Слайд 2
1–
Chapter 1 Managers & Management
Management: what is it
& what its benefits are?
What managers do: the four
principal functions
Pyramid Power: levels & areas of management
Managers’ Roles
Managers’ Skills
What are rewards of studying management?
Review quiz
Слайд 3
1–
L E A R N I N G
O U T C O M E S
At the
end of this lesson, you should be able to:
Explain what is meant by the term management, who are managers
Differentiate between efficiency and effectiveness.
Describe the four primary processes of management.
Classify the three levels of managers and identify the primary responsibility of each group.
Слайд 4
Copyright © 2004 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights
reserved.
1–
L E A R N I N G O
U T C O M E S (cont’d)
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
Summarize the essential roles performed by managers.
Discuss whether the manager’s job is generic.
Describe the three general skills necessary for becoming a successful manager.
Describe the value of studying management.
Слайд 5
1. Management: what is it & what its
benefits are?
Слайд 6
Management Defined
Management
The process of getting things done, effectively
and efficiently, through and with other people
Thus managers are
task oriented, achievement oriented, and people oriented. And they operated within an organization.
Organization – a group of people who work together to achieve some specific purpose.
Common characteristics
Goals
Structure
People
Слайд 7
1–
More formally
Management
Is defined as (1) the pursuit of
organizational goals efficiently and effectively by (2) integrating the
work of people through (3) planning, organizing, leading, and controlling the organization’s resources.
Слайд 8
1–
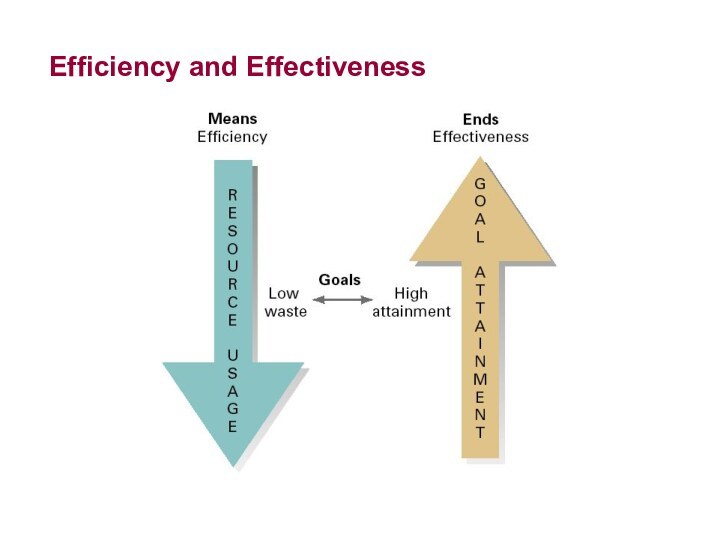
Note the words efficiency & effectively, which basically
means “doing things right”
Efficiency – the means.
Means doing the
thing correctly; refers to the relationship between inputs and outputs; seeks to minimize resource costs
Effectiveness – the ends.
Means doing the right things; goal attainment
Слайд 9
Efficiency and Effectiveness
Слайд 10
Example Boxes, “mini-cases” that use snapshots of
real-world institutions to explain text concepts.
“Your Call” invites
student critical thinking and class discussion at the end of each example.
Слайд 12
2. What managers do: the four principal functions
Слайд 13
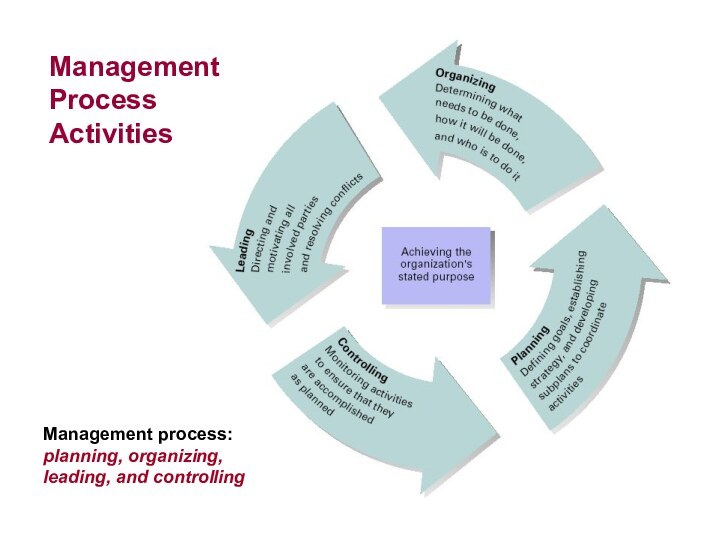
Management
Process
Activities
Management process:
planning, organizing, leading, and controlling
Слайд 14
Management Process
Planning
Includes defining goals, establishing strategy, and developing
plans to coordinate activities
Organizing
Includes determining what tasks
to be
done, who is to do them,
how the tasks are to be
grouped, who reports to
whom, and where
decisions are to be made
Слайд 15
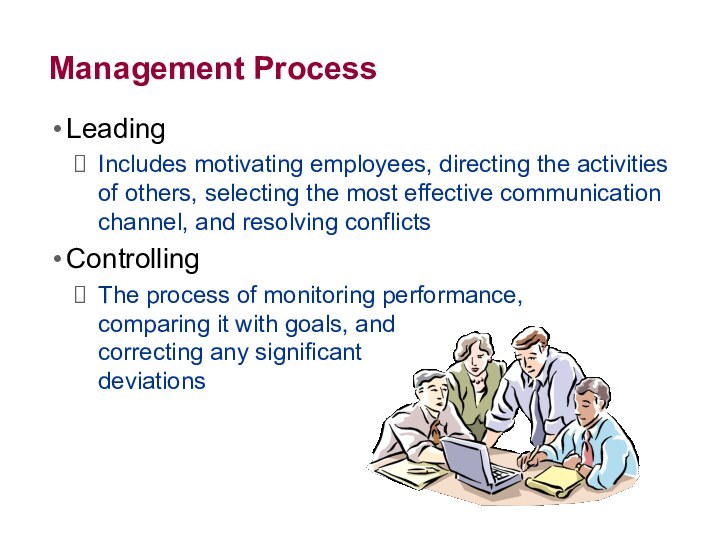
Management Process
Leading
Includes motivating employees, directing the activities of
others, selecting the most effective communication channel, and resolving
conflicts
Controlling
The process of monitoring performance,
comparing it with goals, and
correcting any significant
deviations
Слайд 16
3. Pyramid Power: levels & areas of management
Слайд 18
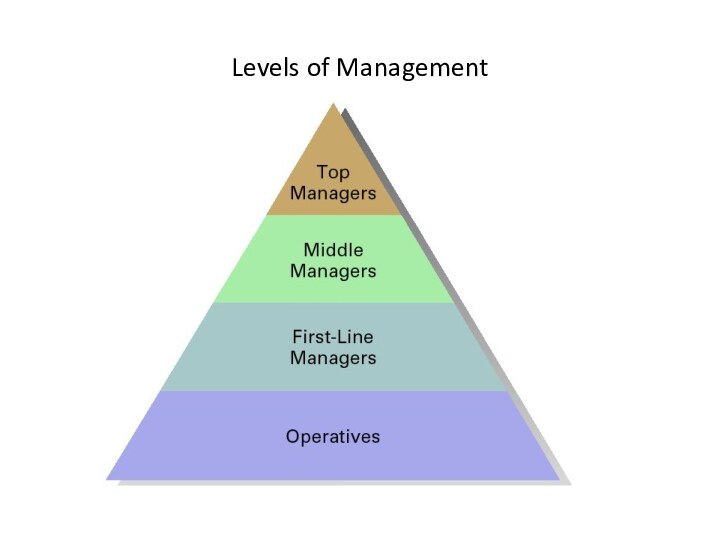
Identifying Managers
First-line managers
Supervisors responsible for directing the day-to-day
activities of operative employees
Middle managers
They implement the policies and
plans of the top managers above them and supervise and coordinate the activities of the first-line managers
Top managers
Individuals who are responsible for making decisions about the direction of the organization and establishing objectives, policies & strategies that affect all organizational members
Слайд 19
One kind of top manager
Jeffrey Immelt, chairman &
CEO, has worked at General Electric for over 28
years. Known for its consumer appliances, CEO also sells aircraft engines, lighting, and medical equipment.
1–
Слайд 20
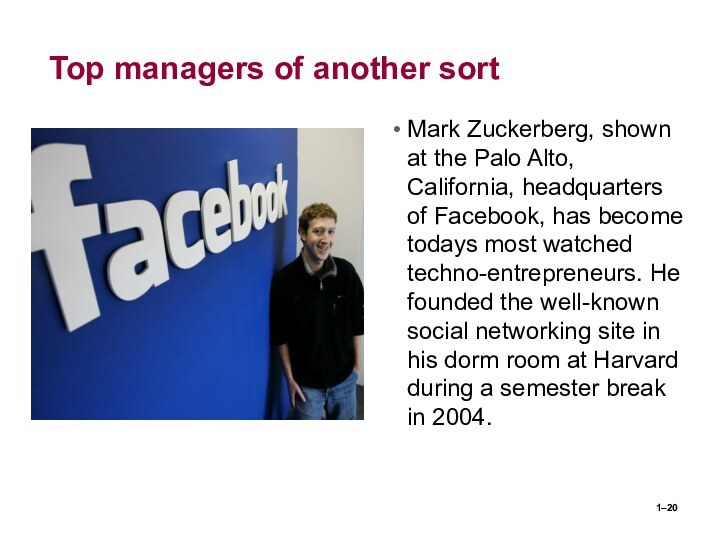
Top managers of another sort
Mark Zuckerberg, shown at
the Palo Alto, California, headquarters of Facebook, has become
todays most watched techno-entrepreneurs. He founded the well-known social networking site in his dorm room at Harvard during a semester break in 2004.
1–
Слайд 21
Copyright © 2004 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights
reserved.
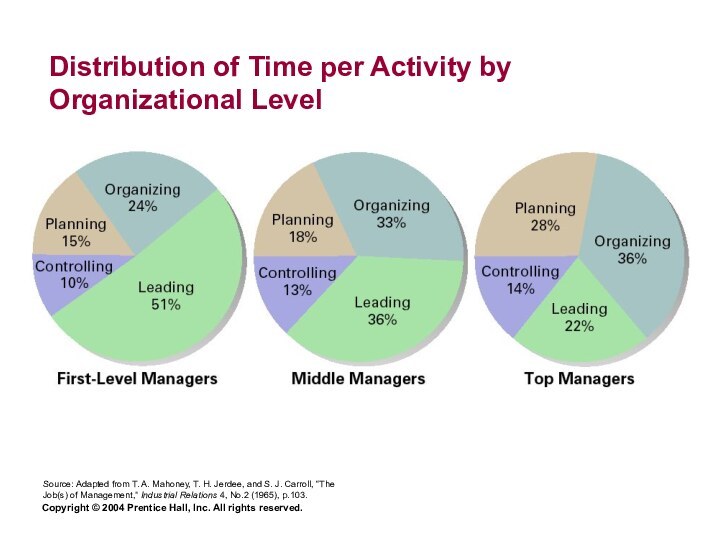
Distribution of Time per Activity by Organizational Level
Source: Adapted
from T. A. Mahoney, T. H. Jerdee, and S. J. Carroll, “The Job(s) of Management,” Industrial Relations 4, No.2 (1965), p.103.
Слайд 22
Areas of Management
Functional managers
Responsible for just one organizational
activity. F. e. Vise President of production, Director of
Finance, Administrator of Human Resources.
General managers
Responsible for several organizational activities. F. e. Executive Vise President, CEO.
Слайд 23
Marissa Mayer
She joined Google as a search company’s
firs female engineer, overseeing the development of Web search,
Google Earth, and Google Desktop, and several other products. Leading this specialized sort of research & development activity makes her a functional manager.
1–
Слайд 24
Examples of general manager
Former CEO Anne Mulcahy
of Xerox Corp.
Small company CEOs Gayle Martz, head of
Shepra’s Pet Traiding Co,, $4 million NY Company with 10 employees that sell travel carriers for dog and cats.
1–
Слайд 25
Types of Organizations
For profit organizations: For making
money
They formed to make money, or profit, by offering
products or services.
Nonprofit organizations: For offering services
Nonprofit organizations may be either in the public sector, such as our University, or in the private sector, such as University of Astana. Examples: hospitals, colleges, and social-welfare agencies.
One type of nonprofit organizations is called commonweal organizations, which offer services for all clients: military services, Postal services, local Fire and Police departments
Слайд 26
Types of Organizations
Mutual-Benefit Organizations: For aiding members
Voluntary
collections of members – political parties, farm cooperatives, labor
unions, trade associations, and clubs – whose purpose is to advance members’ interests.
Слайд 28
Copyright © 2004 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights
reserved.
1–
Mintzberg’s Managerial Roles
Interpersonal
Figurehead
Leader
Liaison
Informational
Monitor
Disseminator
Spokesperson
Decisional
Entrepreneur
Disturbance hander
Resource allocator
Negotiator
EXHIBIT 1.5
Source: Adapted from
The Nature of Managerial Work (paperback) by H. Mintzberg, Table 2, pp.92–93. Copyright © 1973 Addison Wesley Longman. Reprinted by permission of Addison Wesley Longman.
Слайд 29
Copyright © 2004 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights
reserved.
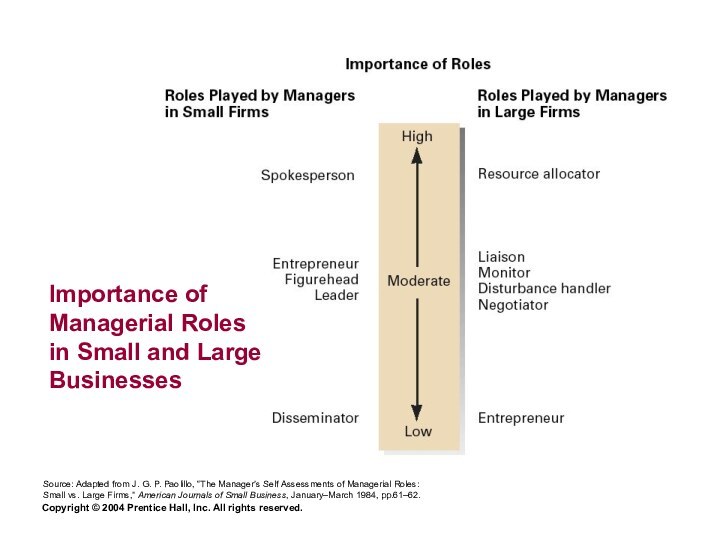
Importance of Managerial Roles in Small and Large Businesses
Source:
Adapted from J. G. P. Paolillo, “The Manager’s Self Assessments of Managerial Roles: Small vs. Large Firms,” American Journals of Small Business, January–March 1984, pp.61–62.
Слайд 31
1–
General Skills for Managers
Conceptual skills
Consists of the ability
to think analytically, to visualize an organization as a
whole and understand how the parts work together. Particular important for top managers.
Interpersonal skills / Human skills
A manager’s ability to work with, understand, mentor, inspire trust and motivate others, both individually and in groups.
Technical skills
A manager’s ability to use the tools, procedures, and techniques of a specialized field. Having the requisite technical skills seems to be most important at lower levels of management.
Слайд 32
1–
Specific Skills for Managers
Behaviors related to a manager’s
effectiveness:
Controlling the organization’s environment and its resources.
Organizing and coordinating.
Handling
information.
Providing for growth and development.
Motivating employees and handling conflicts.
Strategic problem solving.
Слайд 33
6. What are rewards of studying management?
Слайд 34
Copyright © 2004 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights
reserved.
1–
Why Study Management?
We all have a vested interest in
improving the way organizations are managed.
Better organizations are, in part, the result of good management.
You will eventually either manage or be managed
Gaining an understanding of the management process provides the foundation for developing management skills and insight into the behavior of individuals and the organizations.
Слайд 36
What are the common characteristics of organizations?
People /
purpose / structure
Слайд 37
What is doing things the right way?
Efficiency
Слайд 38
What is doing the right things?
Effectiveness
Слайд 39
What is an example of a first line
manager?
“department head” / “foreman” / “supervisor” / “team leader”
Слайд 40
What might be an example of a middle
manager?
“division head” / “plant manager” / “branch sales manager”
/ “dean of faculty”
Слайд 41
What might be an example of a top
manager?
CEO (Chief executive officer), COO (Chief operating officer), President,
Senior Vise President
Слайд 42
What are the four function of management?
POLC