Слайд 2
We will talk about…
What is 3D printing?
How does
3D printing work?
Processes and technologies
Examples and applications of 3D
printing
3D printing in future
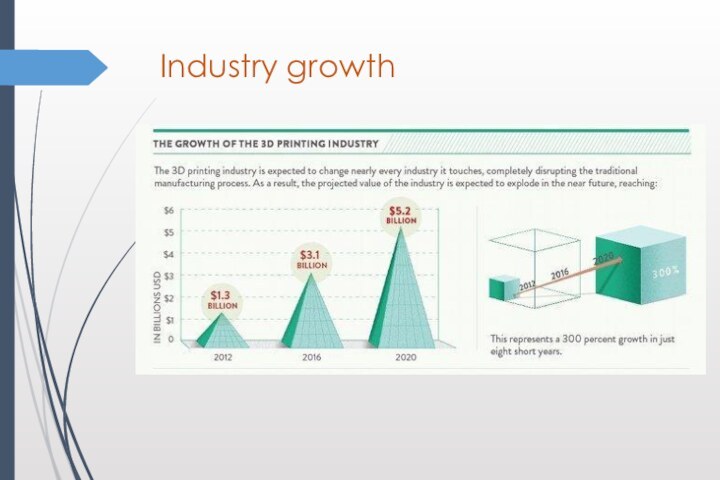
Industry growth
Printers from Russian producers
Our offer and experience
Слайд 3
What is 3D printing?
3D printing or additive manufacturing
is a process of making three dimensional solid objects
from a digital file. The creation of a 3D printed object is achieved using additive processes. In an additive process an object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the entire object is created. Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced horizontal cross-section of the eventual object.
Слайд 4
How does 3D printing work?
It all starts with
making a virtual design of the object you want
to create. This virtual design is made in a CAD (Computer Aided Design) file using a 3D modeling program (for the creation of a totally new object) or with the use of a 3D scanner (to copy an existing object). A 3D scanner makes a 3D digital copy of an object.
3d scanners use different technologies to generate a 3d model such as time-of-flight, structured / modulated light, volumetric scanning and many more.
To prepare a digital file for printing, the 3D modeling software “slices” the final model into hundreds or thousands of horizontal layers. When the sliced file is uploaded in a 3D printer, the object can be created layer by layer. The 3D printer reads every slice (or 2D image) and creates the object, blending each layer with hardly any visible sign of the layers, with as a result the three dimensional object.
Слайд 5
Processes and technologies
Not all 3D printers use the
same technology. There are several ways to print and
all those available are additive, differing mainly in the way layers are build to create the final object.
To be more precise: since 2010, the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) group “ASTM F42 – Additive Manufacturing”, developed a set of standards that classify the Additive Manufacturing processes into 7 categories according to Standard Terminology for Additive Manufacturing Technologies. These seven processes are:
Vat Photopolymerisation
Material Jetting
Binder Jetting
Material Extrusion
Powder Bed Fusion
Sheet Lamination
Directed Energy Deposition
Слайд 6
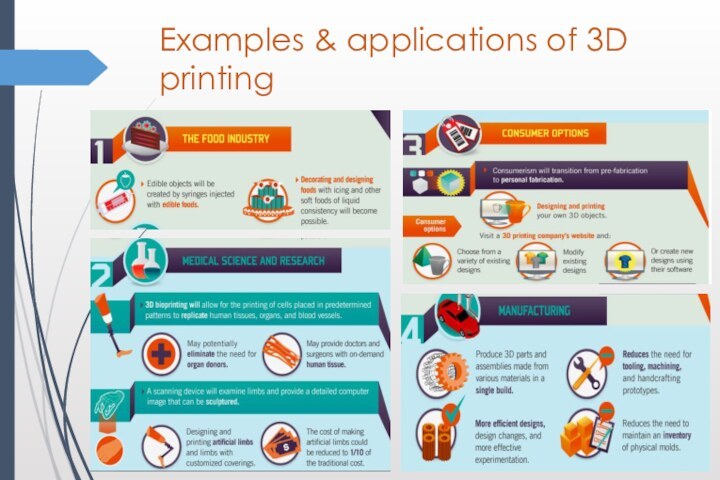
Examples & applications of 3D printing
Слайд 7
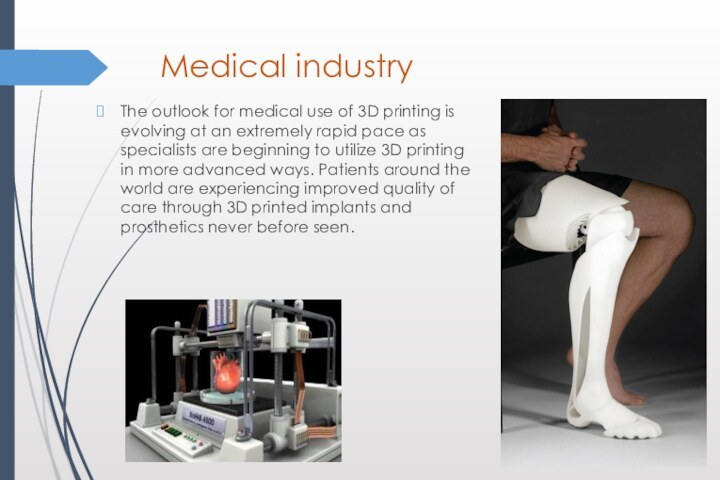
Medical industry
The outlook for medical use of 3D
printing is evolving at an extremely rapid pace as
specialists are beginning to utilize 3D printing in more advanced ways. Patients around the world are experiencing improved quality of care through 3D printed implants and prosthetics never before seen.
Слайд 8
Aerospace & aviation industries
The growth in utilisation of
3D printing in the aerospace and aviation industries can,
for a large part, be derived from the developments in the metal additive manufacturing sector.
Слайд 9
Automotive industry
Although the automotive industry was among the
earliest adopters of 3D printing it has for decades
relegated 3d printing technology to low volume prototyping applications.
Nowadays the use of 3D printing in automotive is evolving from relatively simple concept models for fit and finish checks and design verification, to functional parts that are used in test vehicles, engines, and platforms. The expectations are that 3D printing in the automotive industry will generate a combined $1.1 billion dollars by 2019.
Слайд 10
Industrial printing
In the last couple of years the
term 3D printing has become more known and the
technology has reached a broader public. Still, most people haven’t even heard of the term while the technology has been in use for decades. Especially manufacturers have long used these printers in their design process to create prototypes for traditional manufacturing and research purposes. Using 3D printers for these purposes is called rapid prototyping.
Слайд 11
Personal printing
Personal 3D printing or domestic 3D printing
is mainly for hobbyists and enthusiasts and really started
growing in 2011.
Слайд 12
Future
It is predicted by some additive manufacturing advocates
that this technological development will change the nature of
commerce, because end users will be able to do much of their own manufacturing rather than engaging in trade to buy products from other people and corporations.
3D printers capable of outputting in colour and multiple materials already exist and will continue to improve to a point where functional products will be able to be output. With effects on energy use, waste reduction, customization, product availability, medicine, art, construction and sciences, 3D printing will change the manufacturing world as we know it.
Слайд 14
Printers from Russian producers
Full metal construction
The possibility to
use the plastic of any quality
High speed of printing
without loosing of product quality
Easy in service
No name brand