Слайд 2
Plan of the lecture
1. Definition of peptic
ulcer disease
2. Etiologic factors
3. Classification
4. Clinical presentation of
peptic ulcer disease
5. Treatment
6. The differential diagnosis of peptic ulcer disease
Слайд 3
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) -
- is
polygene inherited chronic recurrent disease, manifested by formation of
ulcer in stomach or duodenum that can be progressive or develop complications
Code after World wide disease classification (WDC) -10:
К 25 – stomach ulcer
К 26 – duodenum ulcer
Слайд 4
PUD morbidity is 1 case for 1000 healthy
children. Before puberty PUD morbidity is the same in
boys and girls, later it’s more frequent in males because of protective influence of female sexual hormones.
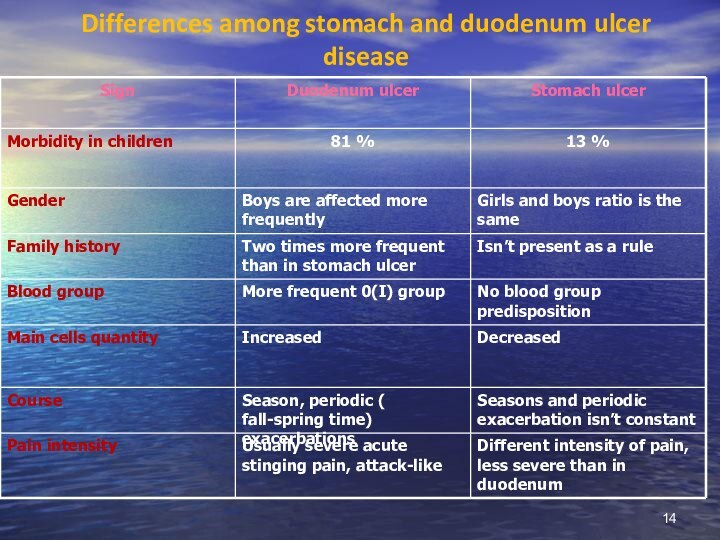
In PUD structure in children PUD of duodenum is more frequent and compound 81% of all cases, 13% are due to stomach PUD and 6% are combination of duodenum and stomach affection.
Слайд 5
Etiology of PUD
The most significant factor of PUD
formation is hereditary predisposition (family load is 60
- 80 %, and as for aggressive features of stomach juice in one of the parents it’s defined in all 100% of cases)
Слайд 6
Predisposing factors
HP contamination
Early formula feeding (it can
induce activation of gastrin produced cells and histamine produced
cells formation in mucous membrane of stomach antrum)
Alimentary inaccuracy
Prolonged consumption of some drugs ( salicylic acid, glucocorticoids, cytostatics etc.))
Peculiarities of family habits – life style, family type of feeding, family relationship
Hypodynamia or physical over loadings
Chronic infection focuses
Intestine parasites
Neuro -psychic over loading
Smoking and drug abuse
Food allergy
Слайд 7
Environment factors
Can change ratio of some regulatory
system compartments, actively influence to peptic acid factor, change
protective properties of mucous barrier.
Prolonged acidity in pyloric and duodenal region induce methaplasia of epithelium in this compartment and predispose to HP invasion. HP can impair epithelium and suppress protective mucous membrane properties , initiate auto-aggressive reactions.
Слайд 8
HP strains of the first type has the
highest cytolytic activity so this strain is 4 times
more in virulence as compared to another strains. In 90% of affected patients this strain is defined.
Слайд 9
Pathogenesis
Hereditary predisposition in PUD has
such features:
Hereditary determined peculiarities of mucous membranes structure –
elevated quantity of gastrin produced and histamine produced cells, hyperplasia of fundal glands with increased quantity of main and acidic cells.
Increased acidic- peptic aggression due to hereditary increased secretion of pepsinogene A( responsible gene is situated in 11 chromosome) and also quality of these pepsinogene with dominating of A type that induce synthesis of PG3 type.
Decreased resistance of mucous membranes due to suppression of mucin and bicarbonates production.
Peculiarities of motor stomach function- decreased obturative reflex that prevent acidic antrum content to pass into duodenum before its alkalizing in antrum.
Слайд 10
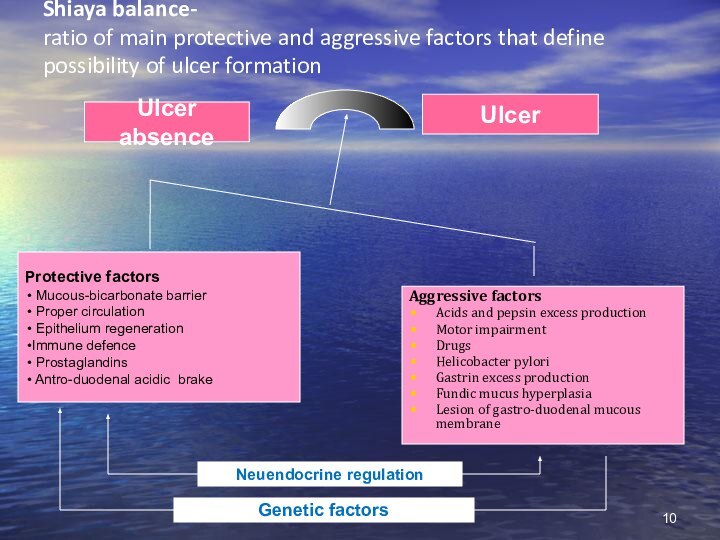
Shiaya balance-
ratio of main protective and aggressive factors
that define possibility of ulcer formation
Protective factors
Mucous-bicarbonate barrier
Proper circulation
Epithelium regeneration
Immune defence
Prostaglandins
Antro-duodenal acidic brake
Ulcer absence
Ulcer
Aggressive factors
Acids and pepsin excess production
Motor impairment
Drugs
Helicobacter pylori
Gastrin excess production
Fundic mucus hyperplasia
Lesion of gastro-duodenal mucous membrane
Neuendocrine regulation
Genetic factors
Слайд 11
Classic clinics of typical pain syndrome in PUD
was described at the beginning of 20 century by
Monigan.
Слайд 12
Clinics
Pain syndrome
Fasting pain appearance or 1,5-2 hours
after feeding ( Moinigan rythm)
Nocturnal pain predominance
Intensity ranges from
slight to severe unbearable
Localized in epigastrium . If accompanied GERD is present it can irradiate retrosternum space.
DYSPEPTIC SYNDROME
Heartburn ( usually together with GERD)
Acidic regurgitation
Vomiting with relieving pain
ABDOMEN PALPATION
Painfulness in epigastrium, sometimes local in pyloric-duodenal region
VAGOTONY SYMPTOMS (in teenagers):
Cold, moist palms
Hyperhydrosis
Acrocyanosis
Decreasing of BP
Pulse lability
SEASONAL FALL –SPRING EXACERBATIONS ARE TYPICAL FOR PUD
Слайд 13
PUD peculiarities in children
Classic clinics can be seen
less than in 50% patients
In 15% children complaints are
absent ( silent ulcer)
In 3% patient first presentation of disease can be complicated ( by bleeding, perforation)
More younger the child more atypical clinics is seen
Слайд 14
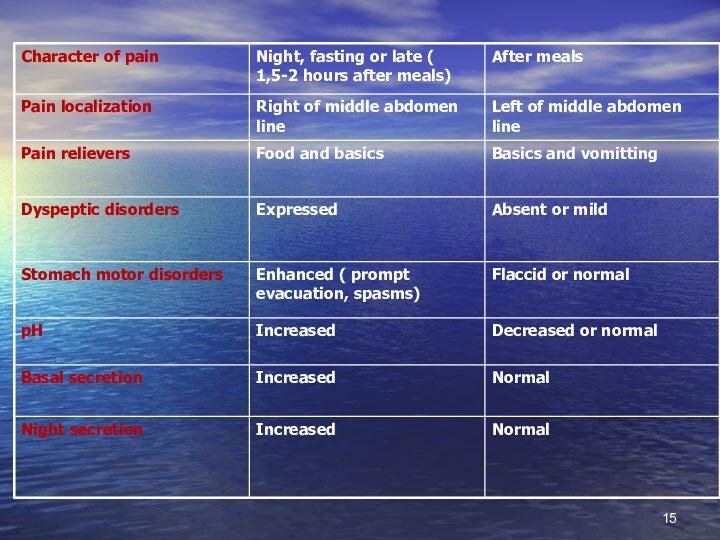
Differences among stomach and duodenum ulcer disease
Слайд 16
Most helpful diagnostic examining
Endoscopy .
X-ray (not obedient for
non-complicated cases).
Examining of secretory function (increasing of basal and
stimulating secretion fractions)- is helpful to define functional disorders but not ulcer itself .
Helicobacter pyloric contamination.
Слайд 17
PUD classification
Severity (first defined, mild-recurrence once per year
and less , moderate – relapse 2 times per
year, severe – recurrence more than 2 times per year and complicatiuons).
Phase – exacerbation, partial remission, remission.
Clinic-endoscopic stage – fresh ulcer, scarring defect, scar, scar-ulcer deformity.
Ulcer localization – Stomach (cardiac, subcardial portion, little, big curvature, pyloric region; duodenum (bulbus, post bulbar region)
Gastritis character (superficial, atrophic, and localization of it) gastroduodenitis (active, erosions, hyperplastic, associated with H.P.)
Functional characteristics (with decreased acidic production, preserved or increased ).
Complications– penetration in pancreas, hepatoduodenal legamentum, gall bladder, liver, colon), acute bleeding , perforation, stenosis (compensated, subcompensated, decompensated, reflux-esophagitis)
Слайд 18
PUD complications
BLEEDING – most frequent (80%) complication.
Clinics: emesis,
melena, symptoms of acute blood loss .
Coffe-like vomiting (Hb
under influence of HCl turn into hematin with dark-brown color)
Melena – is black stool can be seen after the loss of more than 60 ml of blood ( ferrum sulfate realizes under the influence of digestive enzymes)
Symptoms of blood loss appear in the case of big blood loss weakness, nausea, paleness, tachycardia, cold, clammy sweat, BP decreasing, dizziness, vertigo, conscience loss sometimes
Bleeding can be hidden . In stool you can find hidden blood (positive Gregersen reaction)
Слайд 19
Diagnostics approach algorithm in the case of PUD
bleeding
Taking history and patient inspection
Blood group and Rh defining
Endoscopy
and X-ray of stomach and duodenum if necessary
Ultrasound diagnostics of abdomen
Слайд 20
Perforation (8 %) – sudden knife-like pain in
epigastrium, nausea, defans of anterior abdomen wall , vomiting
without condition improvement
Penetration (1,5 %) – spreading of ulcer into surrounding tissues. It can be defined by X-ray examining by changing of the near organs functioning
Pyloro- duodenal stenosis (11 %). Formed steadily . Accompanied by sensation of stomach overfilling, nausea, regurgitation, burning, vomiting with relief of condition. The splash sound in epigastrium. By X-ray stomach dilation with retardation of its emptying.
Слайд 21
Differential diagnosis
Must be performed with acute symptomatic ulcers.
STRESS -ulcers They can appear in burnings, trauma, freezing.
Clinics is scanty. The first presentation can be bleeding, more rae –perforation.
Due to medicine influences Appear after consuming the medications that can disturb barrier properties of mucus (non-steroid and steroid drugs, cytostatics, etc). They are presented by asymptomatic course. Bleeding can be the first manifestation,
Hepatogenic. Can appear if inactivation of gastrin and histamine is impaired in liver. Clinics is vague and atypical, course is torpid, badly corrected by treatment.
Pancreogenic. Appear in the case of decreased production of bicarbonates and increased production of kinins. Pain syndrome is manifested and induced by food consuming. Course is constant.
Слайд 22
Endocrine. Very rare development in diabetes, hypothyroidism. Course
of this ulcer disease id similar to severe course
of PUD.
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome – gastrin produced neoplasms (gastrinoma) . IT’s usually localized in antral part of stomach or in pancreas, in 16% of cases it can be malignant. It’s resistant to PUD therapy. Screening test is elevation of gastrin in fasting condition in serum.
Allergic ulceration more frequently can be developed in the case of food allergy.
In chronic renal failure due to impairment of gastrin degradation in kidneys and as a result disturb of protective barrier in stomach
In diffuse connective tissue disorders due to impairment of microcirculation .
Слайд 23
Clinics of symptomatic ulcers
Diagnostic difficulties
Absence of typical pain
syndrome and dyspeptic symptoms
Absence of seasonal periodic exacerbation
High risk
of life threatening conditions ( bleeding, perforation)
Endoscopic data
Ulcers can be singular or multiple
Ulcer diameter usually is not more than 1 cm .
Shape of ulcer defect is oval or round, so called “punched ulcers”
Bottom of ulcer defect is plant crater-like.
Around the defect there is bright red crown, but inflammatory ring is absent.
Main localization is stomach
Prompt epithelization.
Слайд 24
Treatment goals
To reduce PUD symptoms and provide reparation
of ulcer defect
Eradicate contamination of H.P. of mucus.
Not
only get the healing of defect but restitute functional capacity of mucous membrane.
Prevent development of exacerbations and complications.
Слайд 25
PUD treatment
PUD treatment
is directed to suppress aggression factors like acidic –peptic
factor and contamination of mucous membrane by HELICOBACTER PYLORI .
Main principles :
Reject of smoking, alcohol taking.
Stop to get non-steroid and steroid medications, if it can’t be stopped to decrease dosages.
Rational feeding. It means frequent intake 5-6 times per day with excluding of spicy products. Diet N 1-b in the case of exacerbation signs.
Medication treatment.
HELICOBACTER PYLORI eradication
Suppressing of acidity and peptic factors production
Correct motor evacuative function .
Stimulation of reparative processes.
Слайд 26
Medication treatment of PUD
PUD is obligatory indication for
H.P. eradicative therapy in any stage of disease
Treatment include
first and second line of eradicative therapy.
First line is performed after diagnosis of PUD in any period (exacerbation or remission) and complications.
Control of its efficiency is performed a month later the treatment not earlier predominantly by noninvasive methods: breathing test (carbonic C13 or Helic-test) or test of H.P defining in stool.
If test is positive for H.P. second line therapy is proposed. If test is negative therapy is stopped.
Слайд 27
HELICOBACTER PYLORI eradication provides regression of
inflammatory and dystrophic changes and restitutes protective properties of
stomach mucous membranes.
Antihelicobacter pylori medications – methronidazole, Clarythromycine, Amoxycylline, colloid Bismuthi subcytrate.
Approximal eradicative schemes:
Omeprazol + Clarythromycine + Methronidazole
Omeprazol + Amoxycilline + Clarythromycine
Omeprazole + colloid Bismuthi subcytrate +Methronidazole + Amoxycilline
COMBINED ANTIBACTERIAL MEDICATIONS.
Gastrostat (colloid Bismuthi subcytratis + Tetracycline + Methronidazole)
Gastropak – (colloid Bismuthi subcytratis + Amoxicilline + Methronidazole)
Pylorid (ranitidin + colloid Bismuthi subcytratis )
Helicocide (Amoxicilline+ Methronidazole)
Therapy according to schemes is continued for 7 days, later they live only antisecretory therapy.
Слайд 28
Regulations for antihelicobacter therapy
If usage of the eradication
scheme doesn’t provide complete H.pylori eradication you needn’t to
repeat it once more. It means that H.P . get resistance to one of the components in this scheme.
If usage of one scheme later another scheme don’t provide complete H.P. eradication you need to check susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori to all the spectrum of prescribed antibiotics.
Appearance of H.pylori in patient earlier than one year after eradication means recurrence of infection but not reinfection. You need to choose more effective treatment scheme.
Decreasing of antibiotic quantity in scheme leads to H. pylori resistance formation. After finishing of 7 day combined eradicative treatment you can prolong it for 4-5 days in the case o duodenal ulcer and 7-8 weeks in stomach one with usage of one antisecretory drug.
Слайд 29
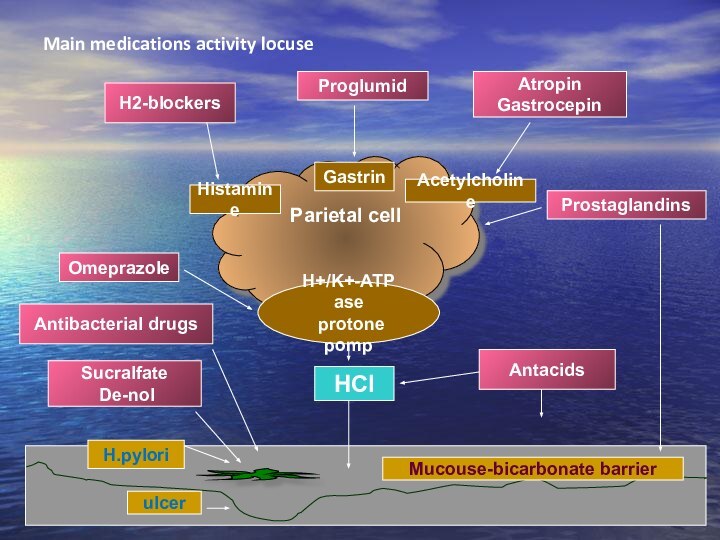
Main medications activity locuse
Parietal cell
Н+/K+-АТP ase
protone pomp
Histamine
Gastrin
Acetylcholine
ulcer
H.pylori
Mucouse-bicarbonate
barrier
Н2-blockers
Proglumid
Atropin
Gastrocepin
Prostaglandins
Omeprazole
HCl
Antacids
Antibacterial drugs
Sucralfate
De-nol
Слайд 30
Antisecretory medications
Selective M-cholinolytics (pirenzepim, gastrocepin)
Н2-histamine receptor
blockers (ranitidin, famotidin)
Protone pomp inhibitors – blockers of Н+/К+АТP
–ase in parietal cells (omeprazole)
Слайд 31
Antisecretory therapy
1. Н2-histamine receptor blockers
Selectively block secretion
of HCl
Decrease volume of gastric juice
Decrease the level
of pepsin
Cimetedine group – 1 generation (Cimetedin, Tagamet, Histodyl, Cimehexal, Neutronorm, rimamet)
Ranitidin group – 2 and 3 generation (Ranitidin, Ranisan, Zantak, Ulkodin, Zoran, Histak, Ranigast, Ranitab, Ranitard, Ranitin)
Famotidin group – 2 and 3 generation (Lecidyl, Gastrocydin, Quamatel, Famocyd, Ulfamid, Famodin)
Nizatidin group (Axid)
Roxatidin group (Roxan)
Слайд 32
2. Peripheral M- choline receptors blockers
(gastrocepin, pyrenzepin, gastrozem,
gastril, pyren)
Suppress HCL and pepsin production
Increase protective properties of
ventricular mucus
3. Н+/К+-АТP ase blockers ( protone pomp inhibitors)
(omeprazol, omez, omeprol, omezak, ornatol, losek)
Inhibit HCl production
Слайд 33
Cytoprotectors
1. Film-forming medications(decrease backward diffusion of Hydrogen ion):
Colloid
Bismuthi subcytrate, De-nol (Tribimol, Ventrixol). Increase prostaglandin production, adsorb
pepsin, has antihelicobacter activity.
Sukralfat (Venter, antepsyn). Connect Aluminium with sulfate polysaccharide, in acidic surroundings get adhesive properties. On the surface of erosions and ulcers perform complex compound with protein –helate and create mechanic protective barrier.
Film-forming medications are basic remedies in peptic ulcers with normal secretory function.
Слайд 34
2. PROSTOGLANDINS – increase bicarbonates and mucus production,
increase protective layer thickness, improve microcirculation. It’s mesoprostol (Arboprostyl,
Enprostyl)
It must be taken before meals and before sleeping. Course is 4 weeks.
Слайд 35
If accompanied dysmotility is present (duodeno-gastral reflux, gastro-esophageal
reflux) DOPA-receptor blockers (cerucal, motilium) 1mg/kg TID or cizaprid
(Coordinax, Propulsid) 0,4-0,5 mg/kg /day can be used.
Spasmolytics (no-spa, Papaverin, Platiohyllin, Buskopan)
Слайд 36
Bleeding treatment
Urgent hospitalization to provide endoscopic treatment (diathermo
coagulation, laser coagulation).
Intravenous infusion of haemostatic medications (Vicasol, Calcium,
Androxol)
Oral intake of 5 % Sol. Of Aminocapronic acid with Thrombin and Androxol
Prescribing of Н2 –histamine blockers IM (Quamatel, 2mg/kg/day IV)
If bleeding is significant transfusion of plasma or blood (only of the same group)
Слайд 37
Duration of hospitalization in the case of Duodenum
PUD is 28 days, in Stomach PUD – 30-35
days, in the case of severe course it can be 6-8 weeks.
After ulcer healing (phase of incomplete remission) treatment can be prolonged at ambulatory regimen. In the phase of remission sanatorium treatment is desirable.
Слайд 38
Efficacy criteria of therapy is clinic and endoscopic
remission, exacerbation symptoms absence, healing of ulcer defect and
absence of inflammatory signs while endoscopic examining. Observation must be provided for 5 years. It can be finished if remission is stable for 5 years.
Слайд 39
Dispensary
Doctor’s examination must be performed 2-4 times
per year depending on severity of disease.
If exacerbations
are absent FGDS must be performed once per year. It will be done in the case of therapy inefficiency “on demand” during exacerbation period.
Stomach secretion must be examined by pH-metry once per year.
Stool analysis for hidden blood must be performed twice per year.
Слайд 40
During complete remission period diet № 1 is
taken for 4-6 mo.
Child is freed from physical
training in the main group.
During dispensary period two times per year ( usually on fall and spring period) prophylactic treatment courses for 3-4 weeks are performed.
Sanatorium treatment can be recommended only in period of complete remission or period of recovery if signs of gastro-duodenitis are absent. If bleeding has been present sanatorium is permitted not earlier than 6 mo after gaining full remission ( such sanatorium will be preferable like Truskavets, Morshin, Berezovsky mineral waters, Ray-Yelenovka etc.)
If child has no exacerbations for 5 years and he is in complete remission he is stopped to undergo dispensary examination.