Telecommunications, the Internet, and
Wireless Technology
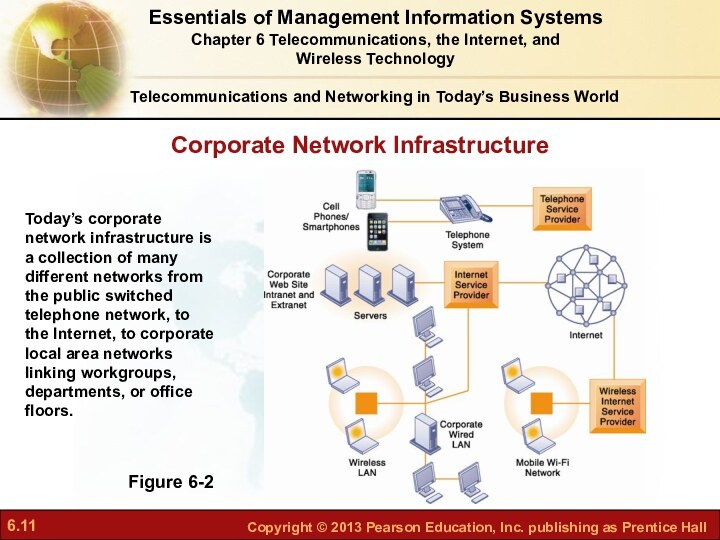
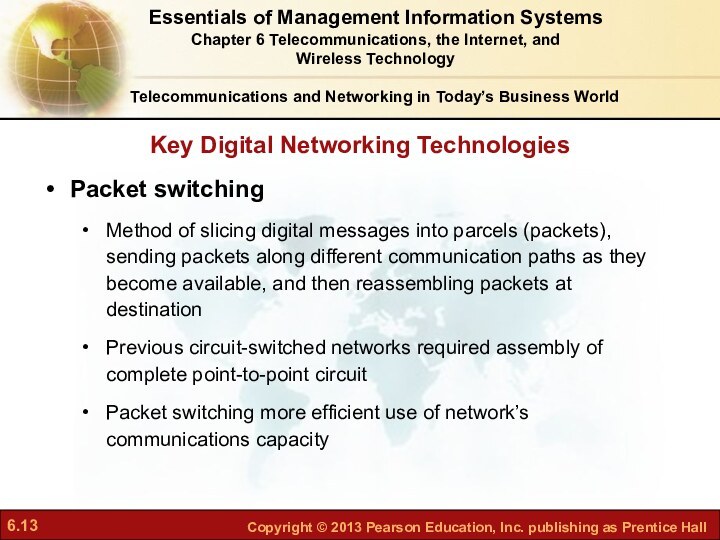
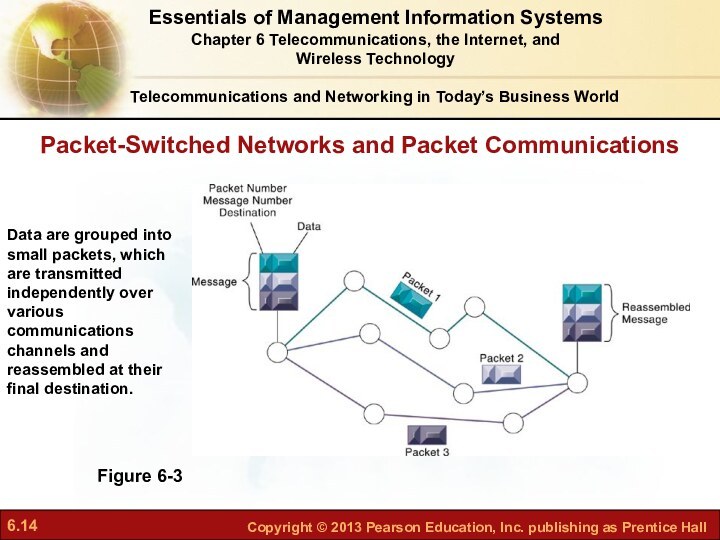
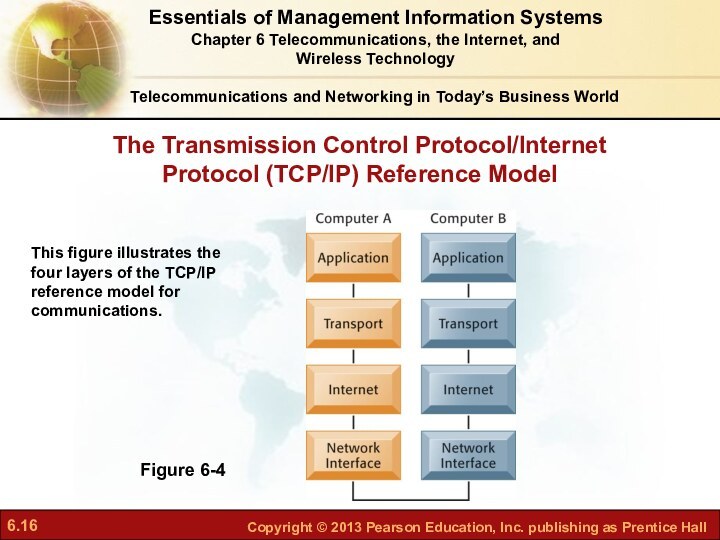
What are the principal
components of telecommunications networks and key networking technologies?What are the main telecommunications transmission media and types of networks?
How do the Internet and Internet technology work and how do they support communication and e-business?