- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему GI Hemorrhage
Содержание
- 2. LOWER GI BLEEDINGDefinition: LGIB is defined as
- 3. LGI hemorrhageSitesColon – 95-97%Small bowel – 3-5%Only
- 4. LGI hemorrhageEtiologyDiverticulosis – 40-55%Right sided lesions >
- 5. LGI hemorrhage diagnosticsLarge caliber NGT on admissionColonoscopyWithin
- 7. CONCLUSION LGIB requires pre op localization to
- 8. Скачать презентацию
- 9. Похожие презентации
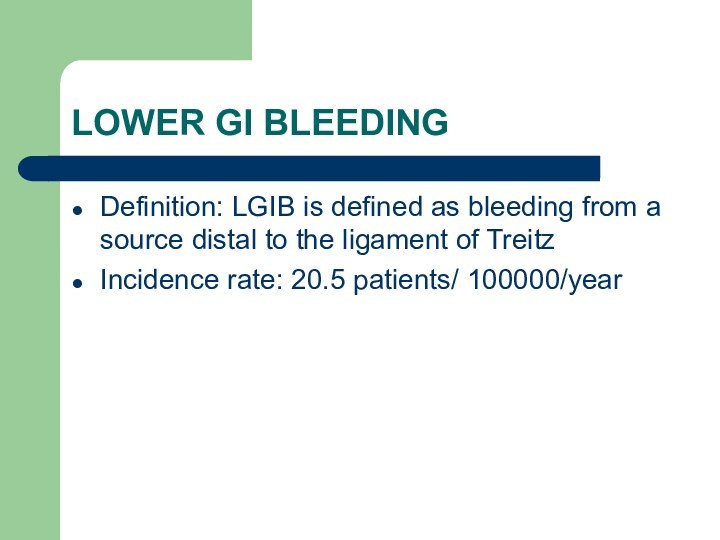
LOWER GI BLEEDINGDefinition: LGIB is defined as bleeding from a source distal to the ligament of TreitzIncidence rate: 20.5 patients/ 100000/year





Слайд 2
LOWER GI BLEEDING
Definition: LGIB is defined as bleeding
from a source distal to the ligament of Treitz
rate: 20.5 patients/ 100000/year
Слайд 3
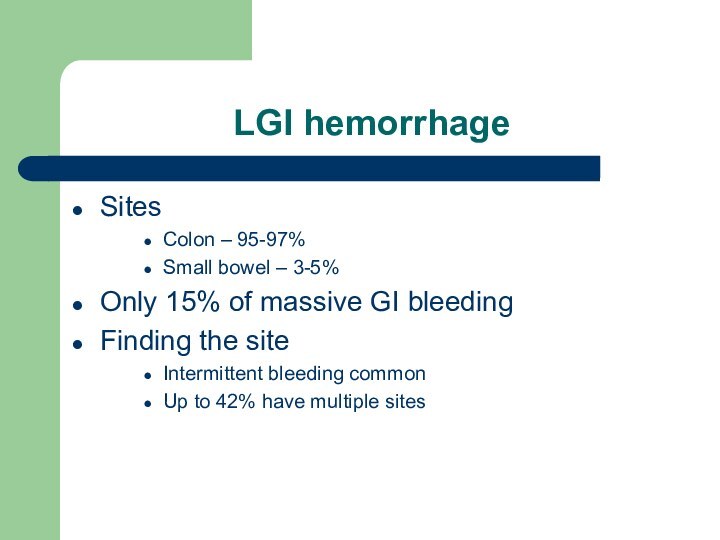
LGI hemorrhage
Sites
Colon – 95-97%
Small bowel – 3-5%
Only 15%
of massive GI bleeding
Finding the site
Intermittent bleeding common
Up to
42% have multiple sites
Слайд 4
LGI hemorrhage
Etiology
Diverticulosis – 40-55%
Right sided lesions > left
90%
stop spontaneously
10% rebleed in 1st year and 25% at
4 yearsAngiodysplasia – 3-20%
Most common cause of SB bleeding in >50 y/o
>50% are in right colon
Neoplasia
Typically bleed slowly
Inflammatory conditions
15% of UC patients, 1% of chron’s patients
Radiation, infectious, AIDS rarely
Vascular
Hemorrhoids
>50% have hemorrhoids, but only 2% of bleeding attributed to them
Others
Слайд 5
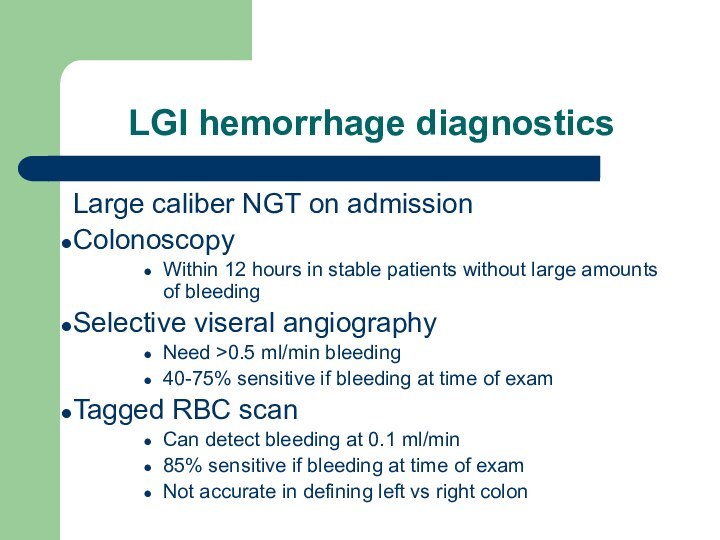
LGI hemorrhage diagnostics
Large caliber NGT on admission
Colonoscopy
Within 12
hours in stable patients without large amounts of bleeding
Selective
viseral angiographyNeed >0.5 ml/min bleeding
40-75% sensitive if bleeding at time of exam
Tagged RBC scan
Can detect bleeding at 0.1 ml/min
85% sensitive if bleeding at time of exam
Not accurate in defining left vs right colon
Слайд 7
CONCLUSION
LGIB requires pre op localization to detect
the bleeding source , including rectoscopy, colonoscopy,angography and nuclear
scan.Interventional treatment by colonoscopy and selective angiographic catheterization and embolization shows good results and low bleeding rates.
If an interventional therapy is not possible, a directed limited colonic or small bowel resection should be considered.