Слайд 2
Announcements
Attendance – will be marked from now on
HW
– Late home works will not be graded from
now on
Mbox – results online, feedback
Read the Guidebook according to the lectures
Katya’s question on Fayol
Слайд 4
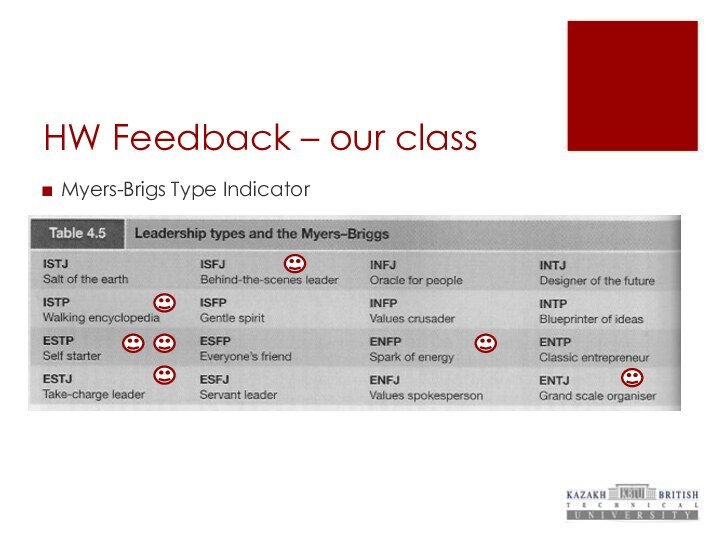
HW Feedback – our class
Myers-Brigs Type Indicator
Слайд 5
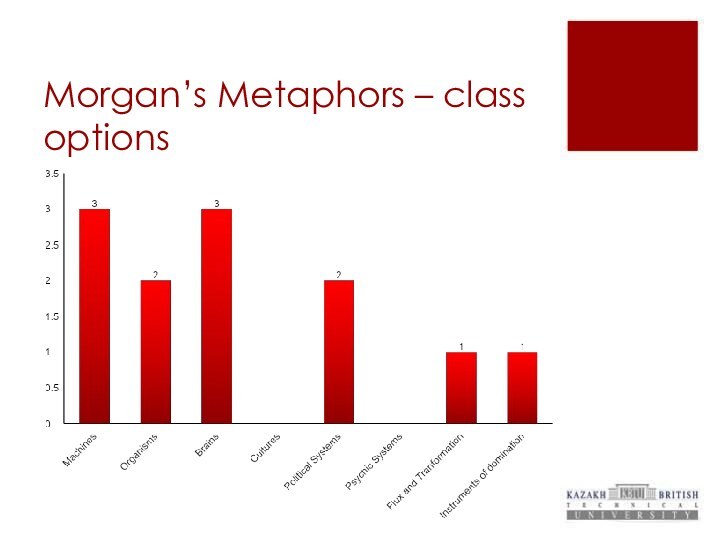
Morgan’s Metaphors – class options
Слайд 6
Recap
What is industrial sociology?
Слайд 7
Recap
What is the difference between introversion and extraversion?
Слайд 8
Recap
Why is the psychological concepts important to managers?
For example, Employee personality?
Слайд 9
Recap
How do you understand Psychological contract and do
we have them in Kazakhstan?
Слайд 10
Recap
Why do we need Stakeholder Model?
Слайд 11
Importance of Organizational Goals and Objectives
“If you do
not know where you are going you cannot tell
if you have arrived!”
CORPORATE STRATEGY – serves to describe organization’s sense of purpose, and plans and actions for its implementation
Слайд 12
Relationship between People and Successful Strategies (by Johnson
et al.)
People as a resource
People and behavior
Organizing people
“Creating a
climate where people strive to achieve success and the motivation of individuals are crucial roles of any manager and are central a part of their involvement in their organization’s strategy”
Слайд 13
Managers’ skills and competencies
Should be strategically aware and
appreciate the origins and nature of change
Possess a comprehensive
set of skills and competencies
Be able to deal effectively with the forces which represent opportunities and threats to organization
Effective strategic management creates a productive alliance between
the nature and the demands of the environment,
the organizations’ cultures and values
the resources that the organization has at its disposal
Слайд 14
Strategy and Synergy
Synergy can be experienced when 2
companies merge
Strategy of the obtained firm should be changed
and adjusted accordingly
The new organization could benefit from combined strength and opportunities, skills and expertise.
It is possible to experience negative Synergy (2+2=3)
Слайд 15
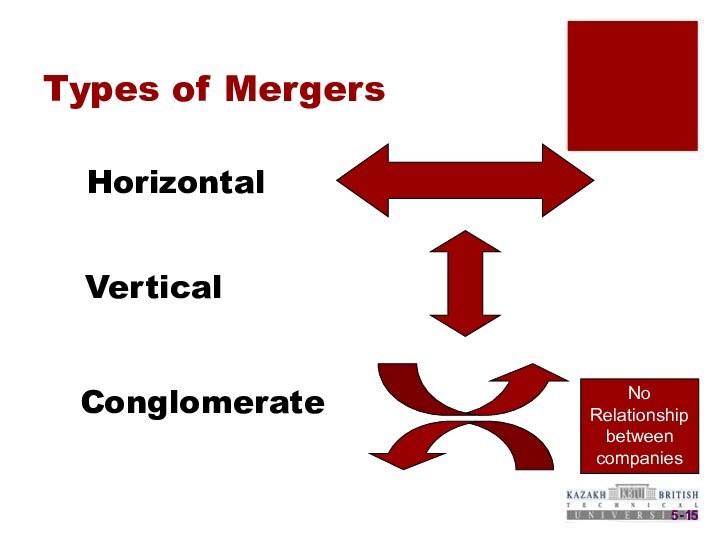
5-
Types of Mergers
Conglomerate
Vertical
Horizontal
No Relationship between companies
Слайд 16
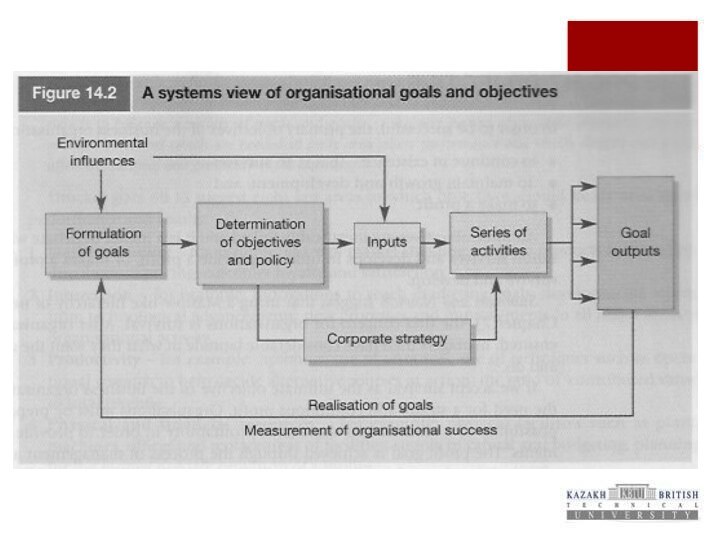
Organizational Goal
Reasons for organizational existence
The activities of the
organization are directed to attain goals
To be effective goals:
Should
be emphasized
Stated clearly
Communicated to all members of organization
Слайд 17
Mission vs. Vision
What is the difference?
Слайд 18
Mission vs. Vision
Vision provides the overall of reference
within which mission statements are written and goals selected
Слайд 19
Mission
Reason for a company’s existence
Sets an organization’s purpose,
guiding values and principles and the way in which
it intends to achieve its objectives, while recognizing the interests of other stakeholders.
Слайд 20
Organizational Goals
If you don’t know where you are
going, you cannot tell if you have arrived
Function of
organization – creation and /or supply of goods and services
Organizational goals – more specific than function
Nature of inputs and outputs
Series of activities through which outputs are achieved
Interactions with external environment
Слайд 21
Functions of goals
Provide a standard of performance
Provide a
basis for planning and management control
Provide guidelines for decision-making
and justification for actions taken
Influence the structure of the organization and help determine the nature of technology used
Help develop commitment of individuals and groups to the activities of the organization
Give an indication of what the company is really like
Serve as basis for the evaluation of change and organizational development
Serve as basis for objectives and policies of the company
Слайд 22
Characteristics of good goals
Understandable
Contain a time element
Carefully drawn
Subject
to alignment
Otherwise, known as SMART goals
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Relevant
Time-bound
Слайд 23
I want to graduate from the University
Vs.
I want
to graduate from ISE with major in management and
minimum GPA 3.5 by June 2013
Слайд 24
Objectives
Objectives set out the specific goals of the
organization, the aims to be achieved and the desired
end results.
They are smaller than goals and represent specific actions in the near future to be taken to achieve the goals
Слайд 25
Objectives and Policy
Objectives – set out more specifically
the goals of organization, the aims to be achieved
and the desired end-results. Main objectives include:
Survive
Maintain growth and development
Make profit
Policy – is developed within the framework of objectives. Is a guideline for organizational action and the implementation of goals and objectives
Translated into Rules, Plans, Procedures
Relates to all activities of the organization at all levels
Слайд 26
Key Areas for Organizational Objectives
Market standing – position
in relation to competitors
Innovation – commitment to R&D
Productivity –
production levels and standards
Physical and financial resources – use, acquisition and maintenance of capital and financial assets
Profitability – target profit
Managerial performance and development – rates of levels of managerial growth
Worker performance and attitude – rates of worker productivity, their desired attributes
Public Responsibility – company’s responsibilities to stakeholders and the extent to which it intends to live up to those responsibilities
Internet usage – extent of usage to reach company’s goals
Слайд 27
Working with Organizational Objectives
An organization should set three
types of objectives:
1. Short-term – 1 year or less
2.
Intermediate-term – 1-5 years
3. Long-term – 5 to 7 years
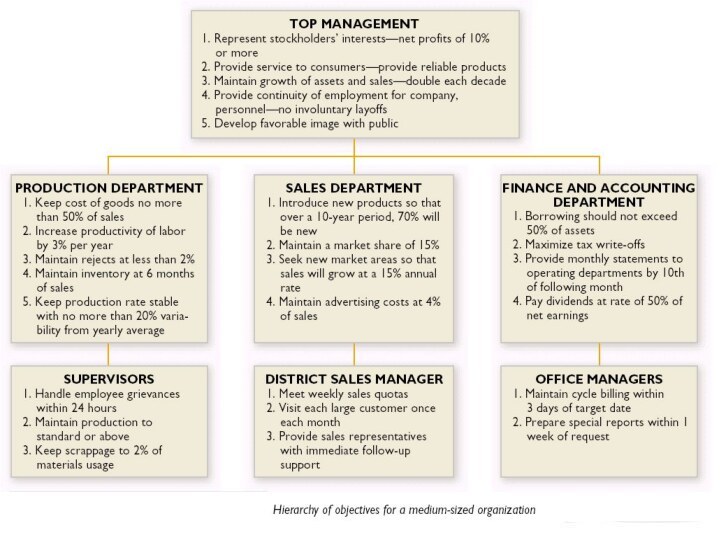
Developing a Hierarchy of Objectives:
Principle of breaking a larger objective into smaller sub-objectives so that individuals at different levels and sections of the organization know what they must do to help reach the overall organizational objective.
Слайд 28
Working with Organizational Objectives
Слайд 29
Guidelines for Establishing Quality Objectives
1. Let those responsible for
attaining objectives have voice in setting them
2. State objectives as
specifically as possible
3. Relate objectives to specific actions whenever necessary
4. Pinpoint expected results
5. Set goals high enough that employees have to strive to meet them
6. Specify when goals are expected to be achieved
7. Set objectives only in relation to other organizational objectives
8. State objectives clearly and simply
Слайд 30
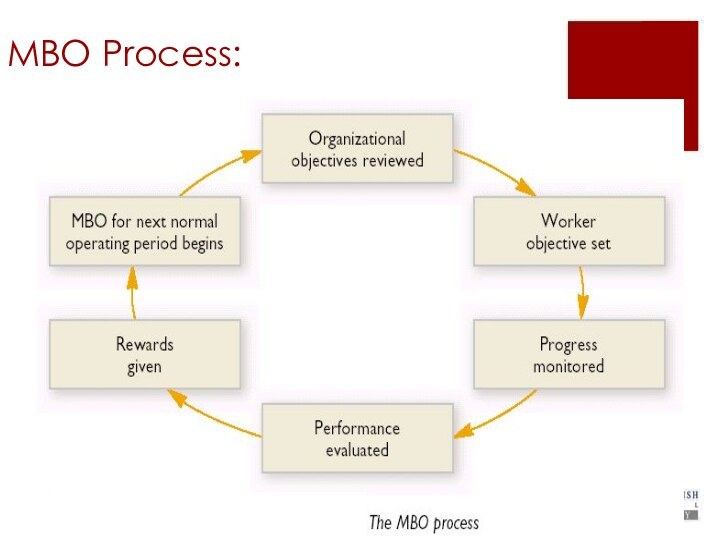
Management by Objectives (MBO)
The MBO strategy:
1. All individuals
are assigned a specialized set of objectives
2. Performance reviews
are conducted periodically
3. Rewards are given to individuals
Слайд 32
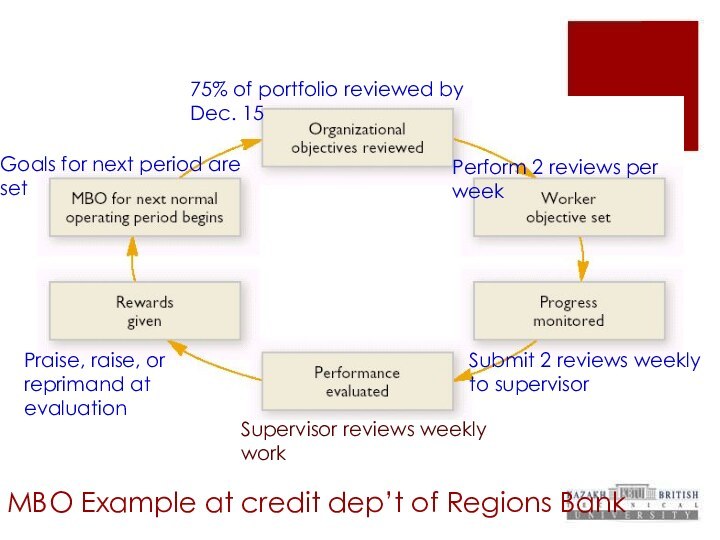
MBO Example at credit dep’t of Regions Bank
75%
of portfolio reviewed by Dec. 15
Perform 2 reviews per
week
Submit 2 reviews weekly to supervisor
Praise, raise, or reprimand at evaluation
Goals for next period are set
Supervisor reviews weekly work
Слайд 33
Factors Necessary for a Successful MBO Program
1) Top management
must be committed and set appropriate objectives
2) Managers and subordinates
must develop and agree on individual’s goals
3) Employee performance should be evaluated against established objectives
4) Management must follow through on employee performance evaluations
Слайд 34
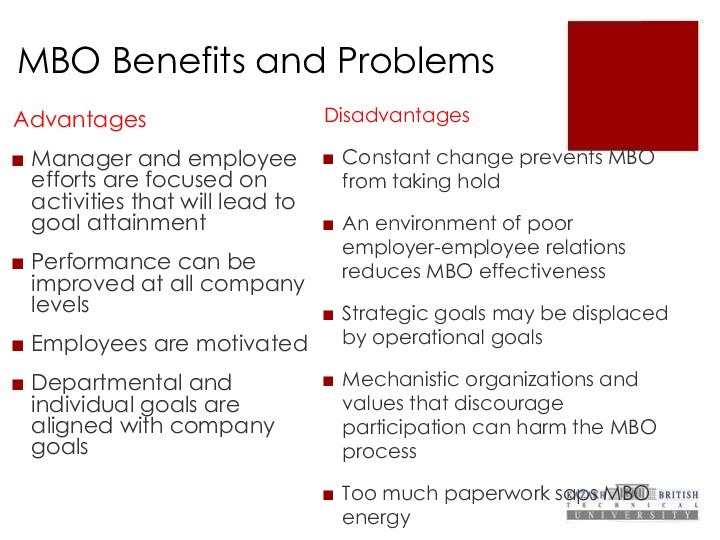
MBO Benefits and Problems
Benefits of MBO
Advantages
Manager and employee
efforts are focused on activities that will lead to
goal attainment
Performance can be improved at all company levels
Employees are motivated
Departmental and individual goals are aligned with company goals
Disadvantages
Constant change prevents MBO from taking hold
An environment of poor employer-employee relations reduces MBO effectiveness
Strategic goals may be displaced by operational goals
Mechanistic organizations and values that discourage participation can harm the MBO process
Too much paperwork saps MBO energy
Слайд 36
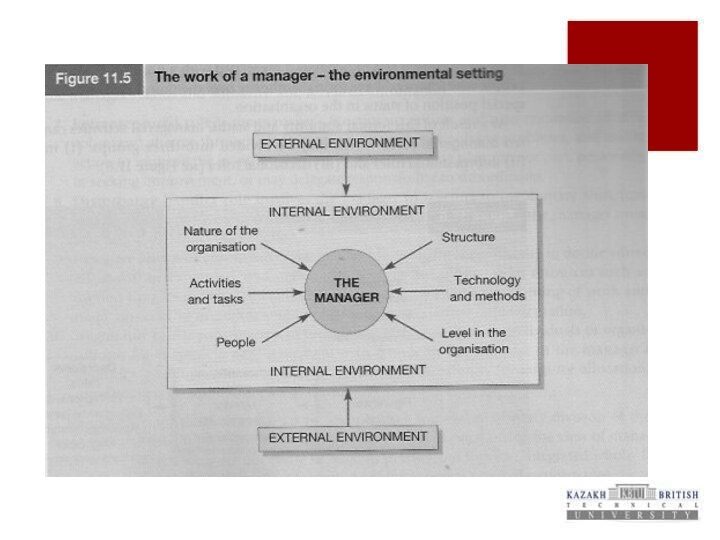
Manager’s role
Manager – a person who is responsible
for coordinating resources and the actions of others, for
the achievement of goals
is involved with leading people to achieve goals
need to coordinate the actions of people, together with other resources, such as money, materials and technology.
Слайд 38
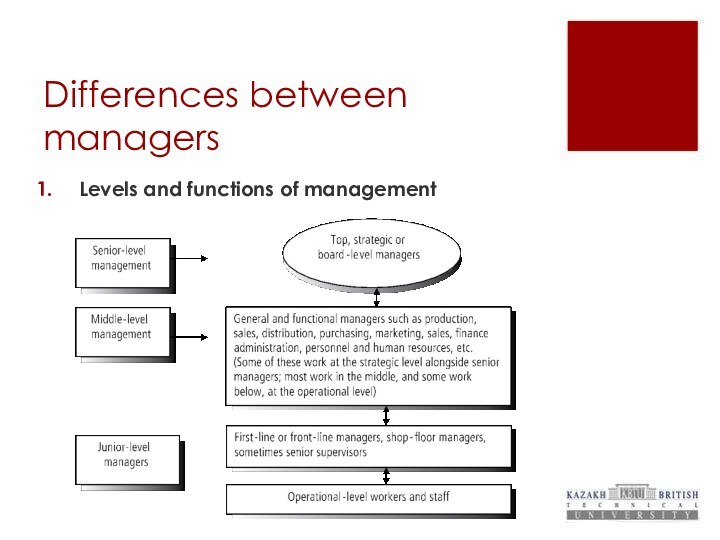
Differences between managers
Levels and functions of management
Слайд 39
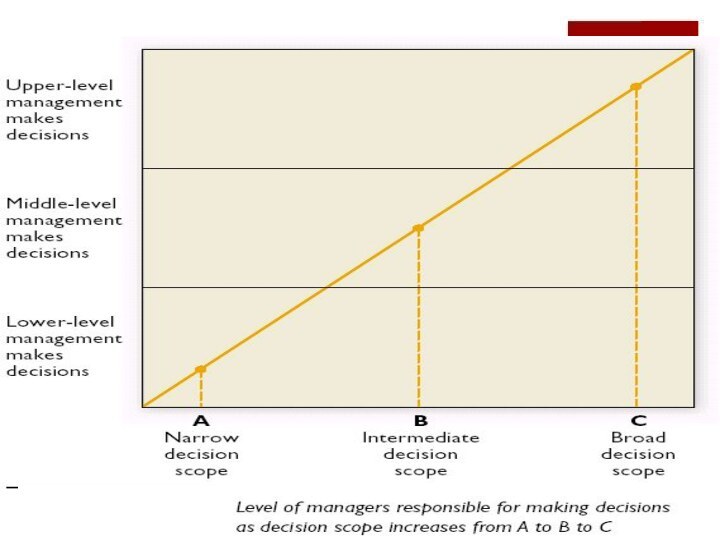
Levels of management
Upper-level management (a/k/a senior-level management)
Strategic planning
and broad decision scope
Middle-level management
Divisional planning and intermediate decision
scope
Lower-level management (a/k/a junior-level management or operational management)
Operational planning and narrow decision scope
Слайд 41
Functional vs. General managers
Functional managers are responsible for
managing a particular section of operations, such as marketing,
finance or communications.
General managers are responsible for the achievement of broader goals, or can be responsible across different functions.
QUESTION: Which one would you want to be?
Слайд 42
Differences between managers
2. Qualities of the Individual Manager
Question:
If you were hiring a manager for your company
– what would you do to learn if he has skills to be a good manager for you
Слайд 43
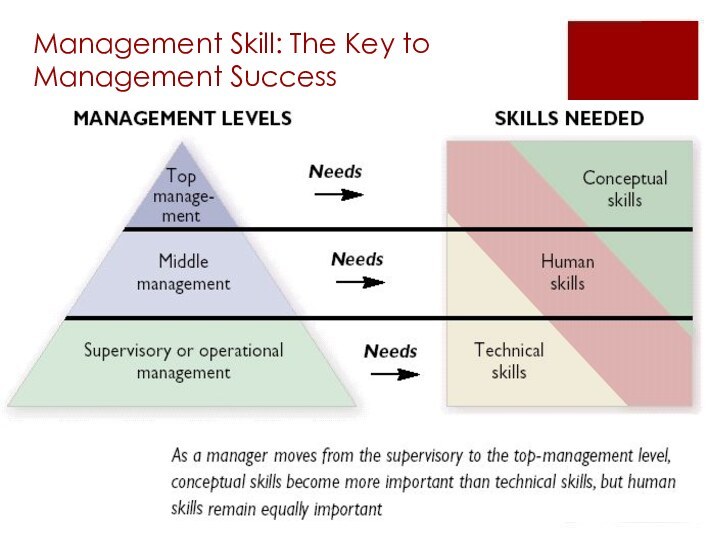
Management Skill: The Key to Management Success
Defining Management
Skill
Ability to carry out a process of reaching organizational
goals by working with and through people and other organizational resources
Remember? Effectiveness and efficiency
Слайд 44
Classic vs. Contemporary view on Management skill
Management Skill:
A Classic View
Technical Skills
Human Skills
Conceptual Skills
Management Skill: A Contemporary
View
1. Define major activities that managers typically perform
2. List skills needed to carry out these activities successfully
Слайд 45
Attributes and qualities
of a manager
Technical competence
The application of
knowledge to tasks
Social and human skills
Interpersonal relationships and judgement
Conceptual
ability
Understanding the complexities of the organisation as a whole and its environment
Слайд 46
Management Skill: The Key to Management Success
Слайд 47
Behaviour pattern of managers:
Despite working in different jobs
and organisations, most managers undertake two common activities:
Agenda-setting
Network-building
Слайд 48
Hard and soft skills
Hard skills are used
for
Conducting disciplinary matters
Fighting one’s corner in debates
Budgeting
Soft skills are
used for
Counselling
Supporting
Advising
Successful managers can adjust their approach across the spectrum of skills.
Слайд 50
Key strategies for future managers
Developing leadership
Driving radical change
Reshaping
culture
Dividing to rule
Exploiting the organisation
Keeping the competitive edge
Achieving
constant renewal
Managing the motivators
Making team working work
Achieving total management quality
Слайд 51
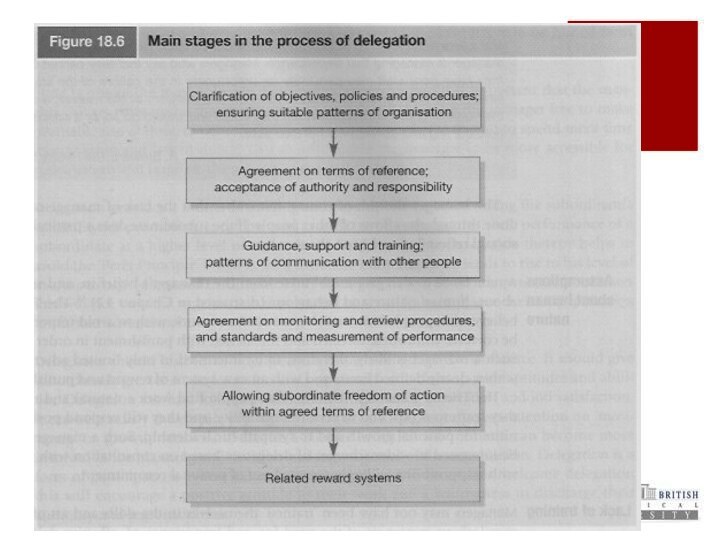
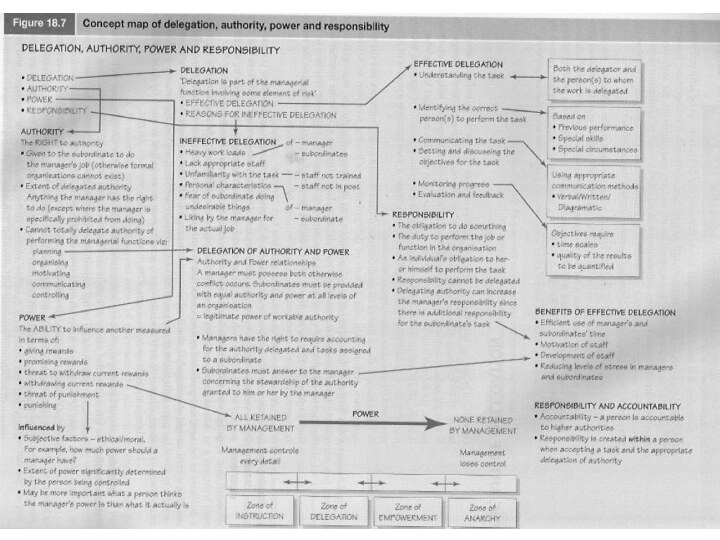
Delegation
- Process of entrusting authority and responsibility to
others through-out the various levels of organization
Upward delegation
Lateral delegation
Downward
delegation
Benefits:
Best use of time
A means of training and development
Strength of the workforce
Слайд 52
Question: Why managers would lack to delegate?
Слайд 54
Question: Do you think most of the students
in the world are lazy or hard-working?
Слайд 56
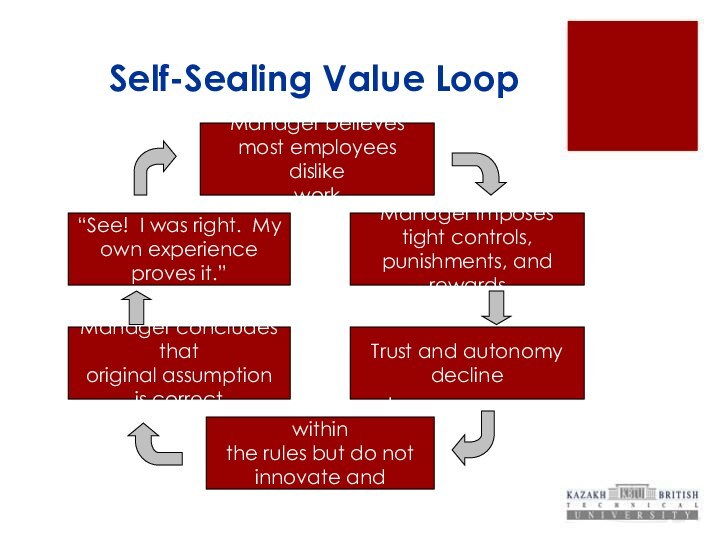
Self-Sealing Value Loop
Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall
4-
Manager believes
most employees
dislike
work
Manager imposes
tight controls,
punishments, and rewards
Trust and autonomy
decline
Employees work
within
the rules but do not
innovate and improve
Manager concludes that
original assumption
is correct
“See! I was right. My
own experience
proves it.”
Слайд 59
Empowerment
- Allowing employees more freedom, autonomy and self-control
over their work, and responsibility for decision-making
Anticipated effects:
Motivated stuff
Quality
customer service
Improved profits
Question: Would you want to empower your employees this way? Will it work for our country?
Слайд 61
Women and minority management
So-called “male values”
Rationality, competition, control,
and self-assertion
So-called “female values”
Intuition, caring, emotion, acceptance, and cooperation
“Glass
ceiling”??
Слайд 63
Glass Ceiling
An invisible barrier separates women and minorities
from top management positions
Fortune 500 Women Corporate Officers
2005 =
16.4%
2000 = 12.5%
1995 = 8.7%
Only eight Fortune 500 companies have female CEOs
Ethical Dilemma: A Man’s World
Слайд 64
Cultural Influences
Culture influences:
the types of people that
are described as managers
the qualities valued in managers
the level and scope of managerial work
styles of management.
EXAMPLES:
in Malaysia, all administrative and managerial personnel are described as managers
in France, executives and professional employees are not included as managers
in South Korea, graduates recruited to white-collar jobs would be defined as managers even though they would not be promoted to managerial work until later in their career.
QUESTION: What about our country?
Слайд 66
Managers’ activities according to Gulick and Urwick
Planning
Organising
staffing
Directing
coordinating
reporting
budgeting.
Слайд 70
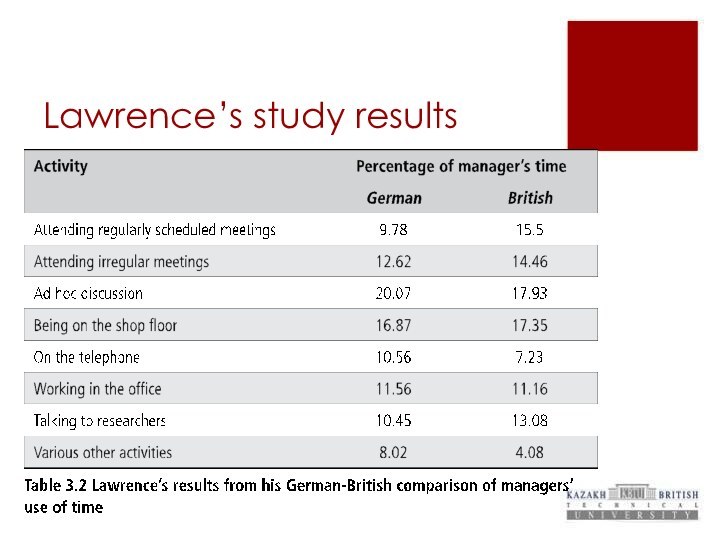
Comparing studies
Managers may in practice do different things
to what the theory states: the ‘roles’ of a
manager may not be what actually happens in practice.
Слайд 71
HW 3 due to Sep 17!
Are the results
shown in studies by Lawrence and Mintzberg consistent with
the situation in Kazakhstan? Explain
Interview one manager to find out his/her main duties
Provide name/occupation/work place
Create a table same to one on p. 52 in your Guide book (you can add or remove activities)
Analyze your table and discuss your findings, did you have any unexpected results? If you could change something, what would it be?