- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему So what is esp?
Содержание
- 2. So what is ESP?English for specific purposes
- 3. ESP programs differ from general English language
- 4. Two approaches to teach EnglishEnglish throughEnglish for
- 5. The process of active learning is illustrated
- 6. Traditional classroom vs. learner-centered classroomNon-learner –centered approachTeacher
- 7. ESP teachers can use various tools to understand their learners` field. Professional profileNeeds analysis
- 8. A professional profile is a description of
- 9. Why is the needs analysis important?Helps to
- 10. Gathering Information about target needsDifferent ways in which information can be gathered about needs:QuestionnairesInterviewsObservationData collectionInformal consultations
- 13. Remember/knowledge (exhibits previously learned material by
- 14. 2.Understand/comprehension (demonstrating understanding of facts and ideas
- 15. 3.Apply/application (solving problems by applying acquired knowledge,
- 16. 4.Analyze/analysis (examining and breaking information into parts
- 17. 5.Evaluate/Synthesis (compiling information together in a different
- 18. 6.Create/Evaluation (presenting and defending opinions by making
- 19. Скачать презентацию
- 20. Похожие презентации
So what is ESP?English for specific purposes (ESP) is an approach to language teaching in which all decisions as to content and method are based on the learners` reason for learning.















Слайд 3 ESP programs differ from general English language courses
and contain the following characteristics:
It is designed to meet
specified needs of the learners;It is related in content (themes and topics) to particular disciplines, occupations and activities;
Use authentic work-specific documents and materials.
Слайд 5 The process of active learning is illustrated by
a Chinese proverb:
Tell me, and I will forget.
Show me,
and I will remember.Involve me, and I will learn.
Слайд 6
Traditional classroom vs. learner-centered classroom
Non-learner –centered approach
Teacher is
the sole leader;
Teacher takes responsibility for all the paperwork
and organization;Discipline comes from the teacher;
Students are allowed limited responsibilities;
A few students are the teacher’s helpers.
Learner-centered approach
Leadership is shared;
Students are facilitators for the operations of the classroom;
Discipline comes from students;
Students share in classroom responsibilities
All students have the opportunity to become an integral part of the management of the classroom.
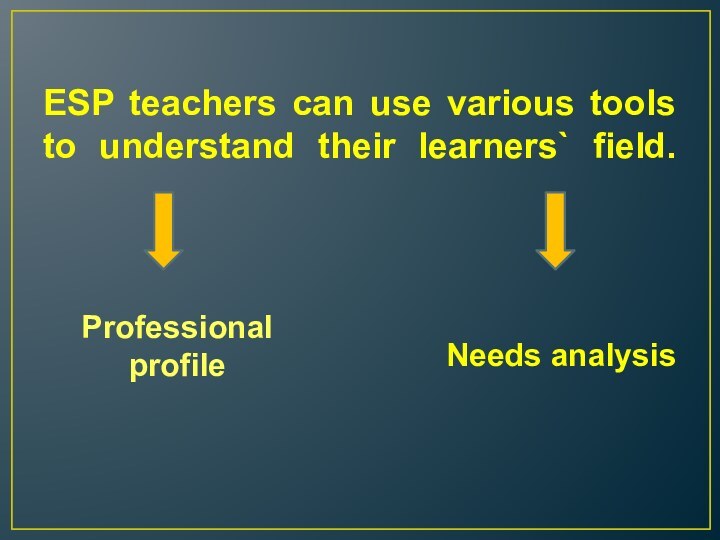
Слайд 7 ESP teachers can use various tools to understand
their learners` field.
Professional profile
Needs analysis
Слайд 8 A professional profile is a description of a
typical person in a given ESP field, and what
that person does on a daily basis in his/her professional life.A needs analysis is a tool for identifying what a specific learner needs, wants or expects from a language course.
Слайд 9
Why is the needs analysis important?
Helps to focus
training;
Separates the “need to do” from the “want to
do”.
Слайд 10
Gathering Information about target needs
Different ways in which
information can be gathered about needs:
Questionnaires
Interviews
Observation
Data collection
Informal consultations
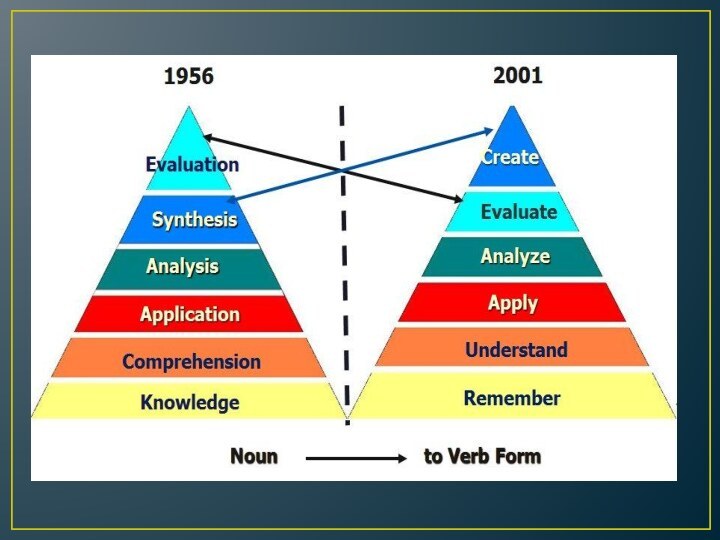
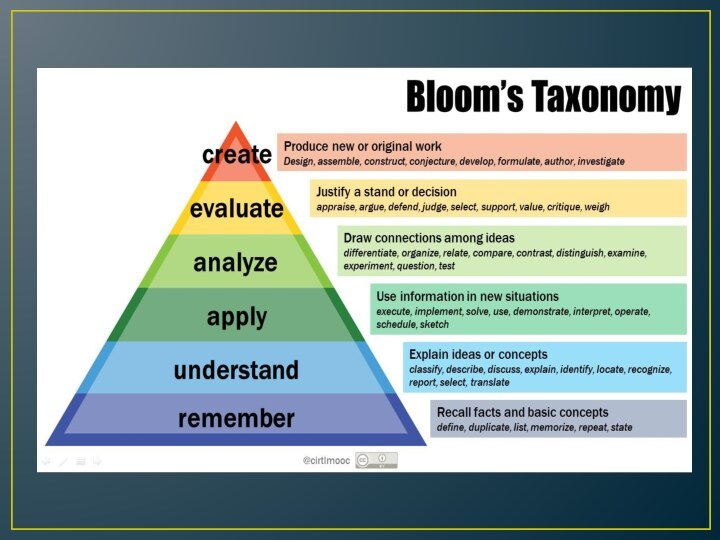
Слайд 13 Remember/knowledge (exhibits previously learned material by recalling
facts, terms, basic concepts and answers).
Key words: define, label,
show, spell, list, match, name, relate, tell, recall, select.Слайд 14 2.Understand/comprehension (demonstrating understanding of facts and ideas by
organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions and stating main
ideas).Key words: compare, demonstrate, explain, extend, illustrate, translate, summarize, show, classify.
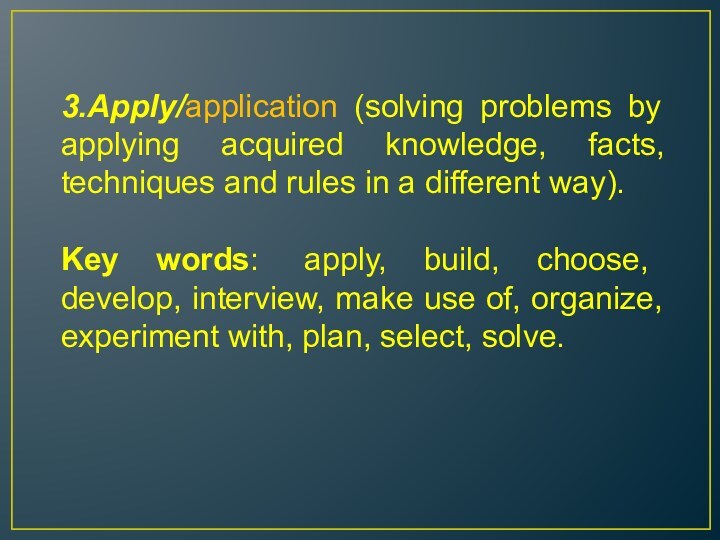
Слайд 15 3.Apply/application (solving problems by applying acquired knowledge, facts,
techniques and rules in a different way).
Key words: apply,
build, choose, develop, interview, make use of, organize, experiment with, plan, select, solve.Слайд 16 4.Analyze/analysis (examining and breaking information into parts by
identifying motives or causes; making inferences and finding evidence
to support generalizations).Key words: analyze, categorize, classify, compare, contrast, discover, divide, examine, inspect, simplify, survey.
Слайд 17 5.Evaluate/Synthesis (compiling information together in a different way
by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing
alternative solutions).Key words: build, choose, combine, compile, compose, construct, create, design, develop, estimate, formulate, imagine, invent, make up, originate, plan.
Слайд 18 6.Create/Evaluation (presenting and defending opinions by making judgments
about information, validity of ideas or quality of work
based on a set of criteria).Key words: award, choose, conclude, criticize, decide, defend, determine, dispute, evaluate, judge, justify, measure, compare, mark, rate.





























