- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Facts about the oxygen
Содержание
- 2. Oxygen is the third most abundant element
- 4. However, its reactivity made it relatively rare
- 6. Oxygen - the most common element of
- 8. Oxygen dissolved in water. Different fish species
- 13. Modern passenger aircraft when flying for 9
- 14. The body of an adult requires 39
- 18. Interestingly that the human as a species
- 20. Only one part of the body, has
- 21. Your brain uses 20% of the total
- 22. Oxygen was the atomic weight standard of
- 23. AURORA The aurora is the name given
- 26. Each element releases specific wavelengths, so the
- 27. above 150 miles -- red -- oxygen up
- 28. The big player in the aurora is
- 30. Скачать презентацию
- 31. Похожие презентации
Oxygen is the third most abundant element in the universe, according to the Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility, but much less than hydrogen and helium, the two most common.

























Слайд 4 However, its reactivity made it relatively rare in
early Earth's atmosphere. It was much more due to
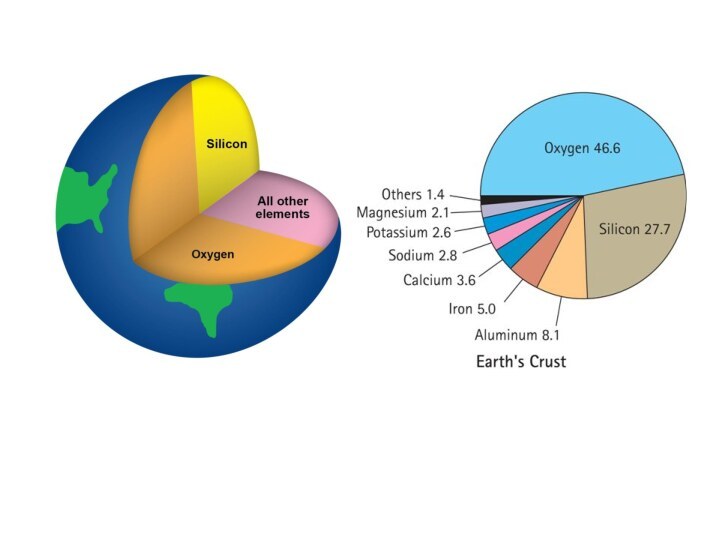
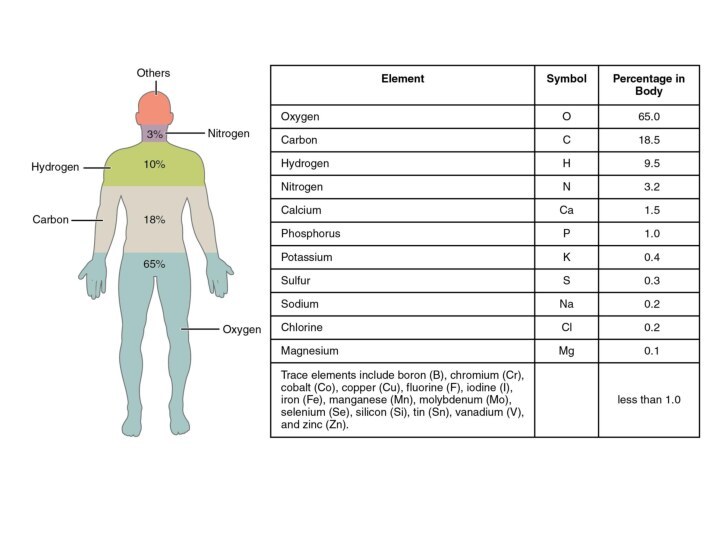
the activity of cyanobacteria and plants. The period of active oxygen generation is called “Great oxygenation event”.Слайд 6 Oxygen - the most common element of the
earth's crust. Its content is 49.13% by weight and
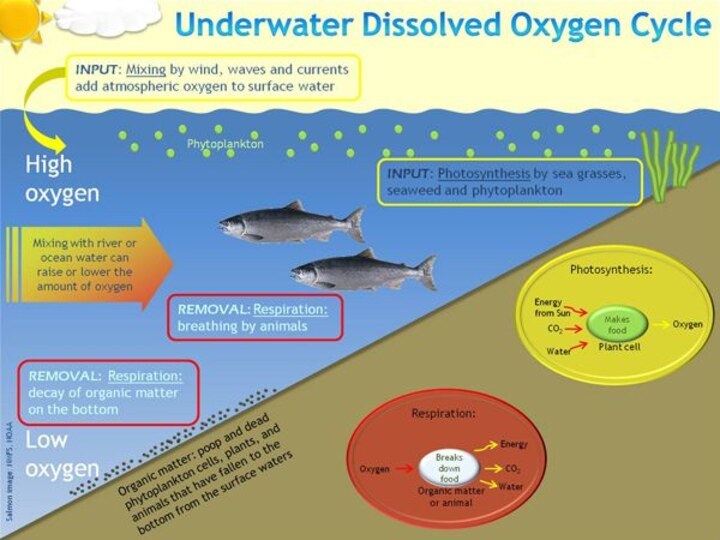
91.8% by volume.Слайд 8 Oxygen dissolved in water. Different fish species need
different amounts of oxygen. The least demanding carp that
lives quietly in an overgrown pond, where almost all the dissolved oxygen is consumed in the oxidation of organic substances. From the most fastidious pond fish in this sense - carp. He needs to oxygen concentration in the water is not less than 4 mg / l. Even more oxygen is required to fish that lives in the rivers, especially the mountain, such as trout.Слайд 13 Modern passenger aircraft when flying for 9 hours
consumes 50-75 tonnes of oxygen. All plants of the
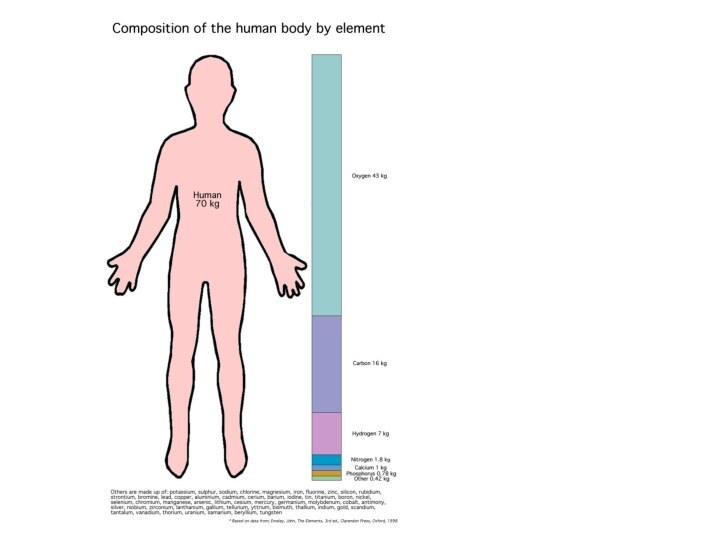
Earth during the year create about 3,000 billion tons of oxygen.Слайд 14 The body of an adult requires 39 kg
of oxygen every day. During the day, a healthy
person at rest is pumped through the lungs 7200l air permanently withdrawing from the atmosphere 720l oxygen. In large cities, the amount of oxygen in the air can be reduced to 18%, and in adverse weather conditions, up to 12-15%. Lack of oxygen a person begins to feel when it is already in the atmosphere reducing to 18%, and are critical to the life of 7%.Слайд 18 Interestingly that the human as a species formed
when the oxygen concentration in the atmosphere has reached
38-40%. For lack of oxygen cause repressed emotions - scientists say. Inhibitions to express strong emotions leads to the fact that people "squeezed", and his breathing becomes intermittent. The main symptoms of hypoxia (lack of oxygen): weakness, fatigue, poor sleep, memory loss, headaches, frequent infections, depression.Слайд 20 Only one part of the body, has no
blood supply - a cornea. It takes oxygen directly
from the air.Слайд 21 Your brain uses 20% of the total amount
of oxygen in the body. It is believed that
people yawn to send more oxygen to the brain, to chill out and wake him up.The brain can live for 4-6 minutes without oxygen, and then begins to die. Lack of oxygen from 5 to 10 minutes can cause irreversible brain damage.
Слайд 22 Oxygen was the atomic weight standard of comparison
for the other elements until 1961 when the International
Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry adopted carbon 12 as the new basis
Слайд 23
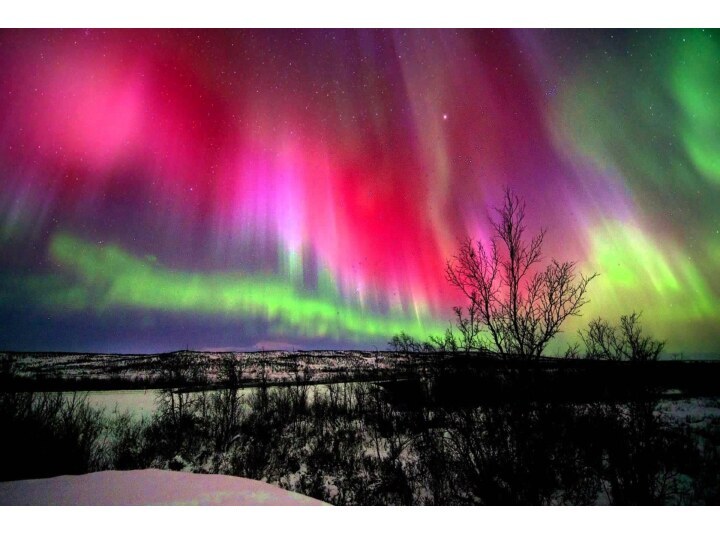
AURORA
The aurora is the name given to the bands
of colored lights seen in the sky at the
higher latitudes. The aurora borealis or Northern Lights are seen mainly near the Arctic Circle. The aurora australis or Southern Lights are seen in the southern hemisphere. The light you see comes from photons released by oxygen and nitrogen in the upper atmosphere. Energetic particles from the solar wind strike the layer of the atmosphere called the ionosphere, ionizing the atoms and molecules. When the ions return to the ground state, energy released as light produces the aurora.Слайд 26 Each element releases specific wavelengths, so the colors
you see depend on the type of atom that
is excited, how much energy it received, and how the wavelengths of light blend with each other. Scattered light from the sun and moon may affect the colors, too. You can see a solid-colored aurora, but its possible to get a rainbow-like effect through the bands. Scattered light from the sun can impart a violet or purple to the top of an aurora. Next, there may be red light atop a green or yellow-green band.There may be blue with the green or below it. The base of the aurora may be pink.
Слайд 27 above 150 miles -- red -- oxygen up to 150
miles -- green -- oxygen above 60 miles -- purple or violet --
nitrogen up to 60 miles -- blue – nitrogenСлайд 28 The big player in the aurora is oxygen.
Oxygen is responsible for the vivid green (wavelength of
557.7 nm) and also for a deep brownish red (wavelength of 630.0 nm).Pure green and greenish yellow aurorae result from excitation of oxygen.