- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Elena a. kruglikovaenglish lexicologyКрасноярск2011
Содержание
- 2. LECTURE 1Language and Lexicology.
- 3. General linguistics studies different and common sides
- 4. Three components in any languageThe grammatical systemThe vocabularyThe system of sounds
- 5. Lexical Studies Lexicology (Gr. ‘lexis’ - word, ‘logos’
- 6. General Lexicology carries out the general study
- 7. VocabularyLexisLexiconDictionary is a selective recording of the
- 8. What is a word?Word is a small
- 9. Word-group Word-group is a group of words which
- 10. Structural aspects of the word The external structure
- 11. Syntagmatic and paradigmatic levelsOn the syntagmatic level,
- 12. Syntagmatic (sequence) The first
- 13. Скачать презентацию
- 14. Похожие презентации
LECTURE 1Language and Lexicology.












Слайд 5
Lexical Studies
Lexicology (Gr. ‘lexis’ - word, ‘logos’ –
learning) studies the vocabulary of the language and the
properties of words (and their combinations) as the main units of the language.Sense relationships between words
Word structure
Word-formation
Properties of words and word-combinations
Principles of classification of the vocabulary
Compilation of dictionaries
Слайд 6 General Lexicology carries out the general study of
the vocabulary, irrespective of the specific feature of any
particular language and it studies linguistic phenomena and properties common to all languages, i.e. so-called language and linguistic universals.Special Lexicology investigates characteristic peculiarities in the vocabulary of a given language. Special lexicology may be historical and descriptive.
Descriptive Lexicology deals with the vocabulary of a given language at a given stage of its development.
Historical Lexicology or Etymology (Greek etumon ‘primary’ or ‘basic word’, ‘original form of a word’) studies the evolution of the vocabulary and its elements: origin, change, development, linguistic and extralinguistic factors modifying their structure, meaning and usage.
Diachronic (Greek dia – ‘through’, chronos – ‘time’)
Synchronic (Greek syn – ‘with, together’).
Contrastive Lexicology works out the theoretical basis on which the vocabularies of different languages can be compared and described.
Phraseology is the branch of lexicology specializing in word groups which are characterized by stability of structure and transferred meaning.
Terminology studies different sides of terms and lexicology gives methods and the scientific apparatus for that.
Слайд 7
Vocabulary
Lexis
Lexicon
Dictionary is a selective recording of the word
stock at a given point of time
The term vocabulary
is used to denote the system formed by the sum total of all the words and word equivalents. It is an adaptive system adjusting itself to the changing requirements and conditions of human communication and cultural surrounding.A lexicon is a list of words in a language – a vocabulary – along with some knowledge of how each word is used.
Слайд 8
What is a word?
Word is a small unit
within a vast, efficient and perfectly balanced system.
Word
is a unit of speech which, as such, serves the purposes of human communication. Thus, the word can be defined as a unit of communication. Word is the total of the sounds which comprise it.
Word is a speech unit used for the purposes of human communication, materially representing a group of sounds possessing a meaning, susceptible to grammatical employment and characterized by formal and semantic unity.
The term word denotes the basic unit of a language of a given language resulting from the association of a particular meaning with a particular group of sounds capable of a particular grammatical employment. A word therefore is simultaneously a semantic and grammatical and phonological unit. It is the smallest unit of the language which can stand alone as a complete utterance. It is a small unit within a vast, efficient and perfectly balanced system.
Слайд 9
Word-group
Word-group is a group of words which exists
in the language as a ready-made unit, has the
unity of meaning, the unity of syntactical function.As loose as a goose
Слайд 10
Structural aspects of the word
The external structure of
the word is its morphological structure.
The internal structure of
the word, or its meaning is the word’s semantic structure.External (formal) unity
Semantic unity
Susceptibility to grammatical employment
Слайд 11
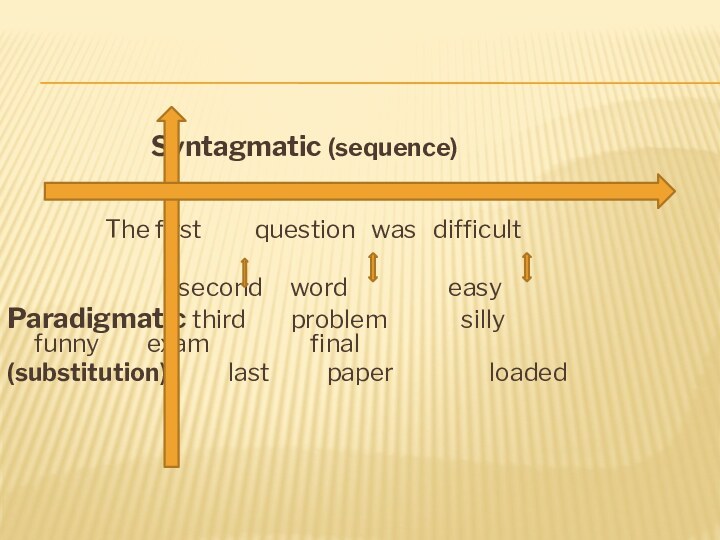
Syntagmatic and paradigmatic levels
On the syntagmatic level, the
semantic structure of the word is analysed in its
linear relationships with neighbouring words in connected speech.On the paradigmatic level, the word is studied in its relationship with other words in the vocabulary system.
.
Слайд 12
Syntagmatic (sequence)
The first
question was difficult
second word easy
Paradigmatic third problem silly funny exam final
(substitution) last paper loaded





























