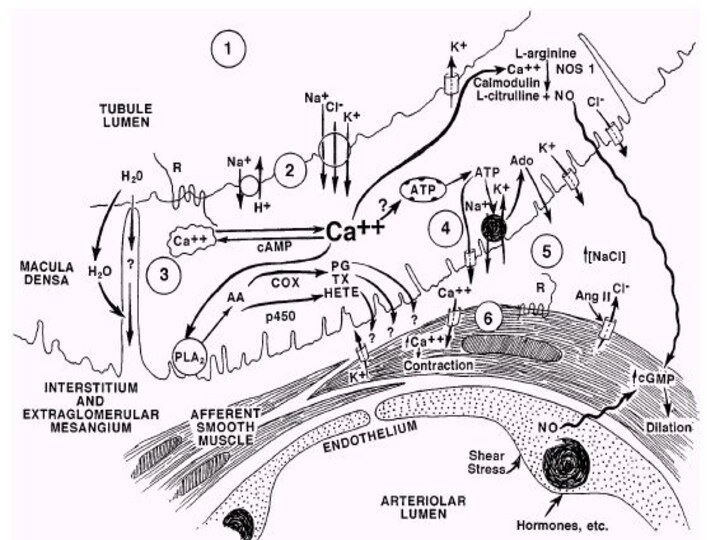
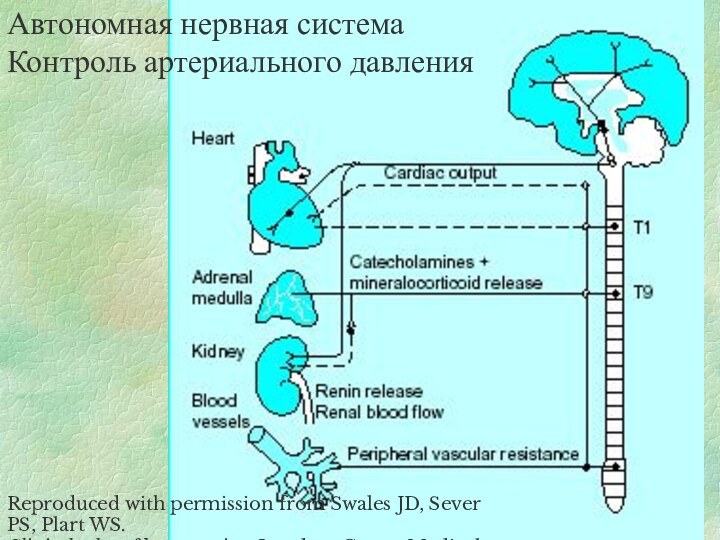
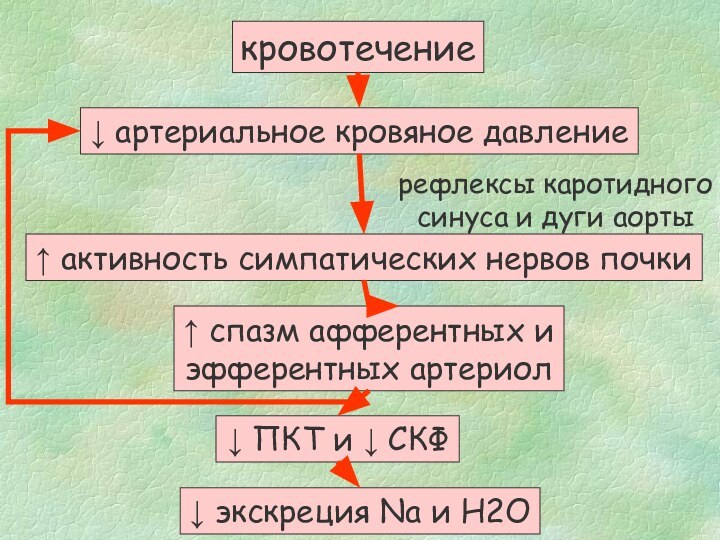
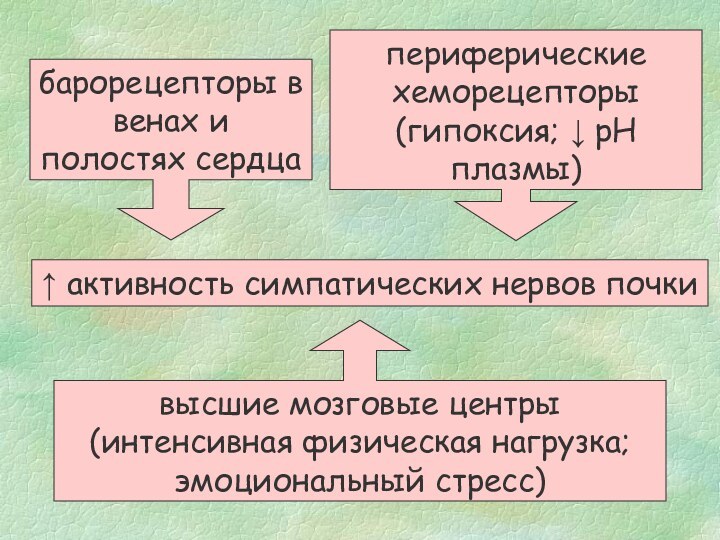
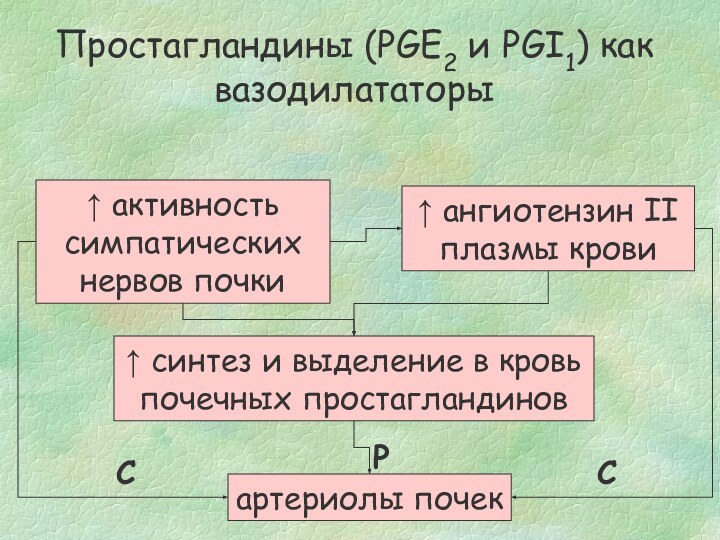
events.
1) Flow-dependent changes in tubular
fluid composition (osmolality, Na1, Cl2,
etc.).
2) Membrane activation such as
membrane depolarization and enhanced
NaCl entry. 3) Intracellular Ca21 mobilization.
4) Intracellular events: formation
and release of arachidonic acid
(AA) metabolites, formation and metabolism
of purinergic agents, formation
of NO. 5) Effects of secreted agents
on membrane potential and activation
of Ca21 channels in vascular smooth
muscle cells. 6) Vascular contractile
responses. COX, cyclooxygenase; TX,
thromboxane; Ado, adenosine; PLA2,
phospholipase A2; R, receptor. [Modi-
fied from Navar et al. (69) and includes
various postulated but not yet proven
mechanisms.]-
[Modified from Navar et al. (69) and includes various postulated but not yet proven mechanisms.]