- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Injections. Punctures
Содержание
- 2. INJECTIONSAn injection is an infusion method of
- 3. METHODS OF INJECTIONThere are several methods of
- 4. INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTIONS Choose muscle tissue of lesser
- 6. SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTIONSGive Subcutaneous injections half way up
- 8. INTRAVENOUS THERAPYIntravenous therapy is the infusion of
- 10. CONSEQUENCES OF POOR INJECTION TECHNIQUESTreatment failure, if
- 11. RECORDS OF TREATMENTAll treatments given to food
- 12. CARDIAC PUNCTURECardiac puncture is a suitable technique
- 13. ARTHROCENTESISArthrocentesis is performed in cases of suspected
- 14. TECHNIQUESedation and local anesthesia - Many animals require
- 15. Procedure - The skin over the joint(s) is
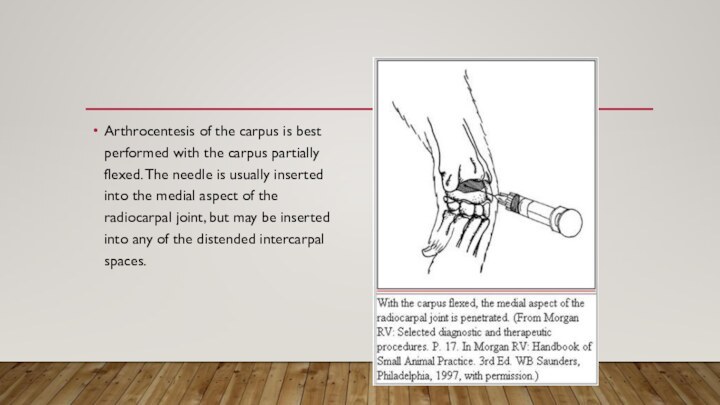
- 16. Arthrocentesis of the carpus is best performed
- 17. Скачать презентацию
- 18. Похожие презентации
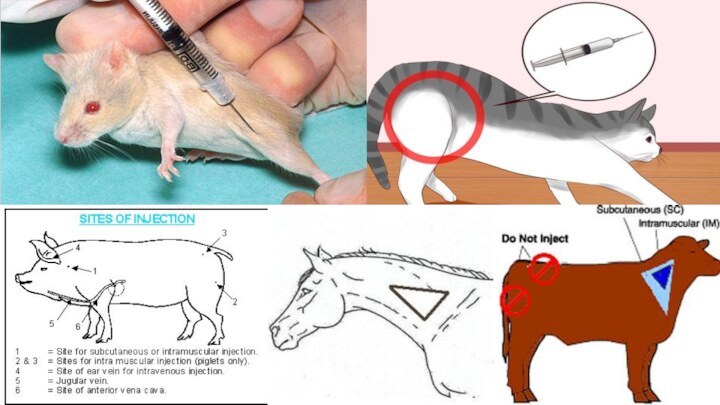
INJECTIONSAn injection is an infusion method of putting fluid into the body, usually with a syringe and a hollow needle which is pierced through the skin to a sufficient depth for the material to be administered














Слайд 3
METHODS OF INJECTION
There are several methods of injection
or infusion used in animals, including intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular,
intravenous, intraosseous, intraperitoneal, intrathecal, epidural, intracardiac, intraarticular, intracavernous, and intravitreal. Rodents used for research are often administered intracerebral, intracerebroventricular, or intraportal injections as well.
Слайд 4
INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTIONS
Choose muscle tissue of lesser value
to consumers for intramuscular injections. In cattle, for example,
intramuscular injections where possible, are often given in the neck area instead of the hip.Give intramuscular injections deep into a muscle. Use a needle long enough to penetrate skin, subcutaneous tissue and fat to reach the muscle. The needle should enter the skin perpendicular to the skin surface.
Insert the needle into the animal, and then attach the syringe to the needle. Check that the needle is not in a blood vessel by pulling back on the plunger and observing for blood flow in the tip of the syringe. If blood appears, remove the needle and put it in a different location at least one inch away from the original injection site.
Слайд 6
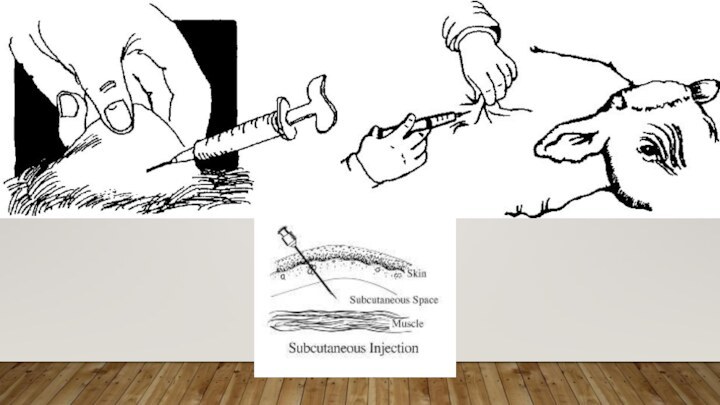
SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTIONS
Give Subcutaneous injections half way up the
neck in front of the shoulder, or over the
ribs well behind the shoulder.Use a 0.5 to 1 inch long needle.
To give Subcutaneous injections for cattle, lift a fold of skin to make a skin "tent". Insert the needle through one side of the tent at an angle of 30 to 45 degrees relative to the surface of the body. For swine, it won't be possible to make a "tent", so slide the needle under the skin at an angle of about 30 degrees from parallel to the skin surface and inject.
Слайд 8
INTRAVENOUS THERAPY
Intravenous therapy is the infusion of liquid
substances directly into a vein. Intravenous simply means "within
vein". Therapies administered intravenously are often included in the designation of specialty drugs. It is commonly referred to as a drip because many systems of administration employ a drip chamber, which prevents air from entering the blood stream (air embolism), and allows an estimation of flow rate.Intravenous therapy may be used to correct electrolyte imbalances, to deliver medications, for blood transfusion or as fluid replacement to correct, for example, dehydration. Intravenous therapy can also be used for chemotherapy.
Compared with other routes of administration, the intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver fluids and medications throughout the body. The bioavailability of the medication is 100% in Intravenous therapy.
Слайд 10
CONSEQUENCES OF POOR INJECTION TECHNIQUES
Treatment failure, if product
absorption is delayed or blocked.
Drug residues in meat or
milk if the drug can not be absorbed and metabolized in a timely manner.Animal suffering and incapacitation due to nerve damage and swelling from tissue reactions.
Excessive trim at slaughter due to abscess, scarring, broken needles.
Shock or death of the animal being treated, if medications unintentionally enter the bloodstream.
Accidental human injection.
Слайд 11
RECORDS OF TREATMENT
All treatments given to food animals
should be permanently recorded to ensure withdrawal time requirements
are met and to improve treatment decisions and success.Keep permanent written records of treatments administered to individuals or groups of animals.
Record the animal's identification, date(s) the treatment was given, product name, amount given, the route, site and time when meat or milk will be ready for sale.
Слайд 12
CARDIAC PUNCTURE
Cardiac puncture is a suitable technique to
obtain a single, large, good quality sample from a
euthanised mouse or a mouse under deep terminal anaesthesia if coagulation parameters, a separate arterial or venous sample or cardiac histology are not required. It is appropriate for all strains of mouse.Cardiac puncture should not be used if the peritoneum needs to be lavaged to harvest cells, as this technique can cause blood to escape into the peritoneal cavity.
Слайд 13
ARTHROCENTESIS
Arthrocentesis is performed in cases of suspected inflammation
or infection of a peripheral joint. Cytologic and microbiologic
analyses of joint fluid help differentiate septic and infectious arthritis from immune-mediated or simple inflammatory arthritis. Aspiration of a joint may also help confirm hemarthrosis following trauma or in association with clotting abnormalities. One or more joints may be aspirated, depending upon the clinical presentation and history. In cases of polyarthritis, multiple joints are often aspirated.Arthrocentesis is also performed for the purpose of insertion of radiologic contrast medium when positive contrast arthrography is undertaken. Occasionally arthrocentesis is used to administer therapeutic medications intrasynovially.
Слайд 14
TECHNIQUE
Sedation and local anesthesia - Many animals require mild
sedation for the procedure. Ill and debilitated animals may
only require manual restraint. A subcuticular infusion of 2% lidocaine provides local anesthesia and is particularly helpful in animals with painful joints. Care must be taken to avoid infusing the lidocaine into the joint space. Contrast arthrography is routinely performed under heavy sedation or general anesthesia.Positioning - The animal is placed in lateral recumbency when arthrocentesis of the shoulder, elbow, stifle or hock joints is performed. The carpal joint may be aspirated in either sternal or lateral recumbency.
Materials - A 3 or 6 ml syringe with a 22 g. needle is most commonly used. An EDTA tube should be available for collection of fluid for cytologic analysis. A culturette in transport medium or thioglycolate broth is used when samples are submitted for bacterial culture.
Слайд 15 Procedure - The skin over the joint(s) is clipped
and prepared using aseptic technique. The joint capsule is
usually distended and is carefully palpated to identify the ideal point of insertion of the needle.When aspirating the stifle, the joint is flexed and the distal portion of the patella is located. The proximal edge of the tibial tuberosity is also palpated and the needle is inserted approximately 2/3 the way between the tuberosity and the patella, just lateral to the patellar tendon. The needle is directed towards the center of the joint, between the two femoral condyles.