- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Lectures №5-6
Содержание
- 2. What is a principle? According to C.C.
- 3. What is a principle? A principle (*
- 4. Principles of didactics Principles of FLT MethodologyGeneral
- 5. Specific principles in teaching: AudingSpeakingReadingWriting
- 6. Didactic principles:1) principle of activity 2) principle
- 7. The Principle of Consciousnessimplies such process of
- 8. The Principle of Consciousness In order to
- 9. The Principle of Activity (Activeness) There
- 10. People learn a language most effectivelythrough activity
- 11. In accordance with the communicative -cognitive approachto
- 12. The principle of Activity (Activeness) requiresactivity of
- 13. In FLT - the principle of
- 14. In FLT - the principle of activeness
- 15. A Сhinese legend says:"Give a man a
- 16. Production activities:gaps of different kinds: information, opinion,
- 17. Production activities:integrated skills.involvement in the actual process
- 18. Methodologists recommend to introduce linguistic games,rhymes, twin
- 19. An activity or process involving a
- 20. The character of ex. is
- 21. The Principle of VisualityWe know that attaching
- 22. A wide use of visuality in teachingall
- 23. The Principle of Systematicness. Every work requires
- 24. The Principle of Accessibility According to this
- 25. The Principle of Durability The Pr. of
- 26. Associations can be: dormant, that is not
- 27. Lasting knowledge and established habits are conditioned by repetitions of 2 kinds: revision drills
- 28. The Principle of ConsecutivenessThe sequence from known
- 29. THE INTEGRATE CONCEPT OF THE COMPETENCY MODEL OF MFL EDUCATIONMETHODOLOGICAL PRINCIPLESCOMMUNICATIVELINGUOCULTURALCOGNITIVESOCIOCULTURALCONCEPTUALDEVELOPMENTAL-REFLEXIVESTUDENT-CENTERED
- 30. Methodological principles, their main characteristics By
- 31. Cognitive principle is the leading one
- 32. In the result of his cognitive activitythe
- 33. Linguacultural principleLinguacultural principle suggests that language and
- 34. The cognitive mental structure havingdifferent aspects-social, linguacultural,
- 35. Скачать презентацию
- 36. Похожие презентации
What is a principle? According to C.C. Кунанбаева «под принципами... понимаются исходные положения, которые, реализуясь в содержании, организации, методах и приемах обучения, определяют стратегию и тактику обучения» (см. «Современное иноязычное образование: методология и теории», Алматы, 2005,


































Слайд 3
What is a principle?
A principle (* lat. principum)
is a guideline to follow, a comprehensive and fundamental
rule, doctrine or assumption / basis or foundation of smth.
Слайд 4
Principles of didactics
Principles of FLT Methodology
General principles
1. Communicativeness
2.
Domineering role of exercises
3. Integration and differentiation
4. Native language
basisSpecific principles
1. Pattern Practice
2. Oral approach
3. Intensive study at the Primary stage
4. Approximation
Слайд 6
Didactic principles:
1) principle of activity
2) principle of
visuality
3) principle of durability
4) principle of consecutiveness
5)
principle of accessability 6) principle of consciences
7) principle of systematicness
Слайд 7
The Principle of Consciousness
implies such process of teaching
when the linguistic phenomena of the language are taught
consciously by means ofcomparing, explanations, demonstrations, historical comments to make the process of acquisition easier, to prevent interference:
Слайд 8
The Principle of Consciousness
In order to ensure
the assimilation of the language by the pupils the
teacher must resort to explanation, demonstration and never allow mechanical cramming (or rote learning). Rules can assist and help.
Слайд 9
The Principle of Activity (Activeness)
There is a
Chinese Proverb saying:
«I can remember 20% - of what
I hear, I can remember 40% - of what I hear and see;
I can remember 80% - of what I participate in».
Слайд 10
People learn a language most effectively
through activity when
solving problems, creating things themselves or when talking about
personal experiences. Participation and flexible exploratory (creative) thinking should be encouraged.
Слайд 11
In accordance with the communicative -cognitive approach
to FLT
pupils must be actively involved with all their cognitive
mechanisms such as memory (long - term memory and short - term memory), thinking and operations of thinking (analysis, synthesis, induction, deduction, comparison, etc) perception and others.
Слайд 12
The principle of Activity (Activeness) requires
activity of both,
on the part of the T and the learners:
choral, individual work, work in small groups (problem - solving, project work, etc). But the T should bear in mind that students are different: extraverts and introverts display their activity differently.Слайд 13 In FLT - the principle of activeness is
realized in the following ways:
From the very beginning pupils
are taught living speech, not just sounds and words. Using living Speech, answering questions in a foreign language is actively using the language while pronouncing sounds and words is just passively following directions to reproduce things, not to create them.Pupils are taught to think in a foreign language. Thinking is an active process.
In the early Stages of FLT the new material is introduced and activated orally. For this different types of oral exercises are used.
Слайд 14 In FLT - the principle of activeness is
realized in the following ways:
Throughout the FLT course! practice
precedes theory.A wide use of choral, individual work, work in pairs, work in small groups of three and four etc... that provide interaction.
Correction of mistakes should be sparing and not interfering. It is not necessary to correct every mistake.
Activeness is largely dependent upon interest.
Слайд 15
A Сhinese legend says:
"Give a man a fish
and he will eat it all day long; show
him how to fish and he will eat all the year round".
Слайд 16
Production activities:
gaps of different kinds: information, opinion,
reasoning
variety of means of classroom organization, learner roles etc.
enjoyment;
it is most likely that learners will be motivated if they find the activity stimulating and interesting.
Слайд 17
Production activities:
integrated skills.
involvement in the actual process of
the lesson.
creativity - giving the learners an opportunity to
use the knowledge and skills in an individual and personal way.atmosphere - creating a positive learning climate so that learners feel that they can participate and lake risks.
Слайд 18
Methodologists recommend to introduce linguistic games,
rhymes, twin -
twisters at the end of the lesson, otherwise the
pupils will not desire to return to the ordinary lesson again:Inky, pinky, ponky. My daddy bought a donkey. The donkey died, daddy cried; Inky, pinky, ponky.
Слайд 19 An activity or process involving a particular skill
or quality and designed to achieve a result is
called an exercise.It is characterized by the following:
an exercise always has an objective;
it is always aimed at smth;
it presupposes numerous repetitions.
Any ex. is based on the formation of stereotypes;
they must provide the formation of habits;
Слайд 20 The character of ex. is different depending
on what habits they form.
the minimum of ex. necessary
for the formation of habits and skills depends on certain conditions of teaching (learning). Ушинский: «Системность упражнений - есть первая основа успеха». The importance of a system of ex-s consists in the fact that it provides organization of the process of teaching and organization of the process of learning.ex-s fulfill different functions depending on the objectives of FLT.
The idea of system of ex-s in FLT in our country was first advocated in the early 40-s - Gruzinskaya.
Слайд 21
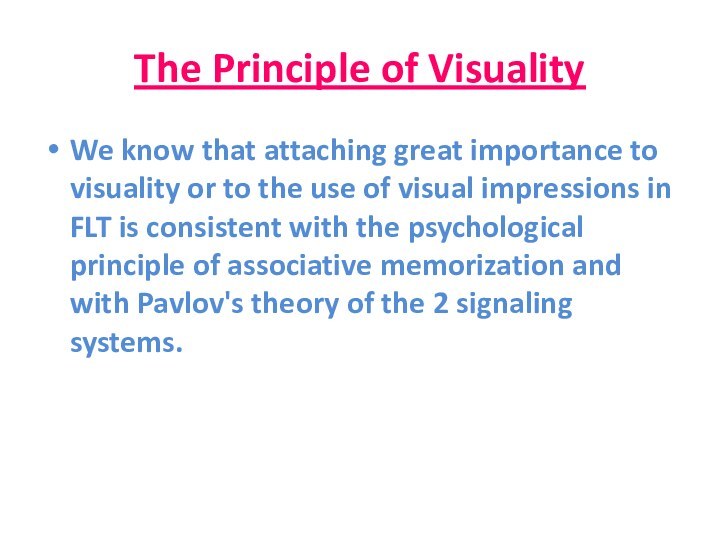
The Principle of Visuality
We know that attaching great
importance to visuality or to the use of visual
impressions in FLT is consistent with the psychological principle of associative memorization and with Pavlov's theory of the 2 signaling systems.
Слайд 22
A wide use of visuality in teaching
all the
subjects is also a main requirements of Modern didactics.
Visuality
is of 3 kinds object
graphic
language
Слайд 23
The Principle of Systematicness.
Every work requires being done
systematically, not mechanically. The didactic principle of systematicness demands
not only planned and systematic work by the teacher but also the acquisition of systematic knowledge by the pupils.
Слайд 24
The Principle of Accessibility
According to this principle:
The material
should correspond to the mental powers of the learners;
it should be neither too difficult, nor too easy or too childish for them; gradation of difficulties is also an indispensable condition of accessibility.it should be rightly dozed;
it should be properly graded.