- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Practical lesson #5education of children with hearing impairments
Содержание
- 2. Psychological experimentsMarshmallow Test: Self-controlS. Freud’s Free Association
- 3. Psychological experimentsOne marshmallow right now or two
- 4. Psychological schools and their representativesBehaviorism: Wundt, J.Watson,
- 5. Classical conditioning Classical conditioning - выработка условного
- 6. Operant conditioningOperant conditioning - выработка инструментального условного
- 8. Gestalt therapy
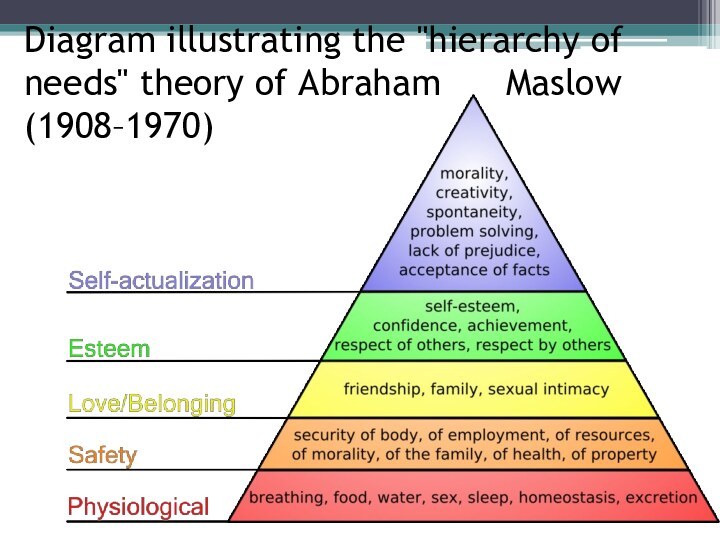
- 9. Diagram illustrating the "hierarchy of needs" theory of Abraham Maslow (1908–1970)
- 11. Sigmund Freud
- 12. Ludwig van Beethoven – genius of his timeMoonlight SonataRequiemSymphony No.5For EliseToccataOde to Joy
- 13. Helen KellerChoose the right answer: Who was Helen Keller?PoliticianWriterSingerLecturerActressPolitical activistAthlete
- 14. Who invented telephone?
- 16. Education of children with hearing impairmentsAim: to
- 17. Answer the questions:What is hearing impairment?What is
- 18. What are types of hearing loss?mild hearing
- 19. What are causes of hearing loss?AgeNoiseGeneticConditions (measles,
- 20. Draw the structure of an ear
- 21. What is sign language? A sign language
- 22. Learn how to say My name is … in English sign language.
- 25. Review: Animals
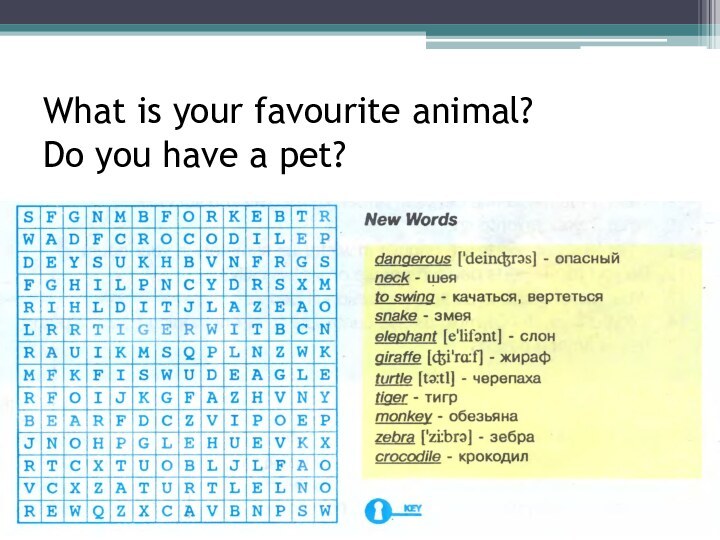
- 26. What is your favourite animal? Do you have a pet?
- 27. Скачать презентацию
- 28. Похожие презентации
Psychological experimentsMarshmallow Test: Self-controlS. Freud’s Free Association methodJ. Watson’s Little Albert Phobia ExperimentFood or security: Harlow’s study on monkey’s attachment





















Слайд 2
Psychological experiments
Marshmallow Test: Self-control
S. Freud’s Free Association method
J.
Watson’s Little Albert Phobia Experiment
on monkey’s attachment
Слайд 3
Psychological experiments
One marshmallow right now or two after
15 minutes.
Vienna – wood, money – bank …
Behavior is
predictable and controllable. The driving force of behavior is fear.Food (wire mother-doll) or security (soft mother doll)
Слайд 4
Psychological schools and their representatives
Behaviorism: Wundt, J.Watson, B.F.Skinner
Cognitivism:
Aaron T. Beck, Albert Ellis
Humanistic: Carl Rogers, Abraham Maslow
Gestalt
therapy: Fritz Perls, Laura Perls and Paul GoodmanPsychoanalysis: S.Freud, K.Jung, A.Adler.
Developmental psychology: E.Erikson
Constructivism is a set of learning theories between cognitive and humanistic views.
Cognitive constructivism: Jean Piaget
Social constructivism: Lev Vygotsky
Слайд 5
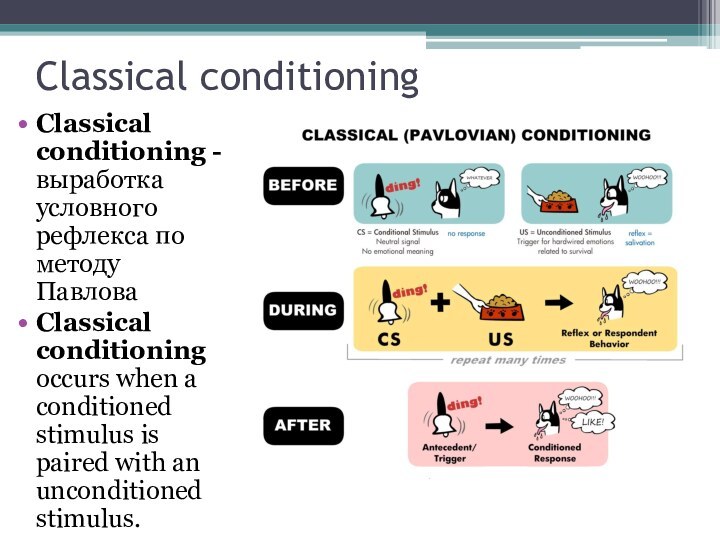
Classical conditioning
Classical conditioning - выработка условного рефлекса
по методу Павлова
Classical conditioning occurs when a conditioned stimulus
is paired with an unconditioned stimulus.
Слайд 6
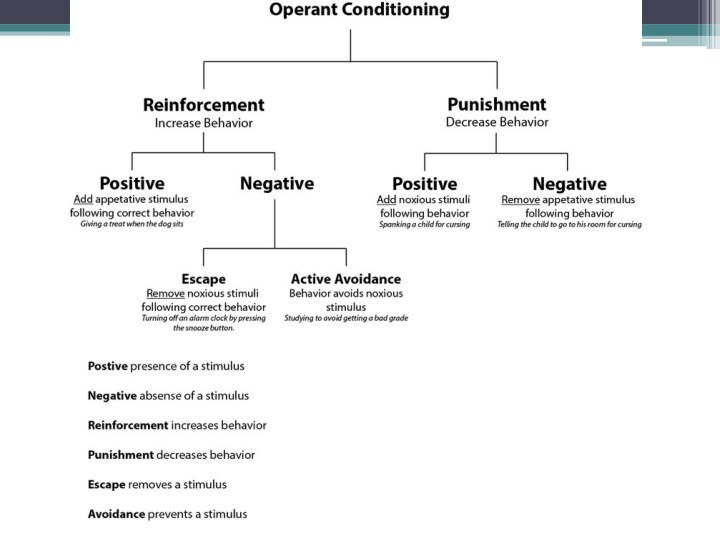
Operant conditioning
Operant conditioning - выработка инструментального условного рефлекса,
выработка оперантного условного рефлекса
Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is
a learning principle in which environmental contingencies—or more specifically, discriminative stimuli (antecedents) influencing its consequences—are controlled and manipulated to change behavior.
Слайд 12
Ludwig van Beethoven – genius of his time
Moonlight
Sonata
Requiem
Symphony No.5
For Elise
Toccata
Ode to Joy
Слайд 13
Helen Keller
Choose the right answer:
Who was Helen
Keller?
Politician
Writer
Singer
Lecturer
Actress
Political activist
Athlete
Слайд 16
Education of children with hearing impairments
Aim: to train
students to define and understand psychological and pedagogical peculiarities
of teaching children with hearing impairments.Key special words: hearing impairment, Cochlear implant, deafness, deaf children, hard of hearing children, hearing loss, surdopedagogy/ deaf-and-dumb pedagogy, mild hearing loss, moderate hearing loss, moderately-severe hearing loss, severe hearing loss, profound hearing loss.
Слайд 17
Answer the questions:
What is hearing impairment?
What is hearing
loss?
What are causes of hearing loss?
What types of hearing
loss are there?What is Cochlear implant?
What other technical aids can use a surdopedagogue while teaching children with hearing impairment?
What are ways / methods of teaching children with hearing impairment?
Слайд 18
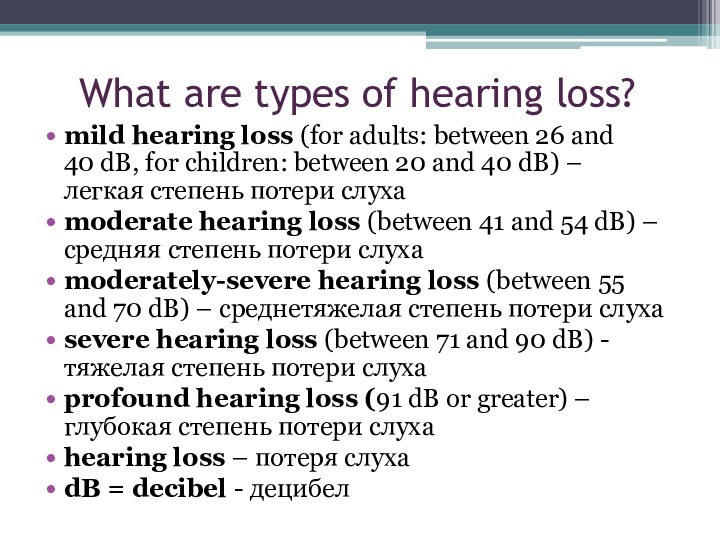
What are types of hearing loss?
mild hearing loss
(for adults: between 26 and 40 dB, for children: between
20 and 40 dB) – легкая степень потери слухаmoderate hearing loss (between 41 and 54 dB) –средняя степень потери слуха
moderately-severe hearing loss (between 55 and 70 dB) – среднетяжелая степень потери слуха
severe hearing loss (between 71 and 90 dB) - тяжелая степень потери слуха
profound hearing loss (91 dB or greater) – глубокая степень потери слуха
hearing loss – потеря слуха
dB = decibel - децибел
Слайд 19
What are causes of hearing loss?
Age
Noise
Genetic
Conditions (measles, meningitis,
mumps, premature birth, syphilis, chlamydia, otosclerosis, brain tumors, excessive
alcohol intake)Neurological disorders (stroke, etc.)
Medications
Chemicals
Physical trauma
Neurobiological factors




























