Слайд 2
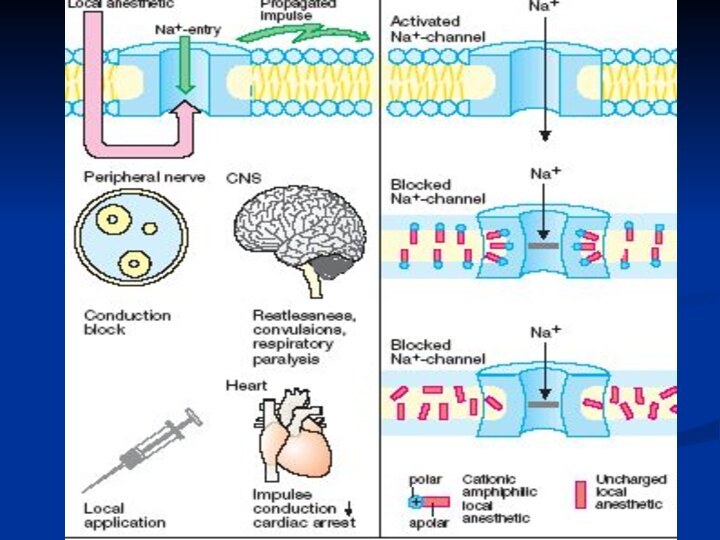
LOCAL (REGIONAL) ANAESTHETICS
1. For Terminal (Superficial) Anaesthesia:
Cocaine
Anaesthesine (Benzocaine)
Dicaine (Tetracaine)
Pyromecaine
2. For Infiltration,
Conductive and Intraspinal Anaesthesia:
Novocaine
Trimecaine
Ultracaine
Bupivacaine
3. For all kinds of Anaesthesia:
Lidocaine
Слайд 3
According to the Chemical structure:
1. Esters of
aromatic acids:
Natural Esters: Cocaine
Derivatives of PABA:
Anaesthetesine
Dicaine
Novocaine
2. Amides: Lidocaine, Trimecaine,
Ultracaine, Bupivacaine
Слайд 5
LAs are Weak Bases.
In order that a
drug manifests its action it must occur hydrolysis and
liberation of lipid dissoluble base that occurs in Alkaline Medium only .
Normally in Tissues pH = 7.35 - 7.4
In Focus of Inflammation pH = 5.0 - 6.0
LAs do not manifest their activity
in Inflamed Tissues since
Salt Hydrolysis does not occur in Acid Medium.
Слайд 6
+ Vasoconstrictor
Adrenaline hydrochloride 0.1% - 1 drop
in 2-10 ml
⇓ the rate of absorption
=>
? Systemic Toxicity
? the Duration of Action.
Premedication with Diazepam IM 0.5% solution 2 ml
provides prophylaxis against seizures.
Слайд 7
Cocaine blockades:
Noradrenaline
Serotonin
Dopamine
reuptake into the Presynaptic Terminals.
?Dopamine in
brain’s Pleasure System (limbic system)=> => Euphoria.
Chronic Intake of Cocaine => Depletes DOPAMINE =>
=> the Vicious Cycle of Craving for Cocaine
Слайд 8
COCAINE:
✶ POTENTIATES the action of Noradrenaline
✶ the «FIGHT
OR FLIGHT» SYNDROME of
ADRENAL STIMULATION:
⮟Tachycardia
⮟
Hypertension
⮟ Pupillary Dilation
⮟ Peripheral Vasoconstriction
Слайд 9
Adverse Effects of COCAINE:
1. Anxiety Reactions:
?BP, ?HR, Sweating,
Paranoia.
2. Depression Reactions
3. Heart Disease
4. Nasal Septum Necrosis
Слайд 10
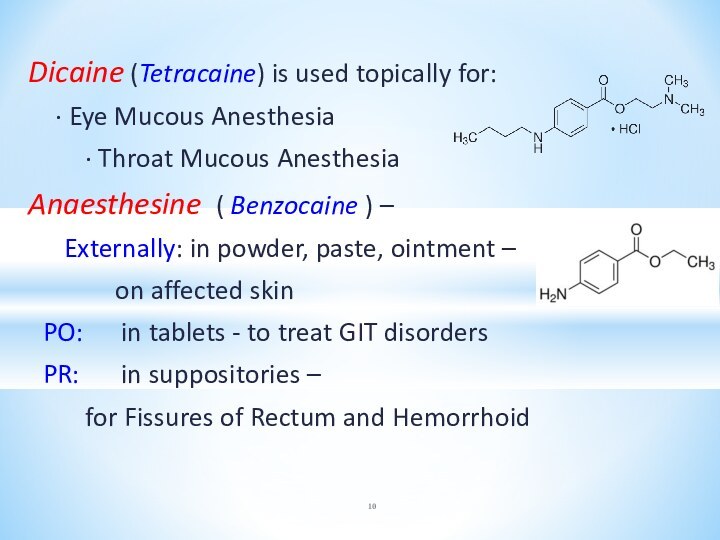
Dicaine (Tetracaine) is used topically for:
∙ Eye Mucous Anesthesia
∙
Throat Mucous Anesthesia
Anaesthesine ( Benzocaine ) –
Externally: in powder, paste, ointment –
on affected skin
PO: in tablets - to treat GIT disorders
PR: in suppositories –
for Fissures of Rectum and Hemorrhoid
Слайд 11
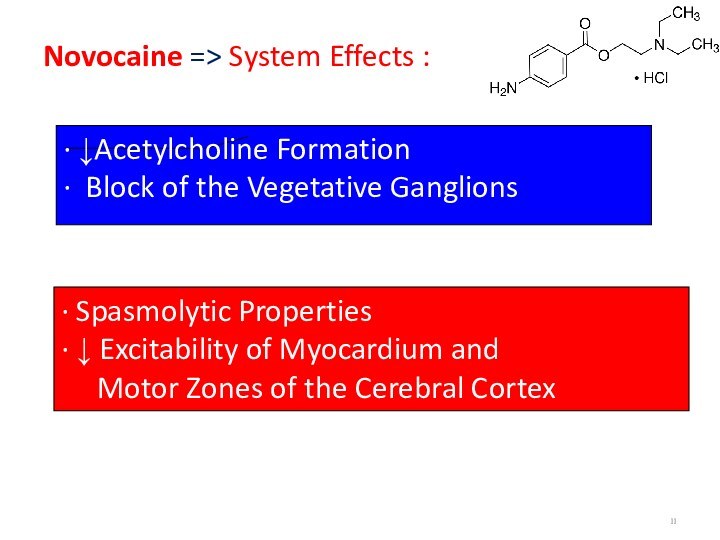
Novocaine => System Effects :
∙ ↓Acetylcholine Formation
∙
Block of the Vegetative Ganglions
∙ Spasmolytic Properties
∙ ↓ Excitability
of Myocardium and
Motor Zones of the Cerebral Cortex
Слайд 12
For infiltration anesthesia:
Novocaine 0.25-0.5% - 200-1000 ml
For conductive anesthesia:
Novocaine 1-2% - 20-25 ml
For intraspinal anesthesia:
Novocaine 5% - 2-3 ml
Слайд 13
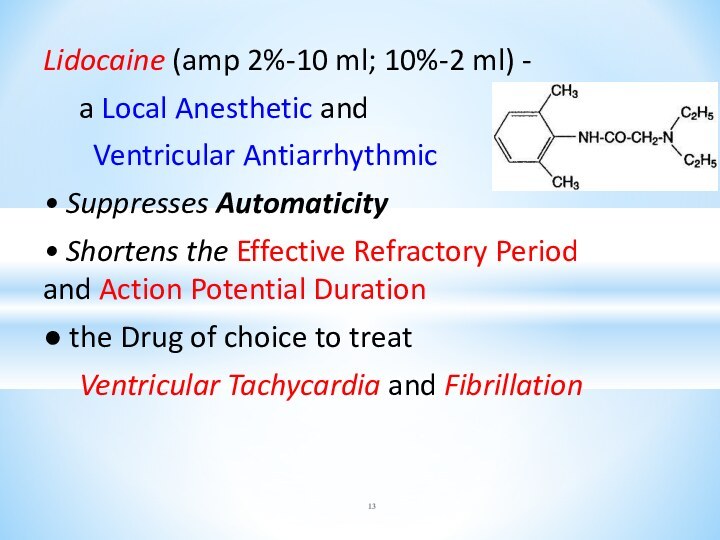
Lidocaine (amp 2%-10 ml; 10%-2 ml) -
a
Local Anesthetic and
Ventricular Antiarrhythmic
• Suppresses Automaticity
• Shortens
the Effective Refractory Period and Action Potential Duration
● the Drug of choice to treat
Ventricular Tachycardia and Fibrillation
Слайд 14
Astringents
1. Organic Compounds:
Tannin
Tannalbin
Oak Bark [Cortex Quercus]
Grass of
st. Johns wort [Herba Hyperici]
Leaves of Salvia
Flowers of Chamomile
Слайд 15
2. Inorganic Compounds:
Bismuth subcitrate [DE-NOL]
Silver
nitrate
Zinc oxide
Lead acetate
Aluminum hydroxide
Almagel,
Maalox
Magnesium hydroxide /oxide
Слайд 16
Range of SHMIDEBERG:
Pb, Al, Bi, Zn Cu,
Ag, Hg
Left Part - forms Dense Albuminates -
=> Protective
Anti-Inflammatory Action
Right one forms Friable Albuminates –
in High concentration => Cell Necrosis - CAUTERIZING action
In Small concentration =>
ASTRINGENT action
Слайд 17
3. GASTROPROTECTORS
Colloidal bismuth subcitrate (De-nol)
Bismuth subsalicylate
Sucralfate
Almagel
Covering agents:
Mucus from Starch
Seeds of Flax
Слайд 18
ADSORBENTs:
TALC
WHITE CLAY ( Bolus Alba)
ACTIVATED CHARCOAL
IRRITATING
AGENTS:
MUSTARD PLASTER
MENTHOL
VALIDOL
TURPENTINE OIL REFINED
AMMONIA SOLUTION
Слайд 19
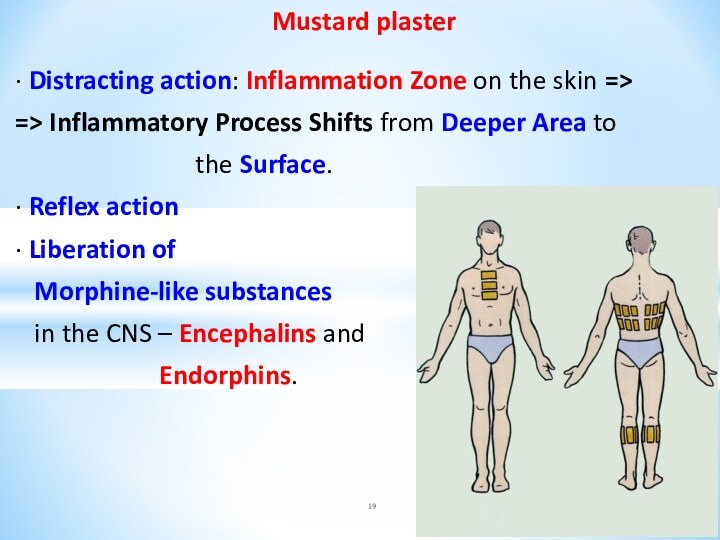
Mustard plaster
∙ Distracting action: Inflammation Zone on
the skin =>
=> Inflammatory Process Shifts from Deeper
Area to
the Surface.
∙ Reflex action
∙ Liberation of
Morphine-like substances
in the CNS – Encephalins and
Endorphins.
Слайд 20
Validol – 25–30% Menthol solution
in Menthol Ether
of Isovalerianic acid
✶ Calming action on the CNS
✶ Reflex
Action => Vasodilation
Mechanism of Action:
Stimulation of Cold Receptors of the Tongue =>
=> Reflex Vasodilatation of Coronary Vessels
Clinical Uses:
∙ Acute Angina Pectoris, Neurosis,
∙ Sea and Air Sickness - as Antiemetic Agent
Слайд 21
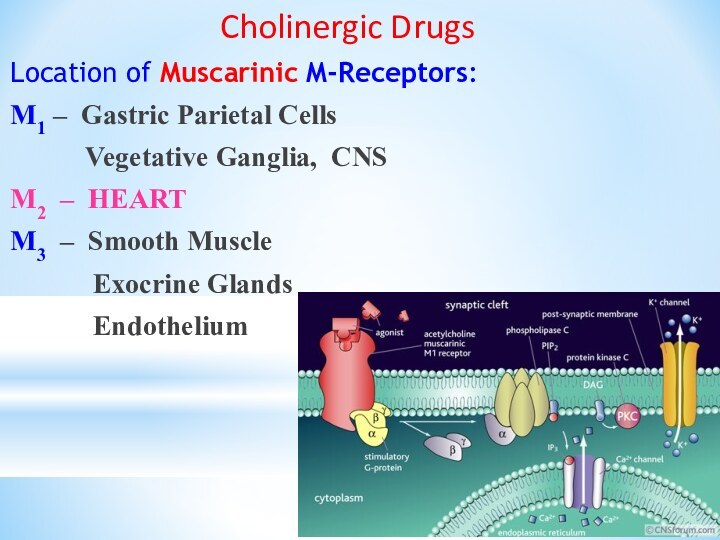
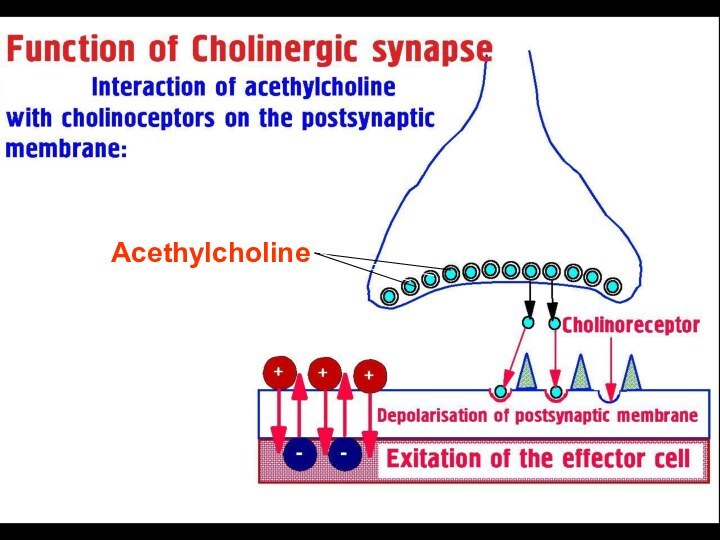
Cholinergic Drugs
Location of Muscarinic M-Receptors:
M1 –
Gastric Parietal Cells
Vegetative Ganglia, CNS
M2 – HEART
M3
– Smooth Muscle
Exocrine Glands
Endothelium
Слайд 22
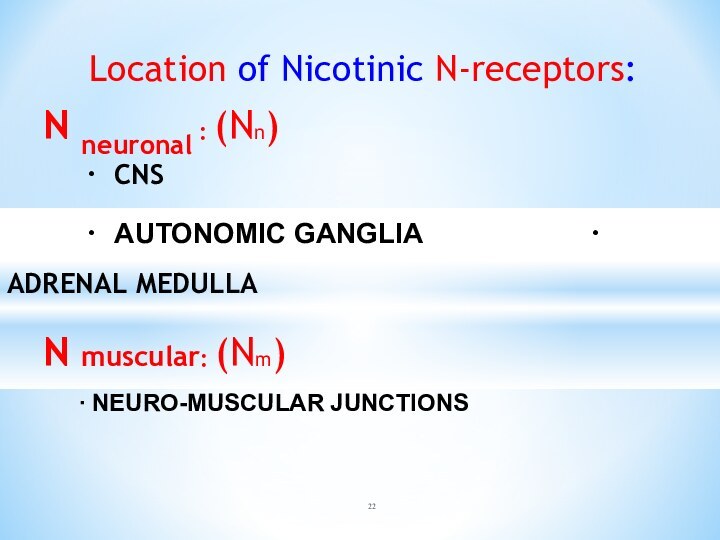
Location of Nicotinic N-receptors:
N neuronal : (Nn)
∙ CNS
∙ AUTONOMIC GANGLIA
∙ ADRENAL MEDULLA
N muscular: (Nm)
∙ NEURO-MUSCULAR JUNCTIONS
Слайд 23
Cholinergic Drugs
I. M,N-cholinergic Agents of Direct Action:
1.
M, N- Cholinomimetics:
Acetylcholine - powder
Carbacholine – 1%
solution - 10 ml
2. M, N- Cholinoblockers:
Cyclodol – Tab. 0.001 g
Norakin – Tab. 2 mg
Amyzyl - Tab. 1 mg
Spasmolytin – powder
Слайд 24
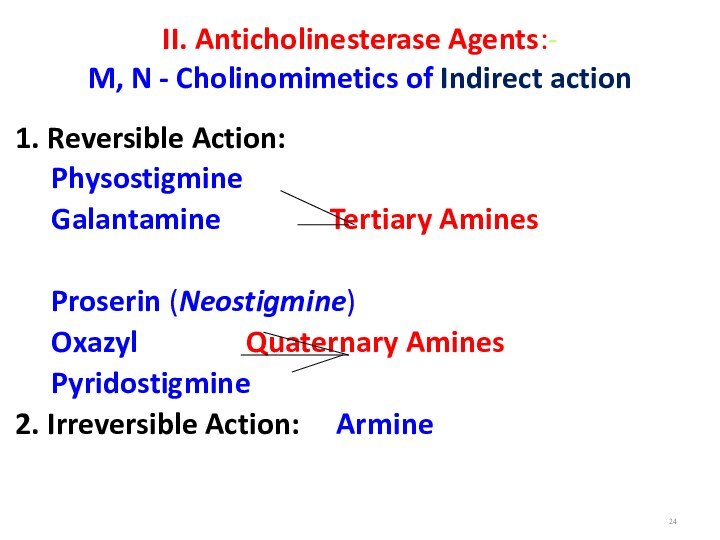
II. Anticholinesterase Agents:-
M, N - Cholinomimetics of Indirect
action
1. Reversible Action:
Physostigmine
Galantamine
Tertiary Amines
Proserin (Neostigmine)
Oxazyl Quaternary Amines
Pyridostigmine
2. Irreversible Action: Armine
Слайд 26
Stimulation M1 and M3 Receptors => Stimulating Action:
the
Receptor interacts with a Gs Protein =>
Activation of
Phospholipase C =>
Hydrolysis of PIP2 => DAG + IP3
IP3 => ? Ca2+
PIP2 – Phosphatidyl-Inositol-bis-Phosphate
DAG - Diacylglycerol
IP3 - Inositol-tris-Phosphate
Слайд 27
Stimulation of M2 Receptors => Inhibiting Action:
the Receptor
interacts with Ginhibitory-Protein =>
=> Adenyl Cyclase Inhibition =>
=> ?
cAMP and ?K+ Conductance :
↓ Heart Rate
↓ Force of Heart Contraction
Слайд 28
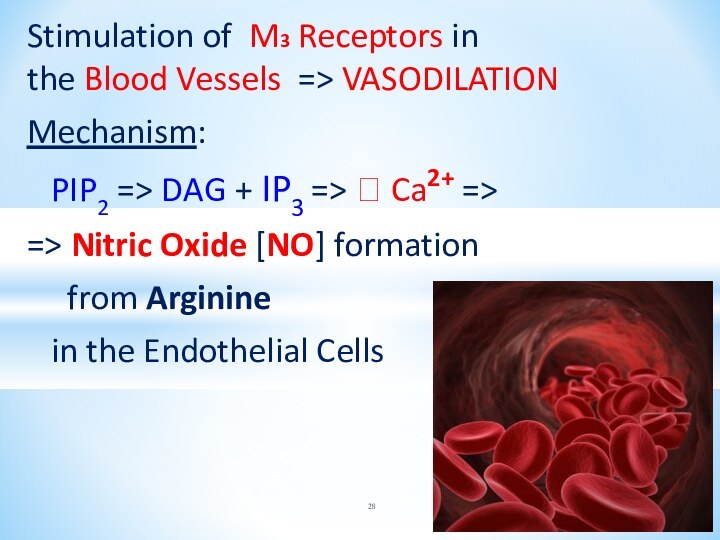
Stimulation of M3 Receptors in
the Blood
Vessels => VASODILATION
Mechanism:
PIP2 => DAG + IP3
=> ? Ca2+ =>
=> Nitric Oxide [NO] formation
from Arginine
in the Endothelial Cells
Слайд 30
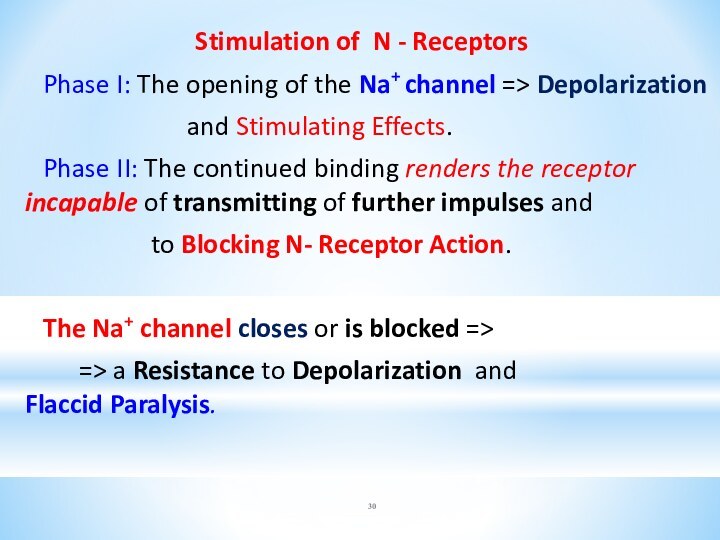
Stimulation of N - Receptors
Phase I: The
opening of the Na+ channel => Depolarization
and Stimulating
Effects.
Phase II: The continued binding renders the receptor incapable of transmitting of further impulses and
to Blocking N- Receptor Action.
The Na+ channel closes or is blocked =>
=> a Resistance to Depolarization and Flaccid Paralysis.
Слайд 31
Proserin (Neostigmine)– Polar Compound => does not enter
the CNS.
Pharmacologic Effects:
Pupil Contraction and Spasm of Accommodation
↑ Smooth
Muscle Tonus of the Bronchi and other Internal Organs
↑ Secretion of the Bronchial, Digestive and Sweat Glands
Heart: Bradycardia, ↓BP, Depression of Conductivity and
Automatism
Dilation of the Pelvic Organs and Skeletal Muscles Vessels
↑ Adrenaline Discharging
Improvement of Neuromuscular Transmission
Слайд 32
Clinical uses of Proserine:
Myasthenia Gravis
Glaucoma
Intestines,
Urinary, Gall Bladder Atonia
Flaccid Paresis and Paralysis
as
Antidote in Myorelaxants and
M-Cholinoblocker Poisonings
Слайд 33
Galantamine - the alkaloid from the roots of
Snowdrop – Galanthus Woronowi
• Penetrates into the CNS
• Produces
local irritative action -
it is not used as eye drops!!
Clinical use:
Myasthenia
Intestines, Urinary and Gall Bladder Atonia
Flaccid Paresis and Paralysis
as Antidote in myorelaxants and M-blockers poisonings
Слайд 34
Reactivators of Acetylcholinesterase:
Alloxim (amp. 0.075 g)
Dipiroxime (amp.
15%-1 ml)
Isonitrosin (amp. 40%-3 ml)
Special Antidotes
in Acute and
Chronic poisoning with:
• Anticholinesterase Agents
• Phosphoorganic compounds:
Chlorophos, Carbophos et al.
Слайд 35
Central M,N-Cholinoblockers:
CYCLODOL
NORAKIN
Clinical use: Parkinson’s Disease Parkinsonism
Adverse effects:
Dry Mouth, Blurred Vision, «sandy eyes», Tachycardia,
Constipation,
Progressive Deterioration of Memory
Слайд 36
M – CHOLINOMIMETICS
Pilocarpine –1%-10 ml, Tab. 5
mg (0.005 g)
Aceclidine – amp. 0.2%-1ml, 3% ointment
Pilocarpine -
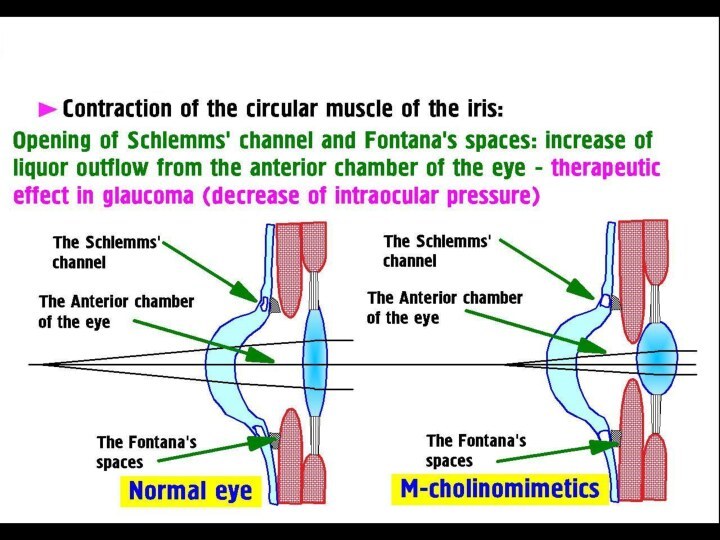
stimulates M-receptors of
the Sphincter Muscles of Iris => Miosis
? Intraocular Pressure
Spasm of Accommodation
Clinical Use: Glaucoma, Xerostomia
Слайд 37
Overdose with Pilocarpine
Taking 100 mg PO is considered
fatal
Muscarinic symptoms:
Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea, Bronchospasm,
Involuntary Defecation and
Urination,
?Bronchial and Salivary Secretions,
Respiratory Depression, Flushing,
Bradycardia, Cardiac arrest.
Treatment:
Atropine - 0.5-1 mg SC or IV
Adrenaline - 0.3-1 mg SC or IV
Lavage, then Activated Charcoal and Cathartics, Support Respiratory and Cardiovascular System.
Слайд 38
M - Cholinoblockers
Atropine sulfate – amp. 0,1%-1 ml
Scopolamine
– amp. 0.05%-1 ml
Platyphyllin – amp. 0.2%-1 ml
Methacin –
amp. 0.1%-1 ml
Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent) – aerozol
Pirenzepine (Gastrozepin) – amp. 0.5%-2 ml, Tab. 0.05 g
Слайд 39
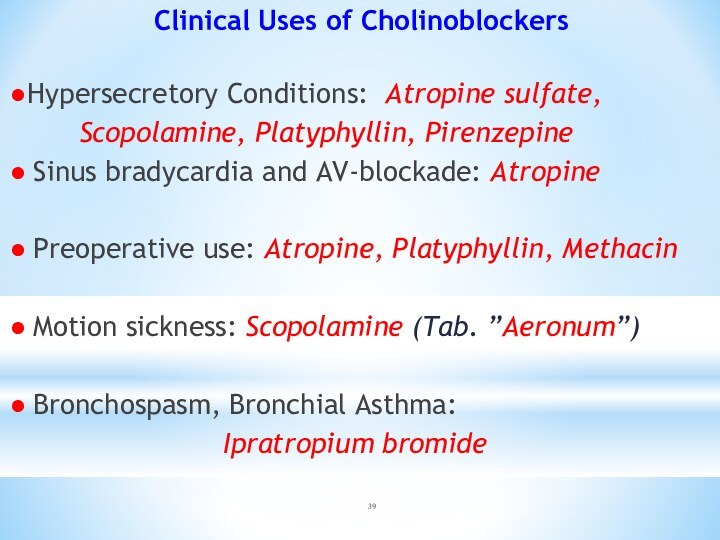
Clinical Uses of Cholinoblockers
●Hypersecretory Conditions: Atropine sulfate,
Scopolamine,
Platyphyllin, Pirenzepine
● Sinus bradycardia and AV-blockade: Atropine
● Preoperative
use: Atropine, Platyphyllin, Methacin
● Motion sickness: Scopolamine (Tab. ”Aeronum”)
● Bronchospasm, Bronchial Asthma:
Ipratropium bromide
Слайд 41
N - Cholinomimetics:
Nicorette – Chewing Tab. 2
mg and 4 mg
Cytiton – amp. 0.15%-1 ml
Lobeline –
amp. 1%-1 ml
Nicorette – exerts nicotine-replacement action.
Clinical uses:
Nicotinic abstinence at refusal from smoking
Adverse effects:
Dizziness, Hypersalivation,
Erosive-ulcerous Defeats of GIT,
Arrhythmias, Allergic Reactions.
Слайд 42
Lobeline and Cytiton-
- Respiratory stimulants with reflector
type of action
Mechanism of action: drugs stimulate N-receptors in
autonomic ganglia and carotid sinus, which is accompanied by Excitement of Respiratory, Vasomotor and other Centers of Oblongatal Brain.
Clinical Use: Reflector Respiratory Arrest
(poisoning with Carbon Oxide, Inspiration of Irritating agents).
Слайд 43
Ganglioblockers
1.The Quaternary Ammonium Compounds:
Benzohexonium
Pentamin
Hygronium
2. The Tertiary Ammonium Compounds:
Pirilen
Pachycarpine
3. Sulfer-containing agent -
Arfonad
Слайд 44
Myorelaxants
1. Non-depolarizing type:
Tubocurarine
Diplacin
Anatruxonium
Pipecuronium (Arduan)
Mellictin
2. Depolarizing
type: Dythiline
3. Mix type: Dioxonium









![Drugs affecting the afferent and efferent nervous system. Cholinergic drugs Astringents 1. Organic Compounds: Tannin Tannalbin Oak Bark [Cortex Quercus] Grass of st. Johns wort](/img/tmb/14/1399326/1eb1db5a48ff1a5a64f26d0a4b298d35-720x.jpg)
![Drugs affecting the afferent and efferent nervous system. Cholinergic drugs 2. Inorganic Compounds: Bismuth subcitrate [DE-NOL] Silver nitrate Zinc oxide](/img/tmb/14/1399326/a64a32a2b4a8fa430f528b3462390e23-720x.jpg)