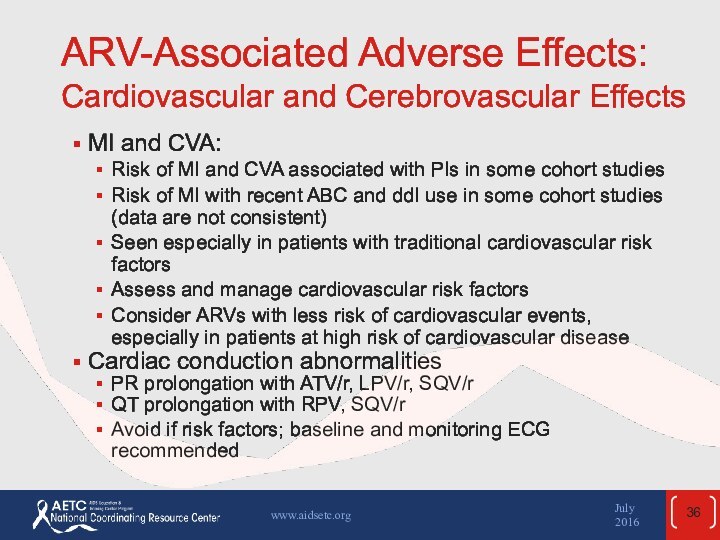
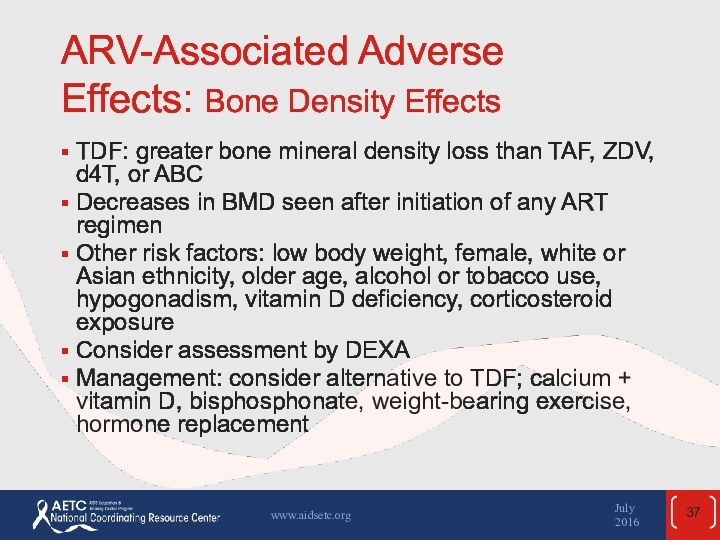
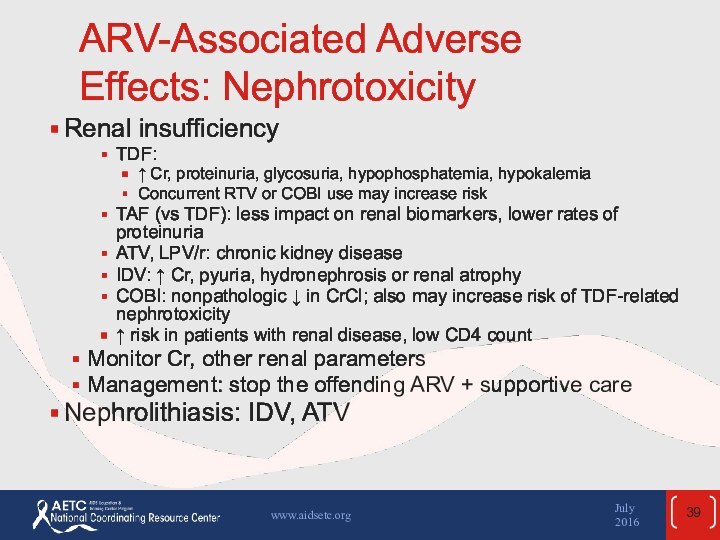
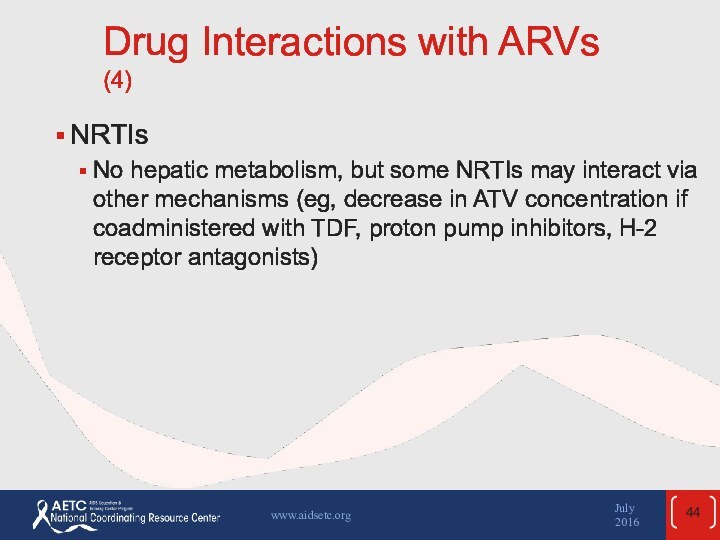
the April 2015 guidelines and updated in July 2016.
The intended audience is clinicians involved in the care of patients with HIV.Because the field of HIV care is rapidly changing, users are cautioned that the information in this presentation may become out of date quickly.
It is intended that these slides be used as prepared, without changes in either content or attribution. Users are asked to honor this intent.
– AETC NCRC http://www.aidsetc.org