with policy for disposal
Wastage
Слайд 12
Medication management processes
4.10. 5 System for disposal of
unused, unwanted or expired medicines is regularly monitored
Q. How
are institutions auditing drug disposals? We can do S8 items but are other hospitals keeping a log of all items returned to their pharmacy departments.A. No. But hospitals need to do a risk assessment of the management of their pharmaceutical waste in terms of work health and safety, environmental safety and security of storage and disposal.
Слайд 13
Medication management processes
4.11: Identifying high risk medicines in
the organisation and ensuring they are stored, prescribed, dispensed
and administered safelyHigh risk medicines - APINCH (Antibiotics, Potassium, Insulin, Narcotics(S8s),Chemotherapy, Heparin (anticoagulants)
What?
4.11.1 Undertake an assessment of how high risk medicines are managed within the organisation
audits
incident analysis
risk assessment tools
drug usage evaluation programs
benchmarking activities.
Слайд 14
Medication management processes
4.11: Identifying high risk medicines in
the organisation and ensuring they are stored, prescribed, dispensed
and administered safely
Слайд 16
Medication management processes
4.11: Identifying high risk medicines in
the organisation and ensuring they are stored, prescribed, dispensed
and administered safelyWhat?
Action taken to reduce risks of storing, prescribing, dispensing and administering high risk medicines (4.11.2)
List of high risk medicines available to staff, include in education
Policies, procedures and protocols
Guidelines for prescribing, dispensing, administering and monitoring specific high risk medicines such as anticoagulants, chemotherapy, opioids, insulin
Pre-loaded infusions potassium, heparin
Training on awareness of high risk meds
Implement safety alerts on high risk medicines
Monitor improvement activities
Warfarin – NIMC audit
Potassium – QUM indicator
Слайд 17
Medication management processes
4.11: Identifying high risk medicines in
the organisation and ensuring they are stored, prescribed, dispensed
and administered safelyQ. What is a high risk medicine?
A. Medicines that have a high risk of causing serious injury or death to a patient if they are misused or used in error. Errors not necessarily more common, effects more devastating.
APINCH
Use to develop own list
Institute of Safe Medication Practices list
www.safetyandquality.gov.au/our-work/medication-safety/medication-alerts/
Q. Can we prioritise actions to address risks with high risk medicines?
A. Yes
Слайд 18
Communicating with patients and carers
The clinical workforce informs
patients about their options, risks and responsibilities for an
agreed medication management plan.Developmental
Слайд 19
Communicating with patients and carers
4.13: The clinical workforce
informing patients and carers about medication treatment options, benefits
and associated risksWhat?
Implement systems that support the provision of patient specific medicines information when medication treatment options are discussed (4.13.1)
Consumer Medicines Information provided (documented on MMP, in clinical notes)
Consumer information on specific medications, for example anticoagulants, chemotherapy
Patient specific medicines information accessible in clinical areas (4.13.2)
Hard copy or soft copy
Слайд 20
Communicating with patients and carers
4.14: Developing a medication
management plan in partnership with patients and carers
Why?
30 –
50% medicines prescribed for long term conditions not used as prescribed 1 Failure to achieve informed agreement or identify and provide support that patient needs to manage their medicines can lead to non-adherence 1
The medication management (action) plan is intended to support health professionals and patients/carers in developing strategies to manage medicines safely and achieve treatment goals
NICE. Medicines adherence – involving patients in decisions about prescribed medicines and supporting adherence Clinical Guideline CG 76 – January 2009
Слайд 21
Communicating with patients and carers
4.14: Developing a medication
management plan in partnership with patients and carers
What?
Undertake assessment
of the patient’s medication risks to identify medication management issuesUse Medication Risk Identification section on National Medication Management Plan
Develop a medication management (action) plan that establishes treatment goals and specifies actions required to achieve medication management goals (4.14.1).
List of medicines, allergies, administration aids
Goals of therapy, action to achieve goals
Communicate plan to patient and with the patient’s consent to other relevant health care professionals
Слайд 22
Communicating with patients and carers
4.14 Developing a medication
management plan in partnership with patients, carers
Q. What is
a medication management plan? Is it the National Medication Management Plan?A. No. It is the consumer medication action plan referred to in APAC Guiding principles to achieve continuity of medication management.
Plan for patient’s medication management
Treatment goals and actions, medicines list, changes
Provided to patient, carer
Commission developing a template late 2013
Слайд 23
Communicating with patients and carers
4.15: Providing current medicines
information to patients in a format that meets their
needs whenever new medicines are prescribed or dispensedWhat?
Identify medicines information resources that are in a format that can be used and understood by patients and carers when new medicines are prescribed/supplied or medicines changed(4.15.1)
Similar evidence to 4.14
Interpreter services available for CALD patients
Written information in patients own language e.g. multilingual medicines lists
NPS MedicineWise resources
Improve medicines information provided in response to patient feedback (4.15.2)
Action taken in response to complaints, patient surveys