- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему The model of perfect competition
Содержание
- 2. Key issuesThe meaning of perfect competitionCharacteristics of
- 3. Assumptions Behind a Perfectly Competitive MarketMany suppliers
- 4. Assumptions Behind a Perfectly Competitive MarketTransactions are
- 5. Examples of Perfectly Competitive Markets?It is rare
- 6. Examples of Perfectly Competitive Markets?Agricultural marketsPig farming,
- 7. Approximations to perfect competitionThe law of one price with tens of bookmakers on a race course
- 8. Approximations to perfect competitionFruit sellers at a weekly local marketChinese restaurants in Chinatown London
- 9. Price Taking FirmsCompetitive firms in competitive markets
- 10. Short run price and outputOutputMCACOutputPricePriceP1MSMDMarket forces determine the price
- 11. Short run price and outputOutputMCACOutputPricePriceP1MSMDMarket forces determine the price
- 12. Short run price and outputOutputMCACOutputPricePriceP1MSMDPrice TakingMarket forces determine the price
- 13. Short run price and outputOutputAR=MRMCP1ACOutputPricePriceP1MSMDPrice TakingMarket forces determine the price
- 14. Short run price and outputOutputAR=MRMCP1ACOutputPricePriceP1MSMDMarket forces determine the priceAssume profit maximising firms
- 15. Short run price and outputOutputAR=MRMCP1ACQ1OutputPricePriceP1MSMDMarket forces determine the priceAssume profit maximising firms
- 16. Short run price and outputOutputAR=MRMCMR=MCMaximum ProfitsP1ACQ1OutputPricePriceP1MSMD
- 17. Short run price and outputOutputAR=MRMCMR=MCMaximum ProfitsP1ACQ1AC1OutputPricePriceP1MSMD
- 18. Short run (abnormal) profits OutputAR=MRMCProfits = (P1-AC1) x Q1P1ACQ1AC1OutputPricePriceP1MSMD
- 19. Abnormal profitsOutputAR=MRMCProfits = (P1-AC1) x Q1P1ACQ1AC1PricePossible for
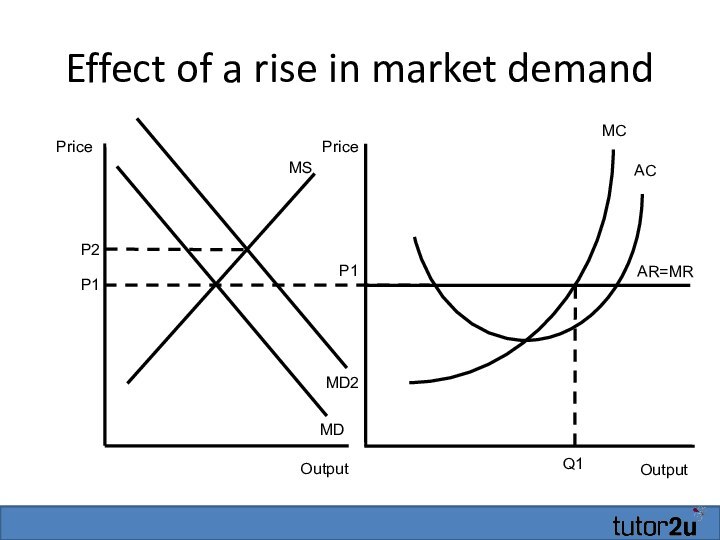
- 20. Effect of a rise in market demandOutputAR=MRMCP1ACQ1OutputPricePriceP1MSMD
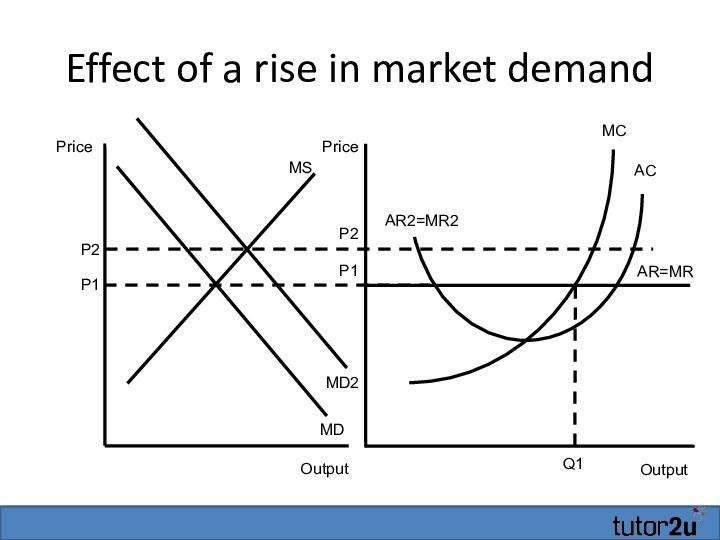
- 21. Effect of a rise in market demandOutputAR=MRMCP1ACQ1OutputPricePriceP1MSMDMD2
- 22. Effect of a rise in market demandOutputAR=MRMCP1ACQ1OutputPricePriceP1MSMDMD2P2
- 23. Effect of a rise in market demandOutputAR=MRMCP1ACQ1OutputPricePriceP1MSMDMD2P2AR2=MR2P2
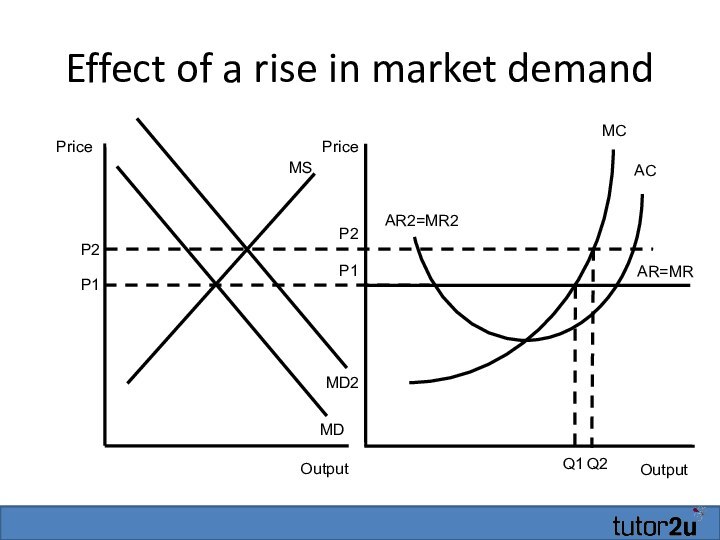
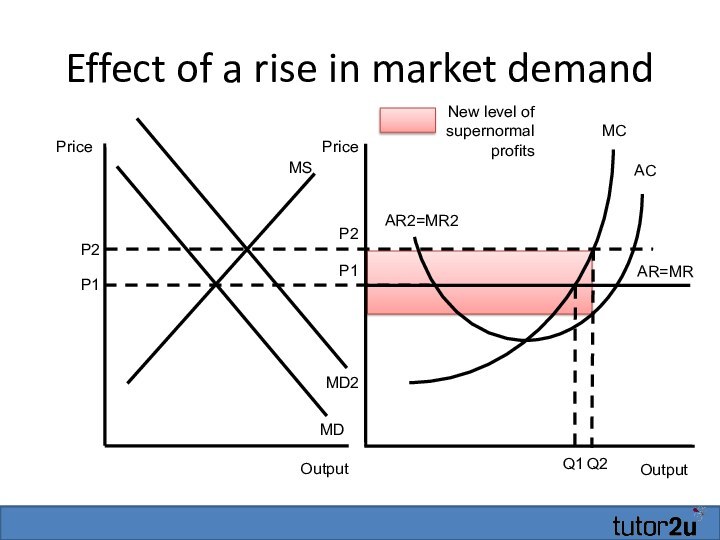
- 24. Effect of a rise in market demandOutputAR=MRMCP1ACQ1OutputPricePriceP1MSMDMD2P2AR2=MR2Q2P2
- 25. Effect of a rise in market demandOutputAR=MRMCP1ACQ1OutputPricePriceP1MSMDMD2P2AR2=MR2Q2P2
- 26. What is a Long Run Equilibrium?Usual interpretation
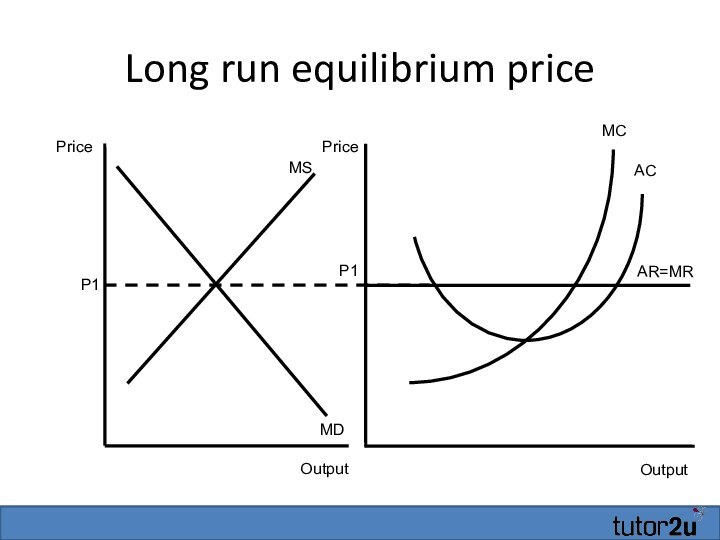
- 27. Long run equilibrium priceOutputAR=MRMCP1ACOutputPricePriceP1MSMD
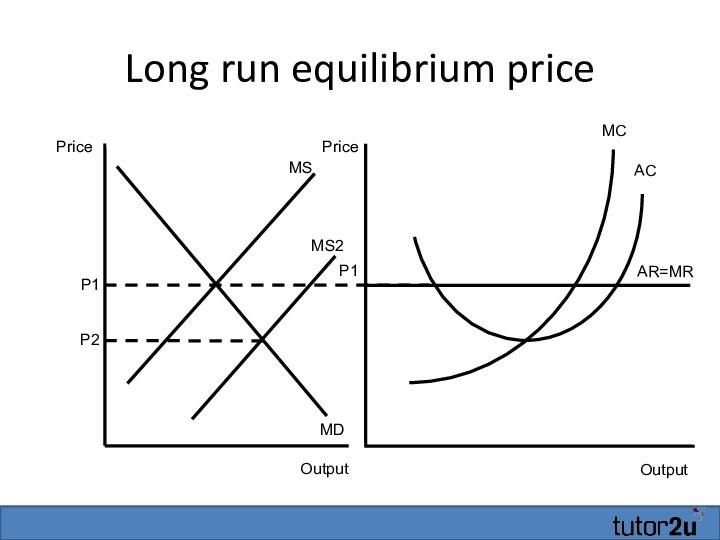
- 28. Long run equilibrium priceOutputAR=MRMCP1ACOutputPricePriceP1MSMDMS2P2
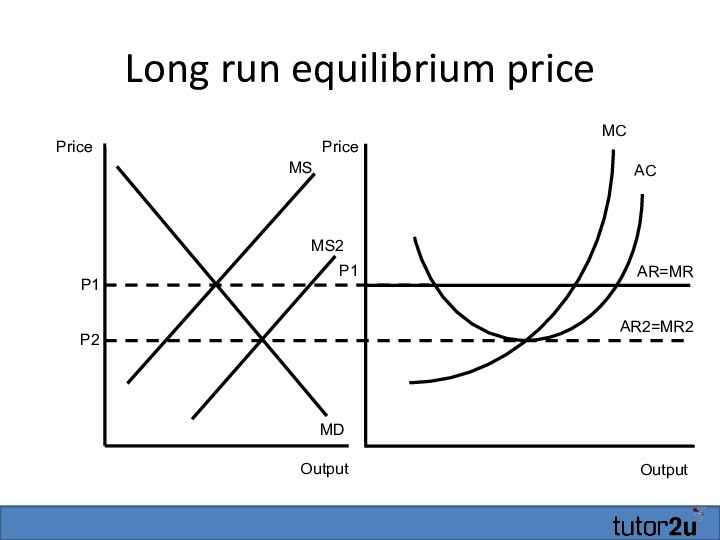
- 29. Long run equilibrium priceOutputAR=MRMCP1ACOutputPricePriceP1MSMDMS2P2AR2=MR2
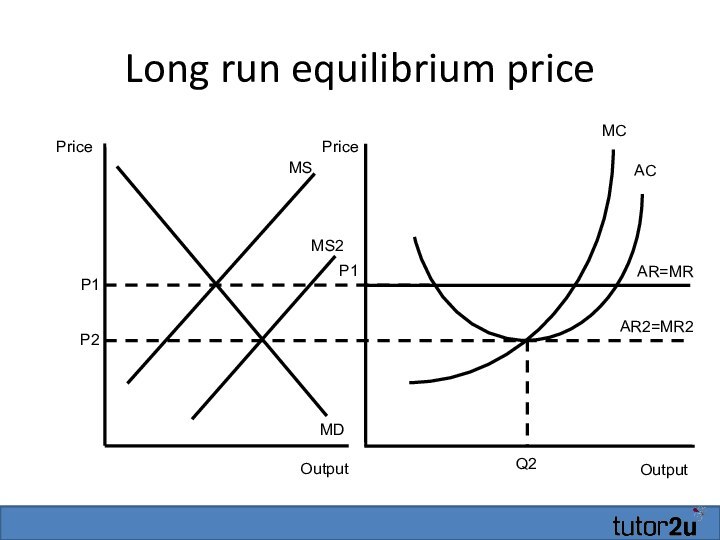
- 30. Long run equilibrium priceOutputAR=MRMCP1ACQ2OutputPricePriceP1MSMDMS2P2AR2=MR2
- 31. The long run equilibriumOutputMCACQ2OutputPricePriceMSMDMS2P2AR2=MR2In the long run
- 32. The long run equilibriumOutputMCACQ2AR2=MR2In the long run
- 33. Competition and Economic EfficiencyEconomic efficiency has several
- 34. Productive EfficiencyOutputCost per unitAC1AC2AC3LRACQ1Q2Q3Productive efficiency occurs when
- 35. Allocative efficiency Allocative efficiency achieved when it
- 36. Allocative EfficiencyOutputPriceMarket DemandMarket SupplyP1Q1When price is equal
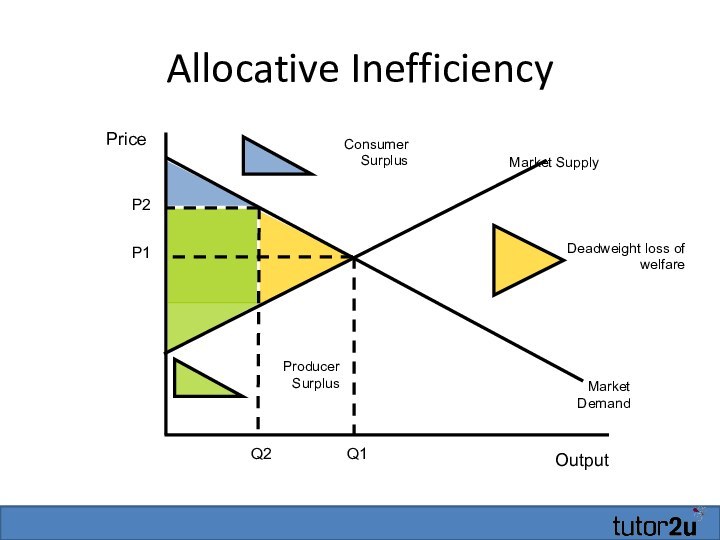
- 37. Allocative InefficiencyOutputPriceMarket DemandMarket SupplyP1Q1P2Q2
- 38. Competition and Economic EfficiencyTechnological efficiency where maximum
- 39. Importance of a Competitive EnvironmentThe standard view
- 40. How useful is model of perfect competition?Assumptions
- 41. Real world – imperfect competition!Most suppliers have
- 42. Скачать презентацию
- 43. Похожие презентации
Key issuesThe meaning of perfect competitionCharacteristics of perfect competitionPrice and output under competitionCompetition and economic efficiencyWider benefits of competition in markets

















Слайд 2
Key issues
The meaning of perfect competition
Characteristics of perfect
competition
of competition in markets
Слайд 3
Assumptions Behind a Perfectly Competitive Market
Many suppliers -
each with an insignificant share of the market
Each firm
is too small to affect price via a change in market supply – each business is a price takerIdentical output produced by each firm – i.e. homogeneous products that are perfect substitutes for each other
Consumers have complete information about prices
Слайд 4
Assumptions Behind a Perfectly Competitive Market
Transactions are costless
- Buyers and sellers incur no costs in making
an exchangeAll firms (i.e. industry participants and new entrants) have equal access to resources (e.g. technology)
No barriers to entry & exit of firms in long run – the market is open to competition from new suppliers
No externalities in production and consumption
Слайд 5
Examples of Perfectly Competitive Markets?
It is rare to
find a pure example of perfect competitions
But there are
some close approximations:Foreign exchange dealing
Homogeneous product - US dollar or the Euro
Many buyers & sellers
Usually each trader is small relative to total market and has to take price as given
Sometimes, traders can move currency markets
Слайд 6
Examples of Perfectly Competitive Markets?
Agricultural markets
Pig farming, cattle
Farmers
markets for apples, tomatoes
Wholesale markets for vegetables, fish, flowers
Street
food markets in developing countries
Слайд 7
Approximations to perfect competition
The law of one price
with tens of bookmakers on a race course
Слайд 8
Approximations to perfect competition
Fruit sellers at a weekly
local market
Chinese restaurants in Chinatown London
Слайд 9
Price Taking Firms
Competitive firms in competitive markets have
little direct influence on the ruling market price
Examples of
price-taking behaviour:Local farmers selling to large supermarkets
A local steel firm selling as much as it can at the ruling international price of steel
The law of one price may hold true – most of the existing firms sell at the prevailing price
Слайд 10
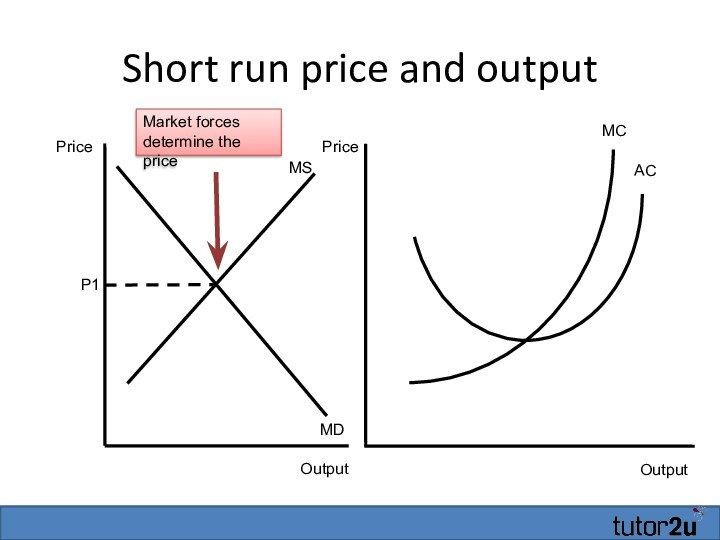
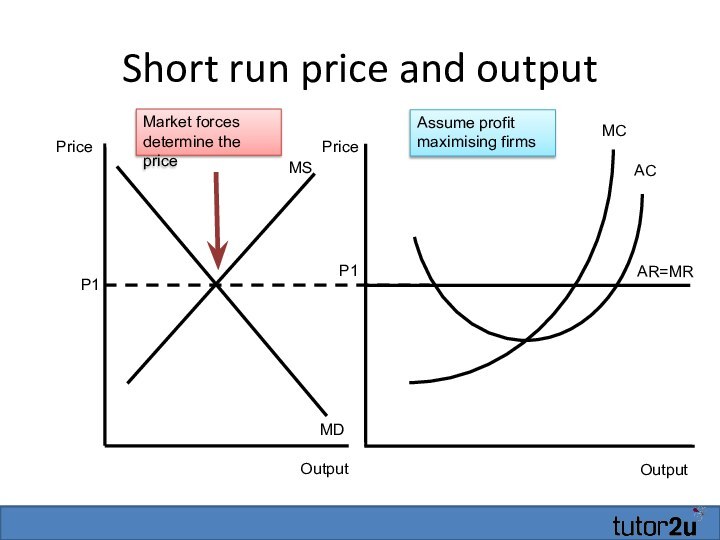
Short run price and output
Output
MC
AC
Output
Price
Price
P1
MS
MD
Market forces determine the
price
Слайд 11
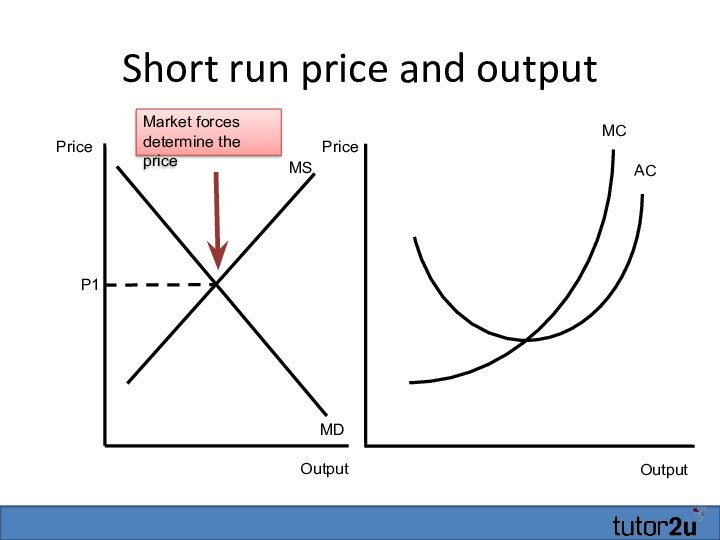
Short run price and output
Output
MC
AC
Output
Price
Price
P1
MS
MD
Market forces determine the
price
Слайд 12
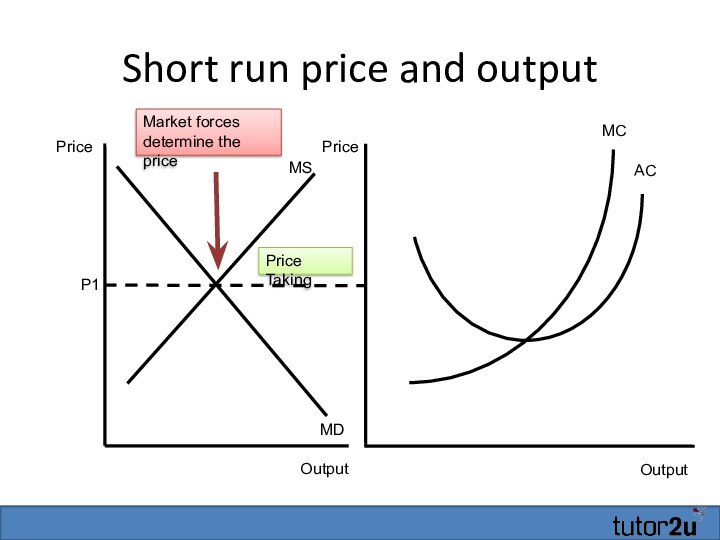
Short run price and output
Output
MC
AC
Output
Price
Price
P1
MS
MD
Price Taking
Market forces determine
the price
Слайд 13
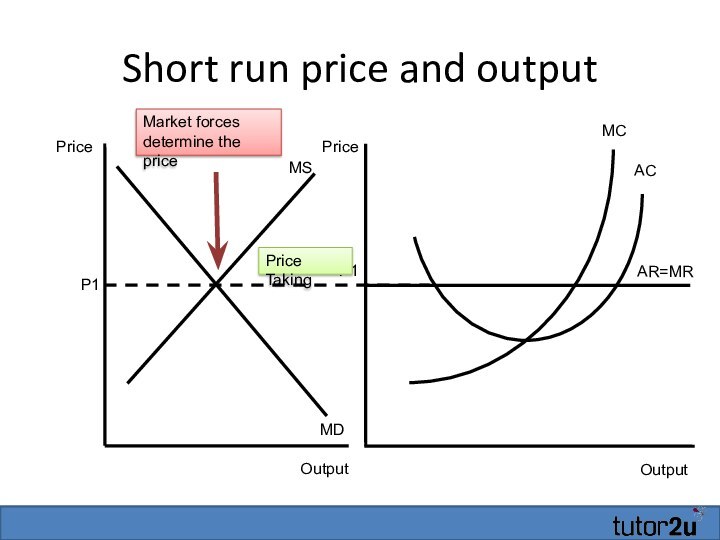
Short run price and output
Output
AR=MR
MC
P1
AC
Output
Price
Price
P1
MS
MD
Price Taking
Market forces determine
the price
Слайд 14
Short run price and output
Output
AR=MR
MC
P1
AC
Output
Price
Price
P1
MS
MD
Market forces determine the
price
Assume profit maximising firms
Слайд 15
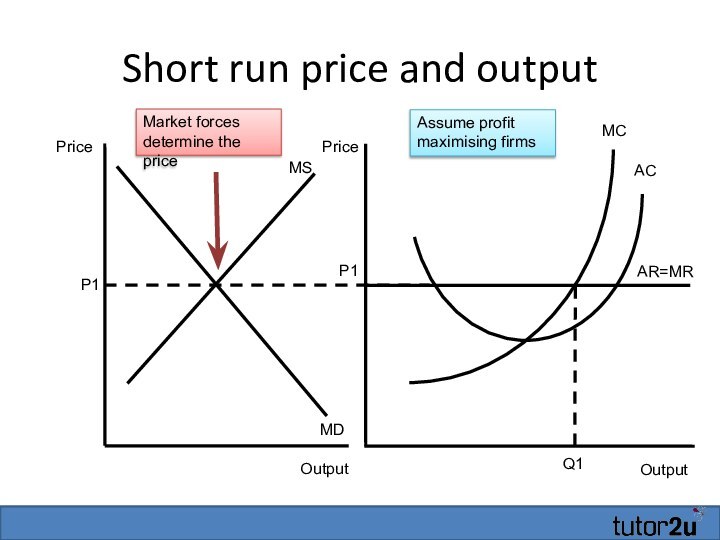
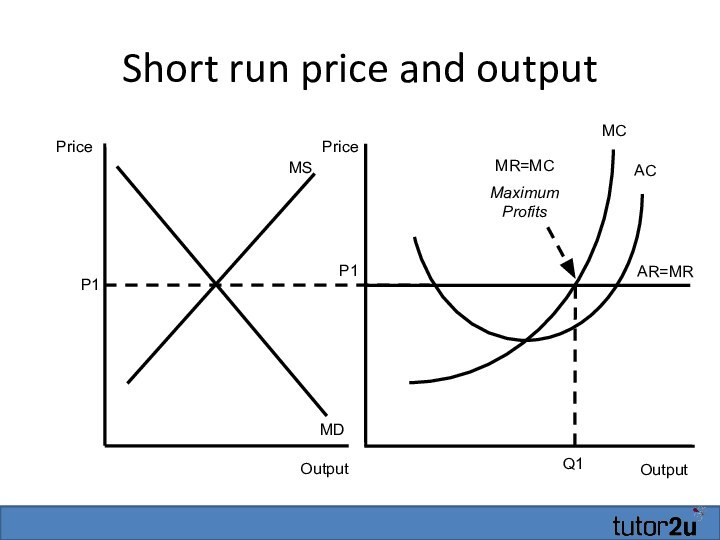
Short run price and output
Output
AR=MR
MC
P1
AC
Q1
Output
Price
Price
P1
MS
MD
Market forces determine the
price
Assume profit maximising firms
Слайд 18
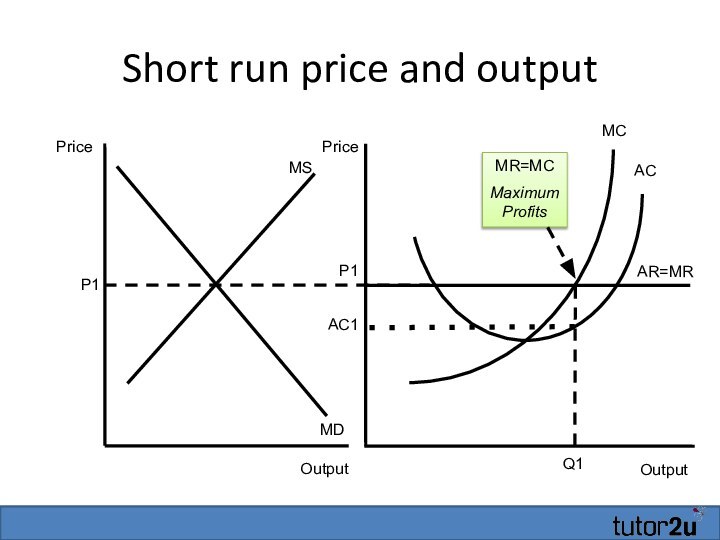
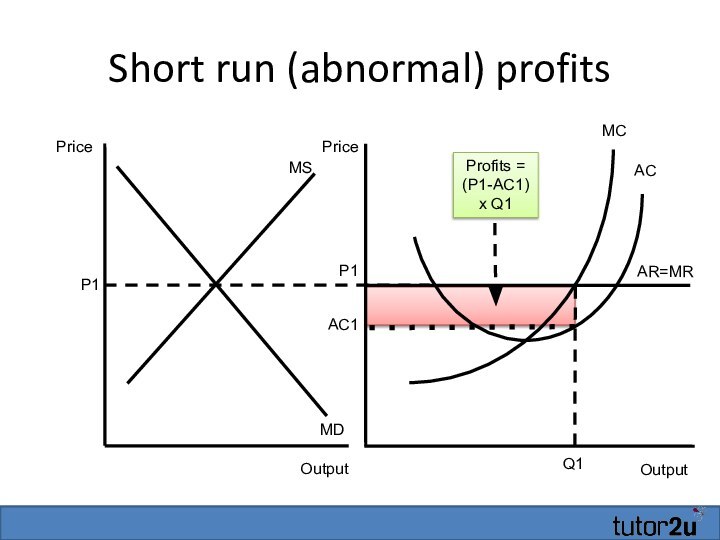
Short run (abnormal) profits
Output
AR=MR
MC
Profits = (P1-AC1) x
Q1
P1
AC
Q1
AC1
Output
Price
Price
P1
MS
MD
Слайд 19
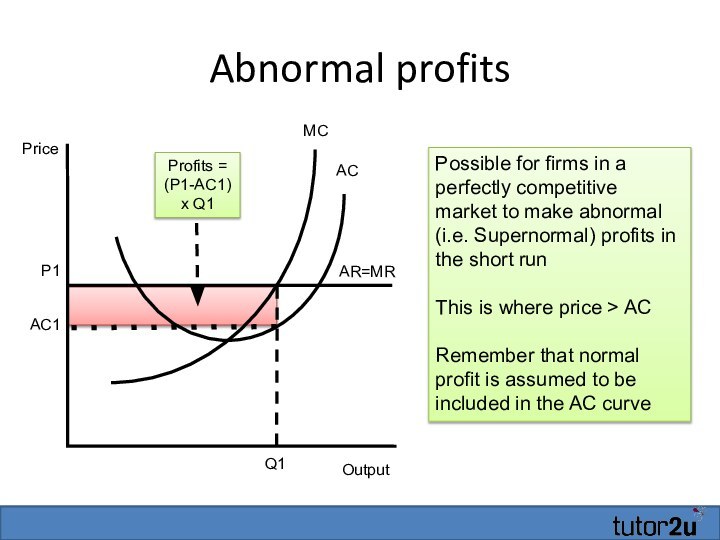
Abnormal profits
Output
AR=MR
MC
Profits = (P1-AC1) x Q1
P1
AC
Q1
AC1
Price
Possible for firms
in a perfectly competitive market to make abnormal (i.e.
Supernormal) profits in the short runThis is where price > AC
Remember that normal profit is assumed to be included in the AC curve
Слайд 26
What is a Long Run Equilibrium?
Usual interpretation of
a long run equilibrium is as follows:
(1) The quantity
of the product supplied in the market equals the quantity demanded by all consumers(2) Each firm in the market maximizes its profit, given the prevailing market price
(3) Each firm in the market earns zero economic profit (i.e. normal profit) so there is no incentive for other firms to enter the market
You Tube video on perfect competition
Слайд 31
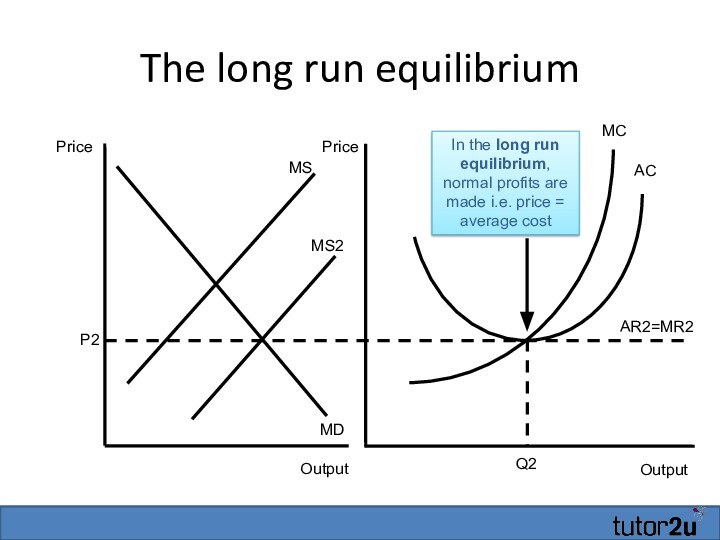
The long run equilibrium
Output
MC
AC
Q2
Output
Price
Price
MS
MD
MS2
P2
AR2=MR2
In the long run equilibrium,
normal profits are made i.e. price = average cost
Слайд 32
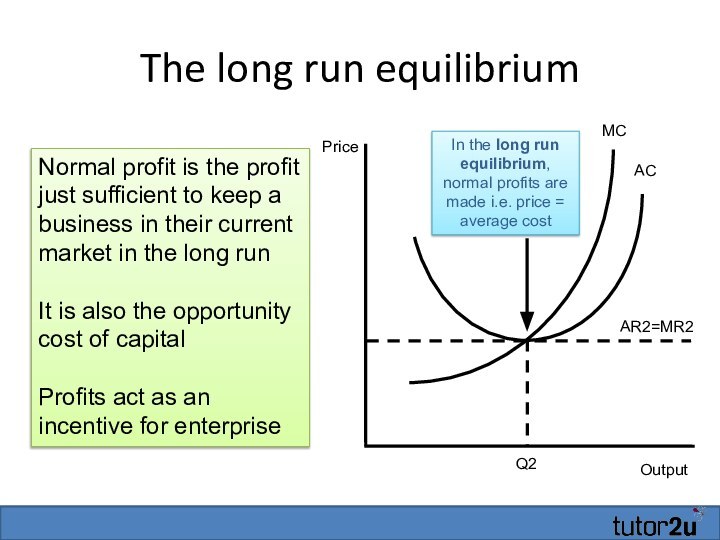
The long run equilibrium
Output
MC
AC
Q2
AR2=MR2
In the long run equilibrium,
normal profits are made i.e. price = average cost
Price
Normal
profit is the profit just sufficient to keep a business in their current market in the long runIt is also the opportunity cost of capital
Profits act as an incentive for enterprise
Слайд 33
Competition and Economic Efficiency
Economic efficiency has several meanings:
Productive
efficiency
when output is produced at the lowest feasible
average cost (either in the short run or the long run)Allocative efficiency
Achieved when the market provides goods and services that meet consumer needs and wants
Achieved when the price of output reflects the true marginal cost of production
This is where price=marginal cost
Слайд 34
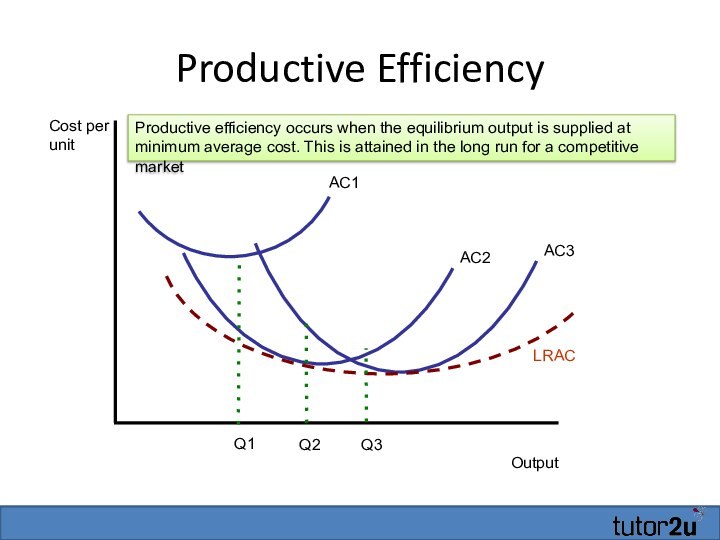
Productive Efficiency
Output
Cost per unit
AC1
AC2
AC3
LRAC
Q1
Q2
Q3
Productive efficiency occurs when the
equilibrium output is supplied at minimum average cost. This
is attained in the long run for a competitive market
Слайд 35
Allocative efficiency
Allocative efficiency
achieved when it is
impossible to make someone better off without making someone
else worse offAlso called Pareto Optimality
No trades are left that would make one person better off without hurting someone else
Occurs when price = marginal costs of production
This occurs in the long run under perfect competition
Слайд 36
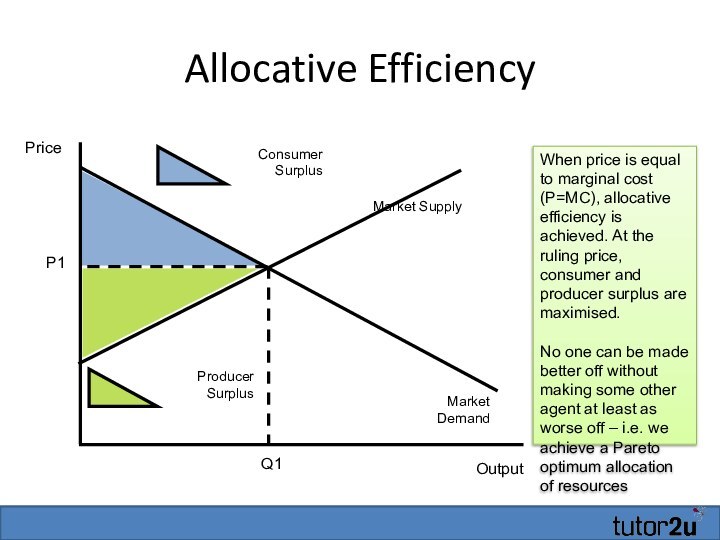
Allocative Efficiency
Output
Price
Market Demand
Market Supply
P1
Q1
When price is equal to
marginal cost (P=MC), allocative efficiency is achieved. At the
ruling price, consumer and producer surplus are maximised.No one can be made better off without making some other agent at least as worse off – i.e. we achieve a Pareto optimum allocation of resources
Слайд 38
Competition and Economic Efficiency
Technological efficiency
where maximum output
is produced from given inputs
Dynamic Efficiency
Refers to the range
of choice and quality of serviceAlso considers the pace of technological change and innovation in a market
Слайд 39
Importance of a Competitive Environment
The standard view is
that competition drives an improvement in welfare and efficiency
Competition
forces under-performing firms out of the market and shifts market share to more efficient firms in the long runCompetition encourages firms to innovate and adopt best-practise techniques
Слайд 40
How useful is model of perfect competition?
Assumptions are
not meant to reflect real world markets where most
assumptions are not satisfiedPure competition is devoid of what most people would call real competitive behaviour by businesses!
The model provides a theoretical benchmark used to compare and contrast imperfectly competitive markets
Consider perfect competition as an interesting point of reference but one with few real world applications
Useful when considering
The effects of monopoly / imperfect competition
The case for free international trade
Слайд 41
Real world – imperfect competition!
Most suppliers have a
degree of control over market supply
Some buyers have monopsony
power against suppliers because they purchase a significant percentage of total demandMost markets have heterogeneous products due to product differentiation and constant innovation
Consumers nearly always have imperfect information and their preferences and choices can be influenced by the effects of persuasive marketing and advertising
Finally there may be imperfect competition in related markets such as the market for essential raw materials, labour and capital goods.





























