- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Redox reactions
Содержание
- 2. The concept of redox reactions Redox reactions
- 3. Oxidation - the process of recoil electrons
- 4. Recovery - the process of
- 5. Recovery - atoms, molecules, or ions
- 6. Oxidants - atoms, molecules or
- 7. On the display of the redox properties
- 8. The degree of oxidation of sulfur: -2,0,+4,+6
- 9. Определение степеней окисления атомов химических элементовThe oxidation
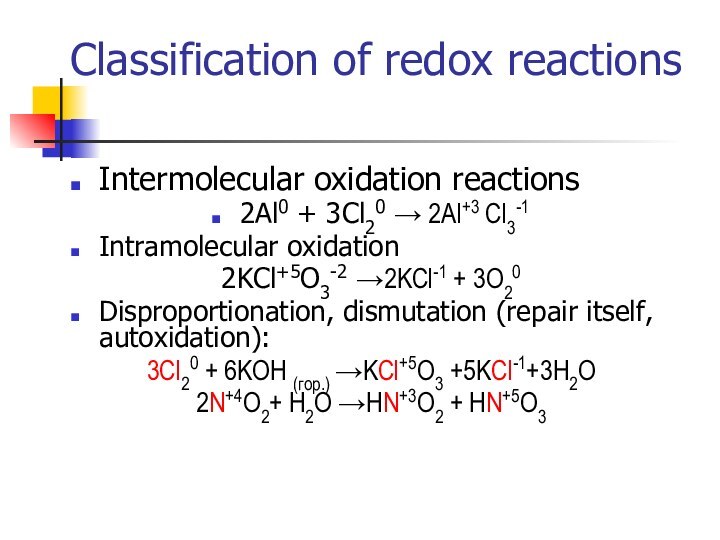
- 10. Classification of redox reactionsIntermolecular oxidation reactions2Al0 +
- 11. The value of redox reactionsRedox reactions are
- 12. Corrosion of metalsMethods corrosion protection
- 13. CORROSION - spontaneous destruction of metals and
- 14. Factors that may cause corrosionOxygen and atmospheric
- 15. gasatmosphericsoilliquid (acid, salt, alkali)chemicalelectrochemicalis uniformnonuniform (or local election)
- 16. CHEMICAL - a failure of metals and
- 17. Electrochemical - a failure of metals, which
- 18. CONDITIONS of electrochemical corrosionThe position of the
- 19. METHODS corrosion protectionThe application of protective coatings
- 20. Скачать презентацию
- 21. Похожие презентации
The concept of redox reactions Redox reactions - chemical reactions that occur with a change in the oxidation state of the elements included in the reactants



















Слайд 3 Oxidation - the process of recoil electrons an
atom, molecule or ion.
Atoms are converted into positively charged
ion: Zn0 – 2e → Zn2+negatively charged ion becomes neutral atom: 2Cl- -2e →Cl20
S2- -2e →S0
The value of the positively charged ion (an atom) is increased accordingly the number of electron donating:
Fe2+ -1e →Fe3+
Mn+2 -2e →Mn+4
Слайд 4 Recovery - the process of accession
of electrons an atom, molecule or ion.
Atom converted to
a negatively charged ionS0 + 2e → S2−
Br0 + e → Br −
The value of the positively charged ions (atoms) reduced by the number of electrons attached:
Mn+7 + 5e → Mn+2
S+6 + 2e → S+4
− or it can go into a neutral atom:
Н+ + е → Н0
Cu2+ + 2e → Cu0
Слайд 5 Recovery - atoms, molecules, or ions donate
electrons. They are in the process redox reaction oxidized
Typical reductants:
● metal atoms with high atomic radii (I-A, II-A group), as well as Fe, Al, Zn
● simple substances, non-metals: hydrogen, carbon, boron;
● negative ions: Cl−, Br−, I−, S2−, N−3. We are reducing the fluoride ion F−.
● metal ions in lower oxidation states: Fe2+,Cu+,Mn2+,Cr3+;
● complex ions and molecules containing atoms with intermediate oxidation state: SO32−, NO2−; СО, MnO2 and others.
Слайд 6 Oxidants - atoms, molecules or ions,
electrons join. They are in the process of oxidation-reduction
reactions are restoredTypical oxidizers:
● nonmetal atoms VII-A, VI-A, VA group consisting of simple substances
● metal ions in the higher oxidation state:
Cu2+, Fe3+,Ag+ …
● Complex ions and molecules containing atoms with the highest and lowest oxidation state:с.о.: SO42−, NO3−, MnO4−, СlО3−, Cr2O72-, SO3, MnO2 and others
Слайд 7
On the display of the redox properties of
the effect of such factors as the stability of
the molecule or ion. The stronger the particle, the less it shows the redox properties
Слайд 8
The degree of oxidation of sulfur: -2,0,+4,+6
Н2S-2 -
reductant
2Н2S+3O2=2H2O+2SO2
S0,S+4O2 – oxidant and reductant
S+O2=SO2
2SO2+O2=2SO3 (reductant)S+2Na=Na2S SO2+2H2S=3S+2H2O
(oxidant)
Н2S+6O4 - oxidant
Cu+2H2SO4=CuSO4+SO2+2H2O
Слайд 9
Определение степеней окисления атомов химических элементов
The oxidation state
of atoms of chemical elements in the simple substance
= 0The algebraic sum of oxidation states of all elements in the ion is the ion charge
The algebraic sum of oxidation states of all elements in the composite material is 0.
K+1 Mn+7 O4-2
1+х+4(-2)=0
Слайд 10
Classification of redox reactions
Intermolecular oxidation reactions
2Al0 + 3Cl20
→ 2Al+3 Cl3-1
Intramolecular oxidation
2KCl+5O3-2 →2KCl-1 + 3O20
Disproportionation, dismutation (repair
itself, autoxidation):3Cl20 + 6KOH (гор.) →KCl+5O3 +5KCl-1+3H2O
2N+4O2+ H2O →HN+3O2 + HN+5O3
Слайд 11
The value of redox reactions
Redox reactions are very
common. They linked the metabolic processes in living organisms,
respiration, rotting, fermentation, photosynthesis.Redox reactions provide the cycling of matter in nature. They can be seen from the combustion and smelting of metal corrosion. With their help prepared alkalis, acids and other valuable chemicals.
Redox reactions underlie energy conversion interacting chemicals in eclectic energy in the battery cell.
Слайд 13 CORROSION - spontaneous destruction of metals and alloys
as a result of chemical and electrochemical interactions with
their environment.This redox reaction in which the metal atoms become ions. The more active the metal, so it is more susceptible to corrosion.
In the role of an oxidant act atmospheric oxygen and hydrogen cations.
Слайд 14
Factors that may cause corrosion
Oxygen and atmospheric moisture
Carbon and sulfur gases contained in the atmosphere
Sea
water Groundwater
Слайд 15
gas
atmospheric
soil
liquid (acid, salt, alkali)
chemical
electrochemical
is uniform
nonuniform (or local election)
Слайд 16 CHEMICAL - a failure of metals and alloys
as a result of their chemical interactions with the
substances of the environment.The protective oxide film on the aluminum surface
Loose film on the iron surface, leading to destruction of metal
Слайд 17 Electrochemical - a failure of metals, which is
accompanied by the appearance of an electric current in
water or another electrolyte medium.Chemical processes - this oxidation metal recoil electrons.
Electrical processes - transfer of electrons from one site to another product.
Слайд 18
CONDITIONS of electrochemical corrosion
The position of the metal
in a series of activity of metal: the farther
they are from each other, the faster corrosion.The purity of the metal: the impurity accelerate corrosion. Irregularities in the metal surface cracks.
Ground water, sea water, the environment of the electrolyte.
Temperature increase.
The action of microorganisms (fungi, bacteria, lichens to metals with high corrosion resistance).
Слайд 19
METHODS corrosion protection
The application of protective coatings (paints,
varnishes, enamels);
Covering other metals (gold-plated, silver, chrome, zinc
plating); Creation and use of corrosion-resistant alloys Introduction to the inhibitors reduce aggressive environment;
Sacrificial protection





























