- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Оборотный капитал ABC & VED анализ
Содержание
- 2. СодержаниеОпределениеСтруктураВоздействующие факторыЦелиУправление запасамиABCVEDЗаключение
- 3. Определение и структураОборотным капиталом является значение разности всех существующих активов и всех существующих обязательств
- 4. Определение и структураТипы:Валовый о.к. & Чистый о.к.Постоянный о.к. & Временный о.к.Положительный о.к. & Отрицательный о.к.
- 5. Определение и структураМетод подсчетаТрадиционный метод
- 6. Факторы, воздействующие на структуру и требования к
- 7. ЦелиУправление запасамиУправление денежными средствамиУправления дебиторской и кредиторской задолженностью
- 8. ЦелиСтимулирование продаж, благодаря грамотному управлению дебиторской и
- 9. Управление запасамиЦели-Для организации постоянного предложения и бесперебойного
- 10. Инструменты управления запасамиФиксирование уровней- Максимальный ур.
- 11. ABC анализABC анализ заключается в классификации наших запасов на предприятииAlways Best Control
- 12. ABC анализThe origin of ABC analysis is
- 13. ШАГИ ABC анализThe steps in computing ABC
- 14. TABLE 1: DETERMINATION OF RANKS BY ANNUAL USAGE IN US$
- 15. TABLE 1: DETERMINATION OF RANKS BY ANNUAL USAGE IN US$
- 16. TABLE 1: DETERMINATION OF RANKS BY ANNUAL USAGE IN US$
- 17. TABLE 2:CATEGORIZING THE ITEMS IN ABC RANKING
- 18. TABLE 2:CATEGORIZING THE ITEMS IN ABC RANKING
- 19. TABLE 2:CATEGORIZING THE ITEMS IN ABC RANKING
- 20. TABLE 3: ABC CATEGORY - SUMMARY
- 21. VED анализIn addition to the intrinsic or
- 22. VED анализThe nuisance Value is the cost
- 23. VED анализThe materials may be classified depending
- 24. VED анализThe materials may be classified depending
- 25. ABC & VED анализ
- 26. ЗаключениеПосле проведения этих 2 анализов становится понятно,
- 27. Скачать презентацию
- 28. Похожие презентации
СодержаниеОпределениеСтруктураВоздействующие факторыЦелиУправление запасамиABCVEDЗаключение


















Слайд 3
Определение и структура
Оборотным капиталом является значение разности всех
существующих активов и всех существующих обязательств
Слайд 4
Определение и структура
Типы:
Валовый о.к. & Чистый о.к.
Постоянный о.к.
& Временный о.к.
Положительный о.к. & Отрицательный о.к.
Слайд 5
Определение и структура
Метод подсчета
Традиционный метод
Выводимые и выводимые средства Упор делается на
ликвидность и ее показателиМетод операционного цикла
Он учитывает производство и другие операции
Упор делается на прибыль и ликвидность
Слайд 6 Факторы, воздействующие на структуру и требования к оборотному
капиталу
Природа бизнеса
Цикл производства
Процесс производства
Факторы внешней среды
Сезонные факторы
Объем производства
Требования к
запасамКредитные требования
Доступность кредита
И многие другие факторы
Слайд 7
Цели
Управление запасами
Управление денежными средствами
Управления дебиторской и кредиторской задолженностью
Слайд 8
Цели
Стимулирование продаж, благодаря грамотному управлению дебиторской и кредиторской
задолженностью и хранения товара
Уменьшение затрат на продукты
Обеспечить надежность и
относительную низкую стоимость потоков финансированияДостигнуть 3 вышеперечисленных цели, при этом не сократив свободные денежные средства до опасного значения
Слайд 9
Управление запасами
Цели-
Для организации постоянного предложения и бесперебойного производства
Уменьшение
затрат и потрь
Внедрение инновационных научных решений в управлении запасов
Уменьшение
затраты на хранение и окончательную стоимость продуктаУменьшение отклонений бухгалтерских и фактических остатков запасов
Слайд 10
Инструменты управления запасами
Фиксирование уровней- Максимальный ур.
Минимальный ур.
Уровень повтор. заказа
Опасный уровень
2. Фиксирование EOQ- 2AO÷C
ABC анализ
VED анализ
FSN /FNSD анализ
Постоянна информационная система
Показатели оборота запаса
JIT анализ
Слайд 11
ABC анализ
ABC анализ заключается в классификации наших запасов
на предприятии
Always Best Control
Слайд 12
ABC анализ
The origin of ABC analysis is PARETO’S
80 – 20 rule.
This rule says that 80
% of country’s economy is controlled by 20% of the people.If we apply this rule to verify its correctness, the results say that it is correct.
Example:
List out all the expenses we do over a period of time and arrange them in the order from highest to lowest. Find the total of expenses and workout percentage of each with respect to the total. We see that only 20 % of items consume 80% of our expenses.
Слайд 13
ШАГИ ABC анализ
The steps in computing ABC analysis
are:
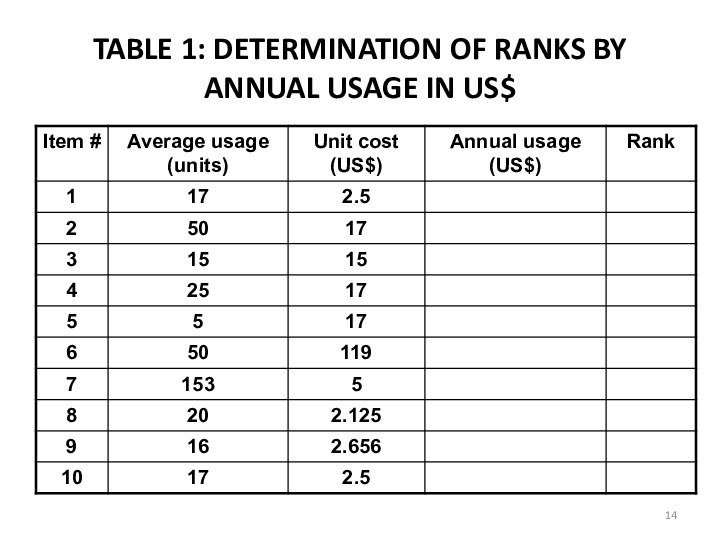
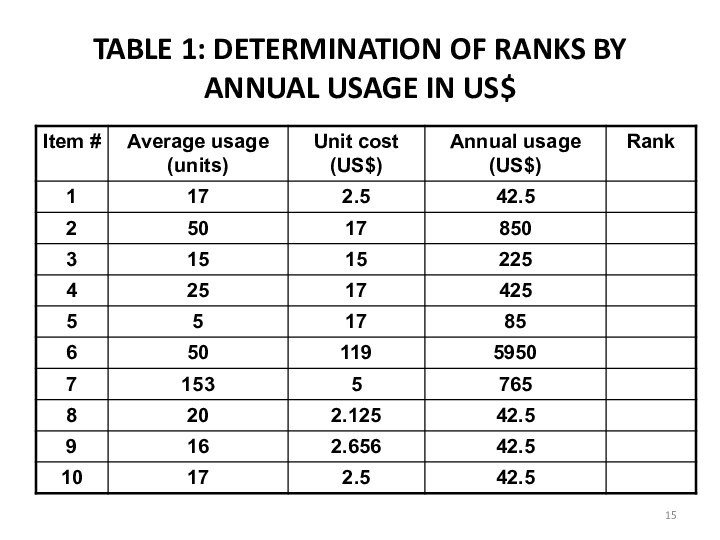
a Determine the annual usage in units for
each item for the past one-year.b. Multiply the annual usage quantity with the average unit price of each item to calculate the annual usage in US$ for each item.
c. Item with highest dollar usage annually is ranked first. Then the next lower annual usage item is listed till the lowest item is listed in the last.
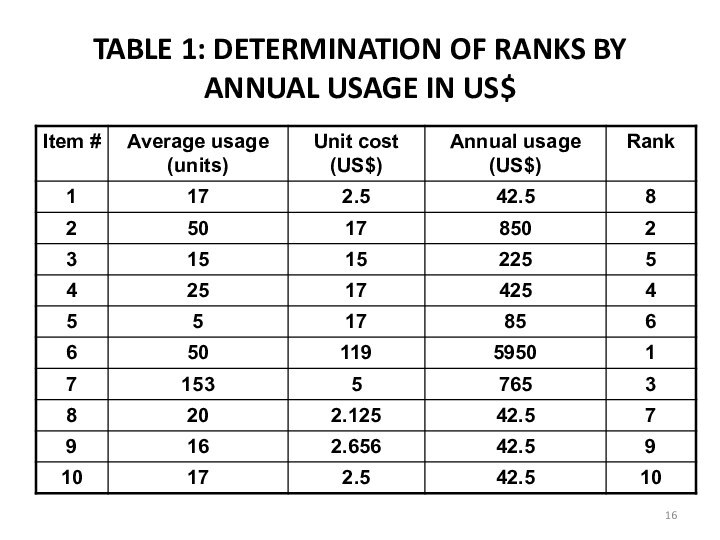
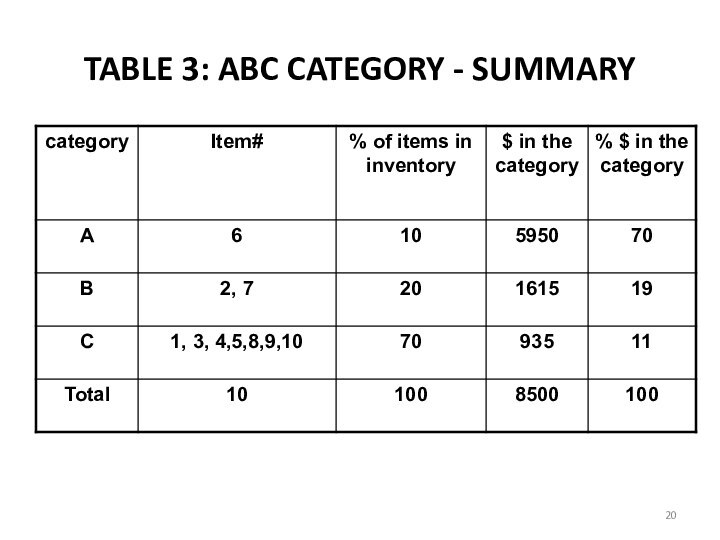
d. Table 1 shows ranks of the items according to the annual usage in US$. for 10 items.
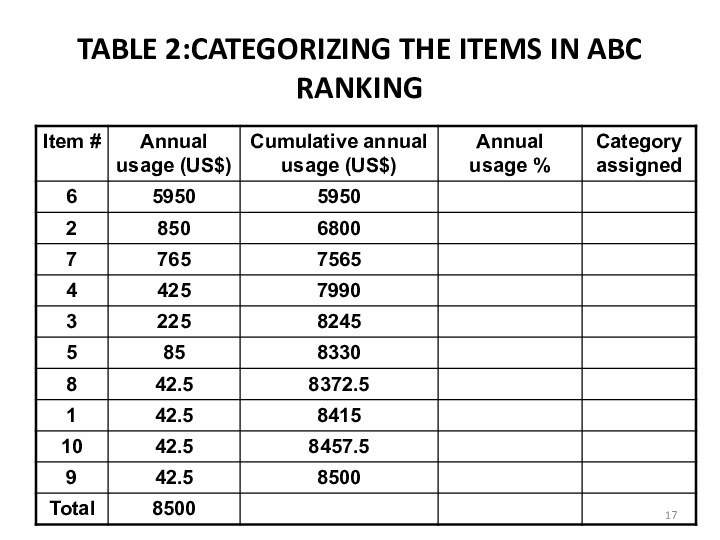
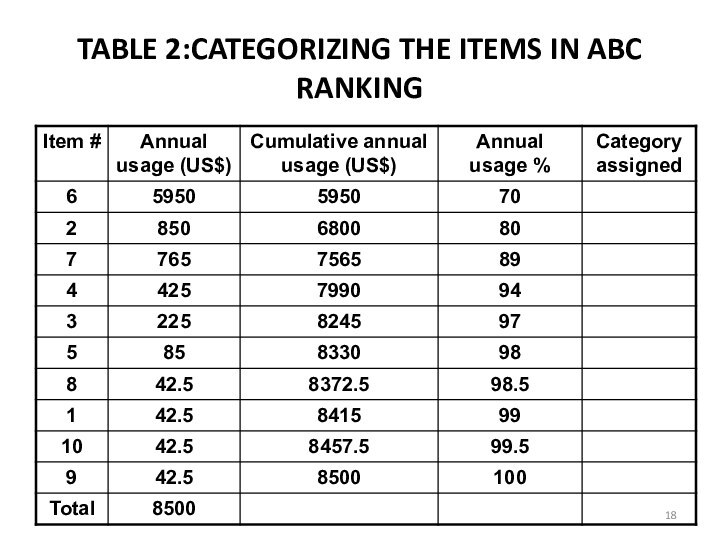
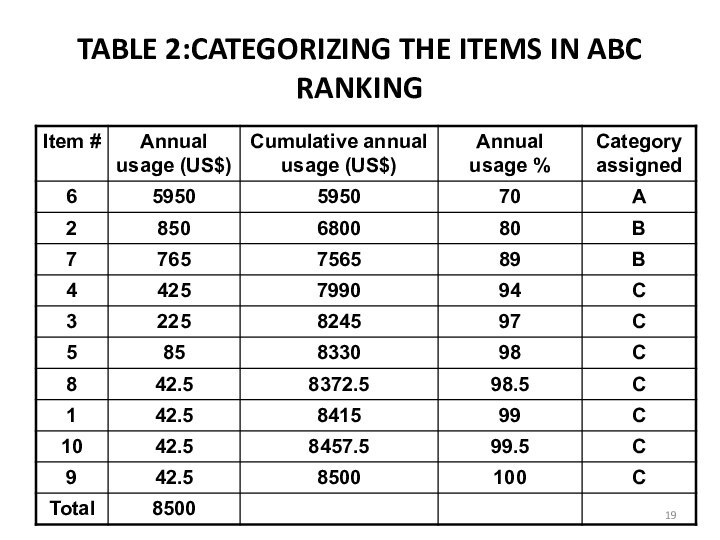
e. Arrange the items in the inventory by cumulative annual usage (dollars) and by cumulative percentage. Categorize the items in A, B , and C categories.
Слайд 21
VED анализ
In addition to the intrinsic or market
value of materials, which is invested in the materials,
there is sometimes a nuisance value to the materials.In ABC analysis, we have seen that annual consumption value; quantity of materials consumed and unit cost plays a vital role.
This is to say that ABC analysis deals with the annual consumption value of the item due to their presence and not any other aspect such as the criticality of the material or the nuisance value.
Слайд 22
VED анализ
The nuisance Value is the cost associated
with materials due to their absence. Some of the
materials are important by their absence.In case they are not available, the whole production system may come to standstill and involve high cost of loss of production.
The investment in these materials may be small but for non – availability of the item the costs or losses the company going to involve will be very high. These are critical items, which are required in adequate quantity.
Слайд 23
VED анализ
The materials may be classified depending upon
their criticality that is on functional basis.
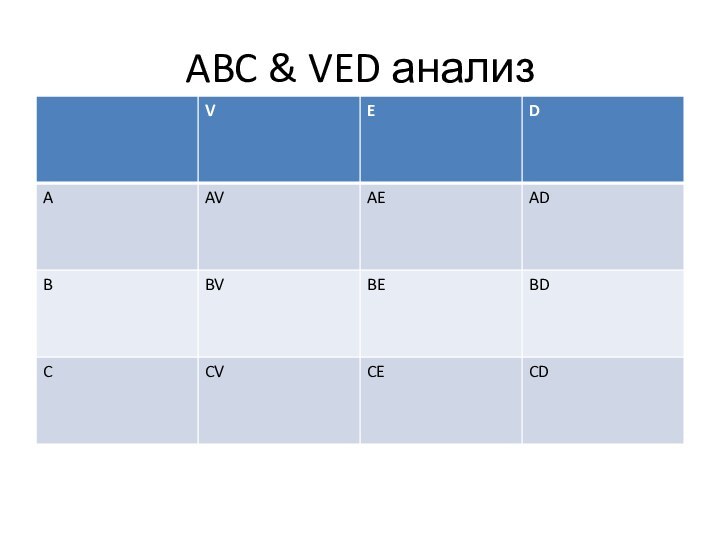
The degree
of criticality can be stated as whether the material is vital to the process of production, or essential to the process of production or desirable for the process of production. This classification is known as VED analysis, V stands for vital, E stands for essential and D stands for desirable items.
Слайд 24
VED анализ
The materials may be classified depending upon
their criticality that is on functional basis.
The degree
of criticality can be stated as whether the material is vital to the process of production, or essential to the process of production or desirable for the process of production. This classification is known as VED analysis, V stands for vital, E stands for essential and D stands for desirable items.
Слайд 26
Заключение
После проведения этих 2 анализов становится понятно, каким
именно образом нужно расставить приоритеты по разным товарам и
запасам в вопросе общего количества остатка на складе, конкретного местоположения на складе, а также способе хранения.Данные 2 анализа проводятся в обязательном порядке на ранней стадии загрузки склада, а также периодически, для проверки рациональности соотношений и показателей.