- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Social Contract Theory
Содержание
- 2. Social Contract TheoryBy SOCIAL CONTRACT – people
- 3. Force Theory
- 4. Force TheoryState was born of forceOne
- 5. Evolutionary Theory
- 6. Evolutionary TheoryState developed NATURALLY out of the
- 7. Divine Right Theory
- 8. Divine Right TheoryFrom 15th – 18th
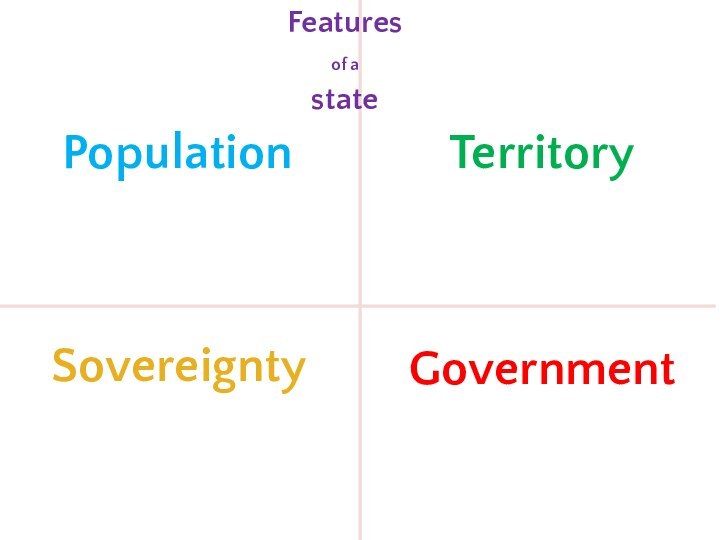
- 9. Features of a state
- 10. PopulationTerritorySovereigntyGovernmentFeatures of a state
- 11. When we are talking about the state…Definition:
- 12. The state –Defined by 4 Things(1) PopulationDefinition:
- 13. The state –Defined by 4 Things(1) PopulationThe
- 14. The state –Defined by 4 Things(2) TerritoryDef:
- 15. The state –Defined by 4 Things(2) Territory**Boundaries
- 16. The state –Defined by 4 Things(3) SovereigntyDef:
- 17. The state –Defined by 4 Things(3) Sovereignty
- 18. The state –Defined by 4 Things(4) GovernmentDef:
- 19. Civil society a ‘political community’, a society
- 20. Is THAT a STATE?Is the Republic of
- 21. THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN?A state can’t have less than 30,000 people.
- 22. Monaco has only 27,000 people! THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN?
- 23. The boundaries of a territory can change.THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN?
- 24. Can you name the three ways that
- 25. Sovereignty means that you have to check with someone above you. THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN?
- 26. Just the opposite! Sovereignty means there is NO ONE above you! THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN?
- 27. Government only exists to keep order and provide security. THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN?
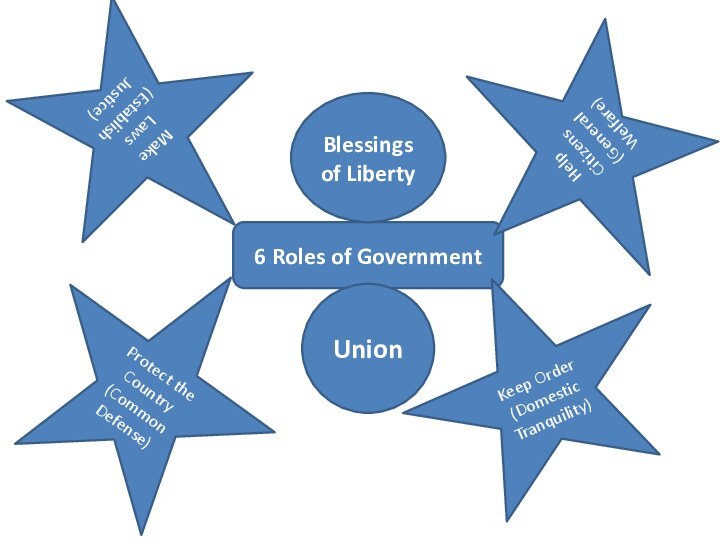
- 28. 6 Roles of GovernmentMake Laws (Establish Justice)Protect
- 29. The 50 states that make up the
- 30. Скачать презентацию
- 31. Похожие презентации
Social Contract TheoryBy SOCIAL CONTRACT – people within a given area agreed to give up (voluntarily) to the state as much power as was needed to promote the safety and well-being of all


























Слайд 4
Force
Theory
State was born of force
One person/small group
claimed control over an area and forced ALL within
it to submit to the person’s/group’s ruleWhen rule was established, all the basic elements of the state were present
Слайд 6
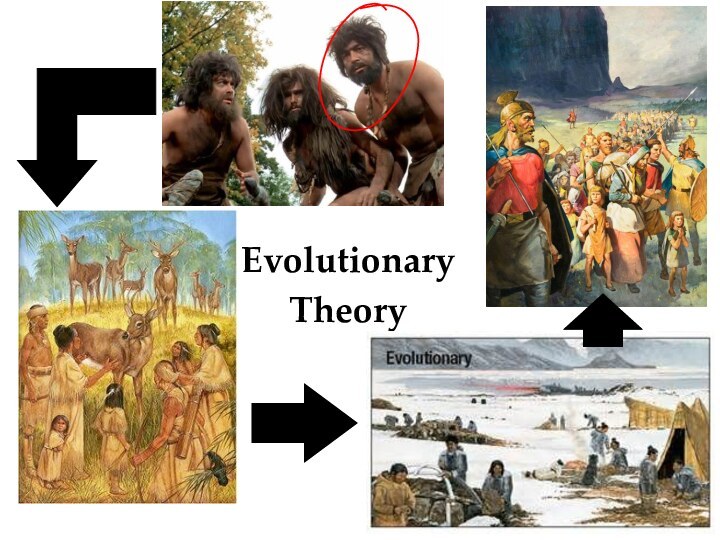
Evolutionary
Theory
State developed NATURALLY out of the early
family
Primitive family (one person was the head - “government”)
Over years, the primitive family became a network of related families [a clan]
The 8 – 20 clans to a tribe
Tribe first turned to agriculture and gave up its nomadic ways (tied to the land)…state
Слайд 8
Divine Right
Theory
From 15th – 18th century, this
was widely accepted in much of Western World
God or
a god/gods created the state and God/god(s) had given those of royal birth a “divine right” to ruleThe people were bound to obey their ruler as they would their God/god(s)
Opposition to “the divine right of kings” was both treason and mortal sin
Слайд 11
When we are talking about the state…
Definition: is
a body of people, living in a defined space,
with the power to make and enforce laws, and with an organization to do this.does not have to check with any higher authority in order to make and enforce laws.
Its own organization, or government, is its highest authority.
Слайд 12
The state –Defined by 4 Things
(1) Population
Definition: the
group of people who are the members or citizens
of a state.*Can be large or small
Ex: China has a population of more than 1.3 billion people, while the island state of Fiji has just over 860,000.
Слайд 13
The state –Defined by 4 Things
(1) Population
The population
of a state also has a
variety of features.
*might
be mainly rural or mostly urban.*A state’s economic situation might mean most people are very poor, with little access to electricity or even water. Or the people might be generally wealthy, enjoying modern homes, running water, and the latest technology.
- Often this is connected to the level of education most people within the population have achieved.
*Populations also have their own cultural traditions, and they usually speak a common language.
Слайд 14
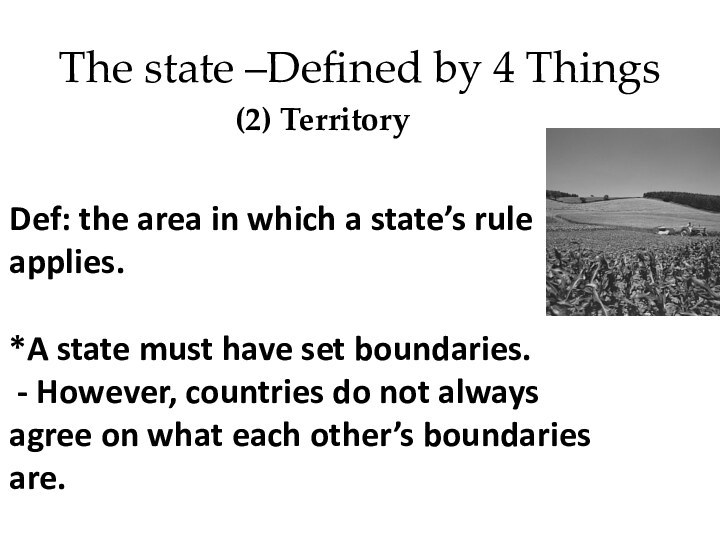
The state –Defined by 4 Things
(2) Territory
Def: the
area in which a state’s rule applies.
*A state
must have set boundaries. - However, countries do not always agree on what each other’s boundaries are.
Слайд 15
The state –Defined by 4 Things
(2) Territory
**Boundaries can
change over time.
- Sometimes they change after
a war, when the states involved agree on new boundaries. - When there is a dispute, states might also negotiate with each other to decide what the actual boundaries should be.- States can purchase territory from other states, although this is less common today than it was in the past.
Ex: In 1867, the U.S. bought Alaska from Russia for $7.2 million.
Слайд 16
The state –Defined by 4 Things
(3) Sovereignty
Def: the
ability to rule absolutely within a territory.
-
all states are considered equal to each other**no state may interfere in the affairs of another state.
Слайд 17
The state –Defined by 4 Things
(3) Sovereignty cont.
In
our world today, the world’s states have created a
higher authority, called the United Nations.States agree to follow the UN’s rules for dealing with each other — but they don’t have to follow them.
**Sovereign states are free to set their own foreign policy, meaning the kind of relationships they will have with other states.
**States also have the power to decide how things will operate inside their own boundaries. Today, though, if a state is unable to keep its population safe and many people are being killed—perhaps even by the government—the UN allows other states to use military force to protect the population.
Слайд 18
The state –Defined by 4 Things
(4) Government
Def: the
organization inside a state that controls the actions and
policies of the state.
Слайд 19
Civil society
a ‘political community’, a society governed
by law, under the authority of a state.
civil society
is distinguished from the state, and is used to describe a realm of autonomous groups and associations, such as business, pressure groups, clubs, families and so on.
Слайд 20
Is THAT a STATE?
Is the Republic of Kazakhstan
just one big state?
Does it have a
population?YES
NO
Does it have a territory?
Does it have sovereignty?
Does it have government?
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO





























