Слайд 2
Gastric cancer encompasses a heterogeneous collection of etiologic
and histologic subtypes associated with a variety of known
and unknown environmental and genetic factors.
It is a global public health concern, accounting for 700,000 annual deaths worldwide, and currently ranks as the fourth leading cause of cancer mortality, with a 5-year survival of only 20%.
The incidence and prevalence of gastric cancer vary widely, with Asian/Pacific regions bearing the highest rates of disease.
Слайд 3
Approximately 3% to 5% of gastric cancers are
associated with a hereditary predisposition, including a variety of
Mendelian genetic conditions and complex genetic traits.
Слайд 4
Gastric cancer has traditionally been subtyped pathologically according
to Lauren’s1 classification published in 1965 and revised by
Carneiro et al.2 in 1995.
The four histologic categories include:
(1) glandular/intestinal,
(2) border foveal hyperplasia,
(3) mixed intestinal/diffuse, and
(4) solid/undifferentiated.
Слайд 5
More clinically relevant, the majority of gastric cancers
can be subdivided into intestinal type or diffuse type.
Diffuse gastric tumors frequently feature signet ring cells
The intestinal subtype is seen more commonly in older patients, whereas the diffuse type affects younger patients and has a more aggressive clinical course.
Слайд 6
ETIOLOGY
Environmental Risk Factors
diet and lifestyle variables.
Infectious Risk Factors
H. pylori infection
Epstein-Barr virus
Genetics
Слайд 7
More than 70% of cases occur in developing
countries, and men have roughly twice the risk of
women.
In 2008, estimates of gastric cancer burden in the United States were 21,500 cases (13,190 men and 8,310 women) and 10,880 deaths. The median age at diagnosis for gastric cancer is 71 years, and 5-year survival is approximately 25%.
Only 24% of stomach cancers are localized at the time of diagnosis, 30% have lymph node involvement, and another 30% have metastatic disease. Survival rates are predictably higher for those with localized disease, with corresponding 5-year survival rates of 60%.
Слайд 8
PATHOLOGY AND TUMOR BIOLOGY
Approximately 95% of all
gastric cancers are adenocarcinomas.
Слайд 9
PATTERNS OF SPREAD
Carcinomas of the stomach can
spread by local extension to involve adjacent structures and
can develop lymphatic metastases, peritoneal metastases, and distant metastases.
These extensions can occur by the local invasive properties of the tumor, lymphatic spread, or hematogenous dissemination.
Слайд 10
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND PRETREATMENT EVALUATION
Because of the
vague, nonspecific symptoms that characterize gastric cancer, many patients
are diagnosed with advanced-stage disease.
Patients may have a combination of signs and symptoms such as weight loss (22% to 61%)37; anorexia (5% to 40%); fatigue, epigastric discomfort, or pain (62% to 91%); and postprandial fullness, heart burn, indigestion, nausea, and vomiting (6% to 40%). None of these unequivocally indicates gastric cancer. In addition, patients may be asymptomatic (4% to 17%). Weight loss and abdominal pain are the most common presenting symptoms at initial encounter. Weight loss is a common symptom, and its clinical significance should not be underestimated.
Dewys et al. found that in 179 patients with advanced gastric cancer, >80% of patients had a >10% decrease in body weight before diagnosis. Furthermore, patients with weight loss had a significantly shorter survival than did those without weight loss
Слайд 11
Up to 25% of the patients have history/symptoms

of peptic ulcer disease. A history of dysphagia or
pseudoachalasia may indicate the presence of a tumor in the cardia with extension through the gastroesophageal junction. Early satiety is an infrequent symptom of gastric cancer but is indicative of a diffusely infiltrative tumor that has resulted in loss of distensibility of the gastric wall.
Delayed satiety and vomiting may indicate pyloric involvement. Significant gastrointestinal bleeding is uncommon with gastric cancer; however, hematemesis does occur in approximately 10% to 15% of patients, and anemia in 1% to 12% of patients. Signs and symptoms at presentation are often related to spread of disease.
Ascites, jaundice, or a palpable mass indicate incurable disease. The transverse colon is a potential site of malignant fistulization and obstruction from a gastric primary tumor. Diffuse peritoneal spread of disease frequently produces other sites of intestinal obstruction.
A large ovarian mass (Krukenberg’s tumor) or a large peritoneal implant in the pelvis (Blumer’s shelf), which can produce symptoms of rectal obstruction, may be palpable on pelvic or rectal examination.
Nodular metastases in the subcutaneous tissue around the umbilicus (Sister Mary Joseph’s node) or in peripheral lymph nodes such as in the supraclavicular area (Virchow’s node) or axillary region (Irish’s node) represent areas in which a tissue diagnosis can be established with minimal morbidity. There is no symptom complex that occurs early in the evolution of gastric cancer that can identify individuals for further diagnostic measures. However, alarming symptoms (dysphagia, weight loss, and palpable abdominal mass) are independently associated with survival;
increased number and the specific symptom is associated with mortality.
Слайд 12
PRETREATMENT STAGING
Tumor markers – CEA, CA19-9,CA125
EUS
CT
MRI
PET-CT
Staging Laparoscopy
and Peritoneal Cytology
Слайд 13
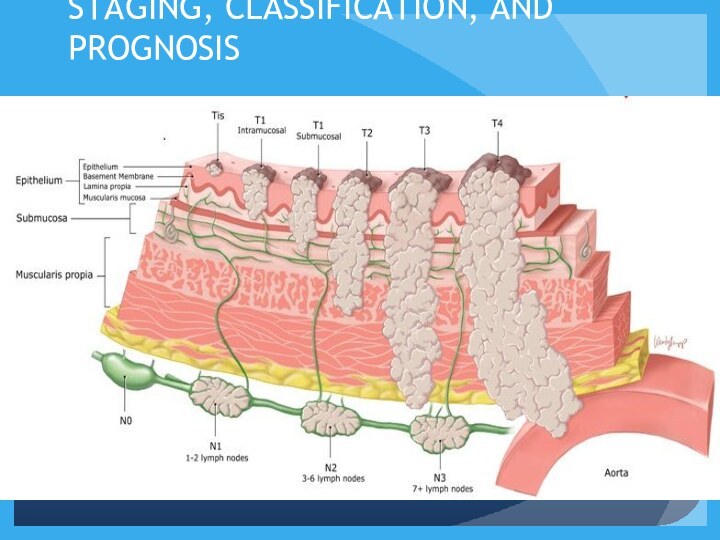
STAGING, CLASSIFICATION, AND PROGNOSIS
Слайд 14
TREATMENT OF LOCALIZED DISEASE
Stage I Disease (Early
Gastric Cancer)
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
Limited Surgical Resection
Gastrectomy
Слайд 15
Stage II and Stage III Disease
GASTRECTOMY
Слайд 16
Adjuvant Therapy
Adjuvant therapy indicates administration of a
treatment following a potential curative resection of the primary
tumor and regional lymph nodes.
Therapy after resections that leave microscopic or gross disease are not adjuvant treatment, but rather therapy for known disease, which is palliative in nature.
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy involves the use of systemic treatment before potentially curative surgery.
Слайд 17
There are several theoretical reasons for beginning adjuvant
therapy soon after operation (perioperative chemotherapy). Studies have shown
a rapid increase in cell growth of metastases after a primary tumor has been removed related to a decline in certain circulating factors, which serve to inhibit angiogenesis or other cell-cycle promotors, once the primary tumor is removed.
Perioperative or neoadjuvant chemotherapy has been studied because the ability to perform a R0 resection in gastric cancer is difficult. In addition, a substantial number of patients undergoing gastrectomy have prolonged recovery.
Слайд 18
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy has a dual goal: allowing a
higher rate of R0 resections and treatment of micrometastatic
disease early in the course of treatment.
Слайд 20
Rationale for Preoperative Therapy in Proximal Gastric Cancer
Studies demonstrating benefit of preoperative chemotherapy over surgery alone1
Evidence of role of induction chemoradiation therapy in distal esophageal CA2
1MAGIC Trial. Cunningham et al. Radiother Oncol 104 (2012)
2CROSS Trial. van Hagen et al. NEJM (2012)
Слайд 21
Importance of Preoperative Staging When Considering Neoadjuvant Therapy
Accuracy
of predicting nodal involvement is 60-80%
Surgery alone may be
sufficient for Stage II disease
Neoadjuvant therapy may be overtreating some patients
Слайд 22
Rationale for Up Front Surgery in Patients With
Gastric Cancer
Pathologic staging may result in more appropriate
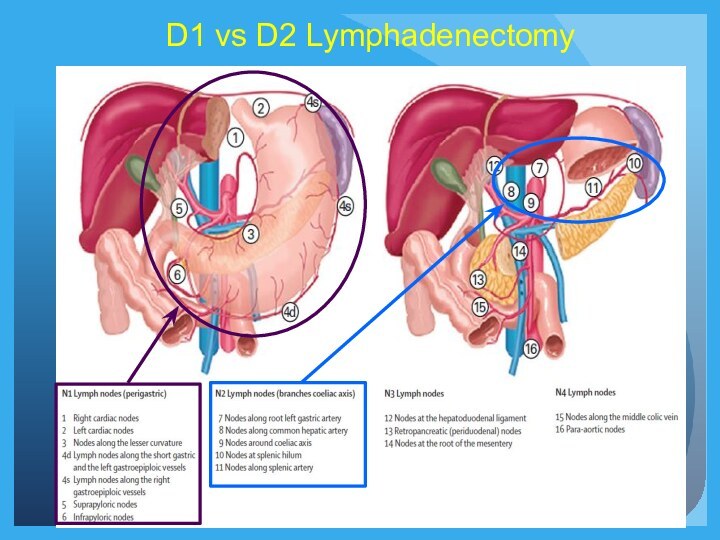
choice of adjuvant therapy (accurate stage II vs III, D1 vs D2, margins).
Symptomatic patients may require initial surgery.
In reality, gastrectomy is often performed before MDT consultation.
Слайд 23
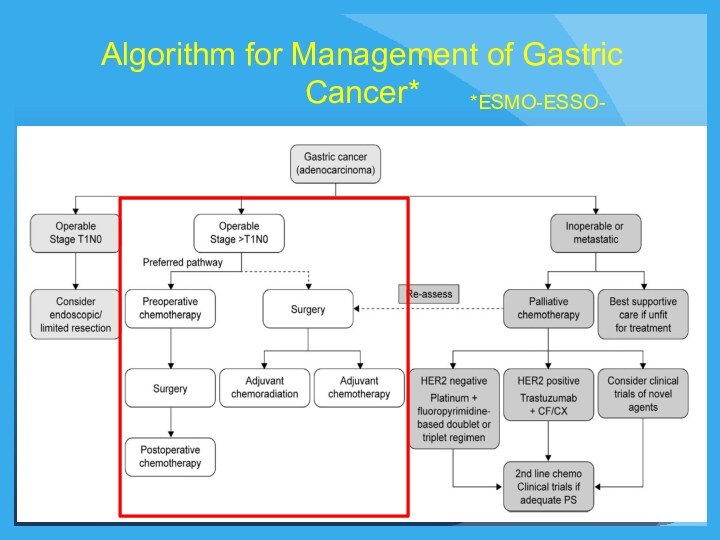
Algorithm for Management of Gastric Cancer*
*ESMO-ESSO-
Слайд 24
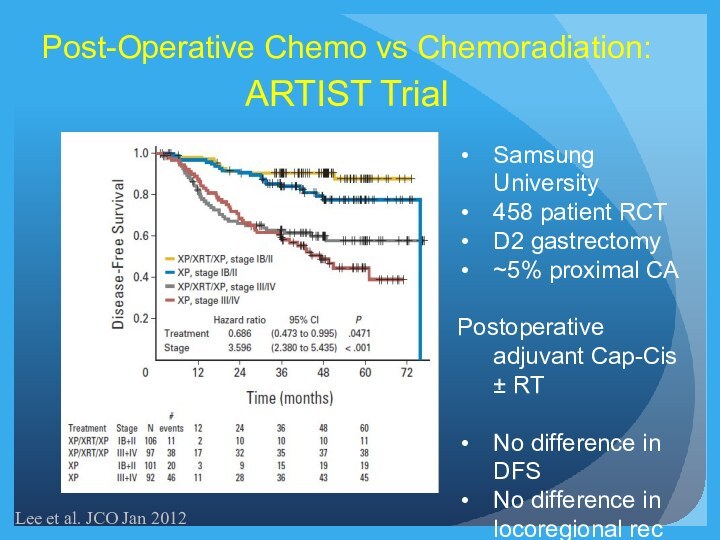
Post-Operative Chemo vs Chemoradiation:
ARTIST Trial
Lee et al. JCO
Jan 2012
Samsung University
458 patient RCT
D2 gastrectomy
~5% proximal CA
Postoperative adjuvant
Cap-Cis ± RT
No difference in DFS
No difference in locoregional rec
Слайд 25
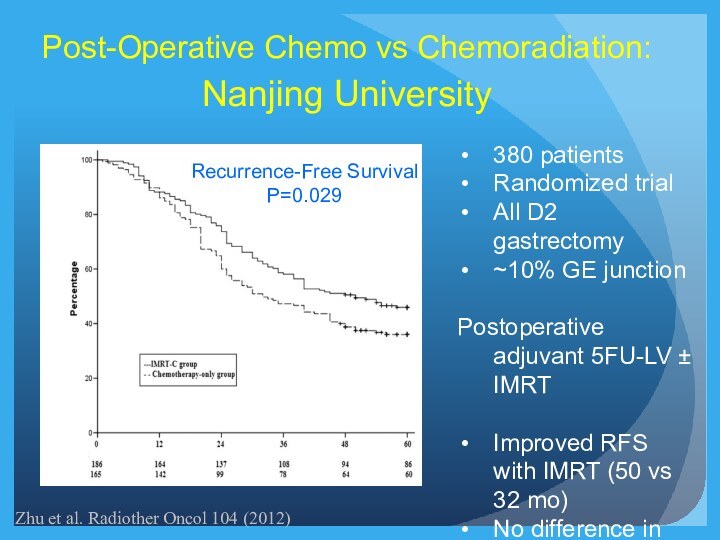
Recurrence-Free Survival
P=0.029
Post-Operative Chemo vs Chemoradiation:
Nanjing University
380 patients
Randomized trial
All
D2 gastrectomy
~10% GE junction
Postoperative adjuvant 5FU-LV ± IMRT
Improved RFS
with IMRT (50 vs 32 mo)
No difference in OS
Zhu et al. Radiother Oncol 104 (2012)
Слайд 26
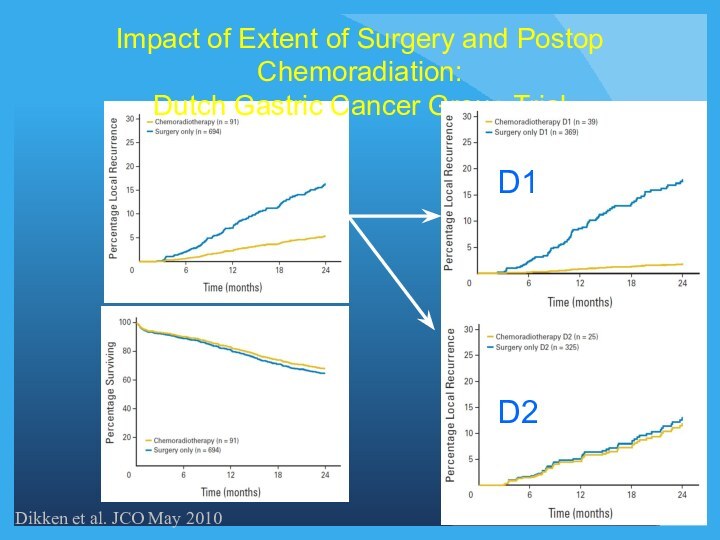
Impact of Extent of Surgery and Postop Chemoradiation:
Dutch
Gastric Cancer Group Trial
Dikken et al. JCO May 2010
Слайд 27
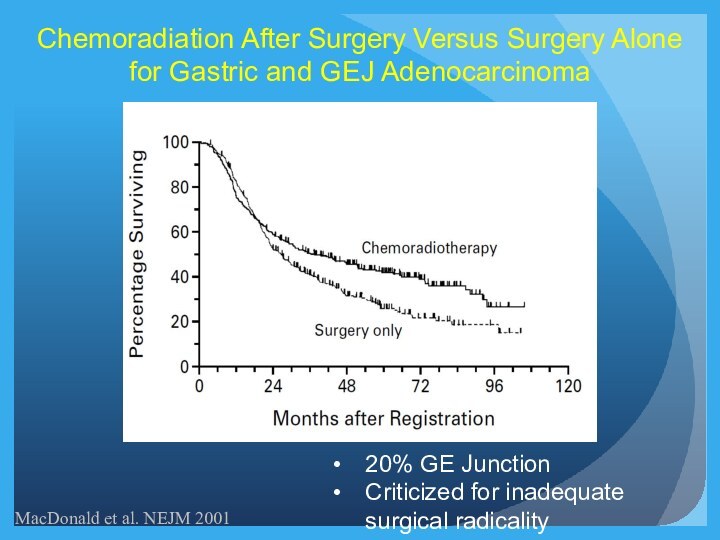
MacDonald et al. NEJM 2001
Chemoradiation After Surgery Versus
Surgery Alone for Gastric and GEJ Adenocarcinoma
20% GE Junction
Criticized
for inadequate surgical radicality
Слайд 28
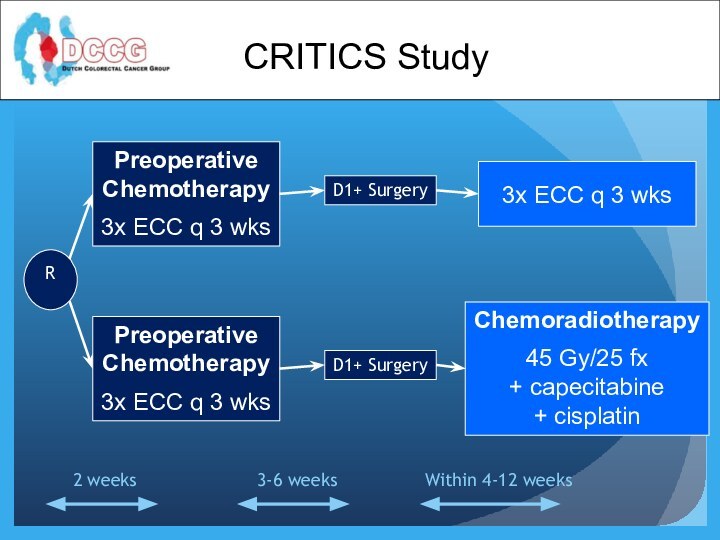
Preoperative
Chemotherapy
3x ECC q 3 wks
Preoperative
Chemotherapy
3x ECC q 3
wks
D1+ Surgery
D1+ Surgery
3x ECC q 3 wks
Chemoradiotherapy
45 Gy/25 fx
+
capecitabine
+ cisplatin
R
Within 4-12 weeks
3-6 weeks
2 weeks
CRITICS Study
Слайд 29
Summary
Adjuvant Therapy for Proximal Gastric Cancer
While preoperative therapy
may be preferred in most cases, initial gastrectomy is
being commonly performed.
While R0 gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy is recommended, less radical surgery is common.
Chemoradiation appears to have a role in reducing local recurrence.
Postoperative chemoradiation should be considered when managing a post-op patient, particularly when