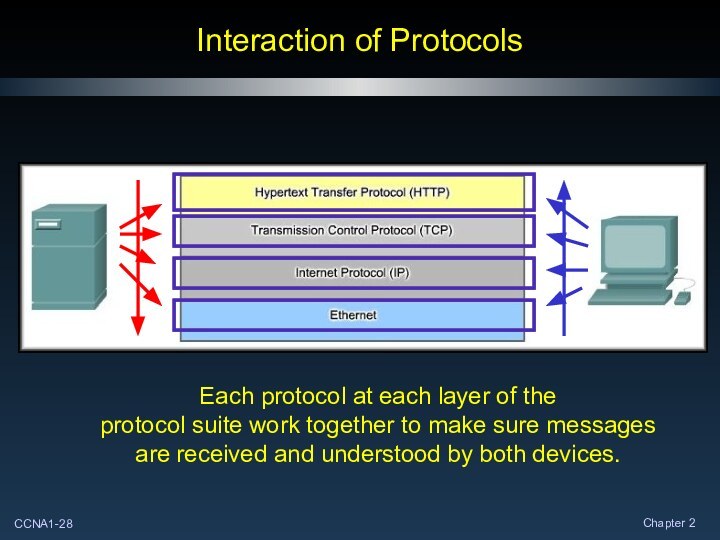
Слайд 2
Communicating Over the Network
The Platform for Communications
Слайд 3
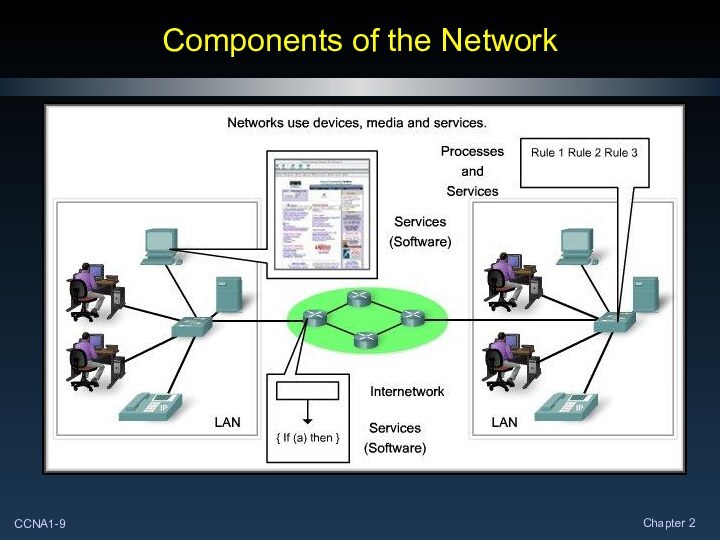
Elements of Communication
People communicate in many different ways.
Vocal,
a look, a hand signal, body language…
All of the
methods have three things in common.
There is source for the message or a sender.
There is a destination for the message or a receiver.
There is a channel that consists of the media that provides the pathway for the message.
Слайд 4
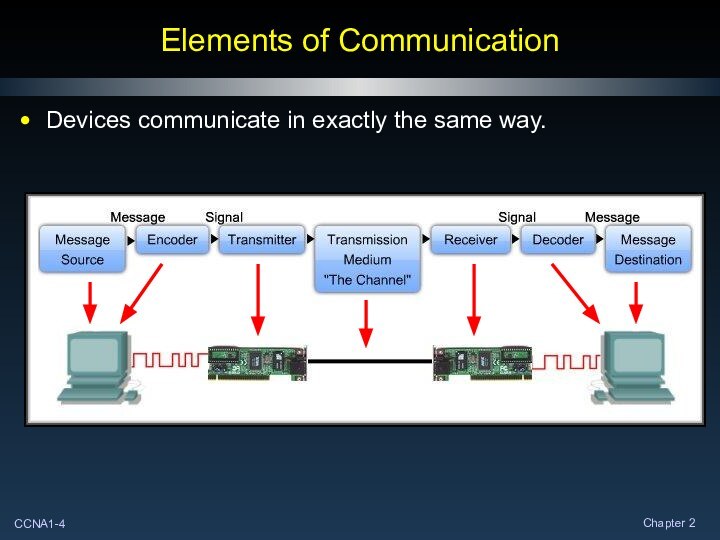
Elements of Communication
Devices communicate in exactly the same
way.
Слайд 5
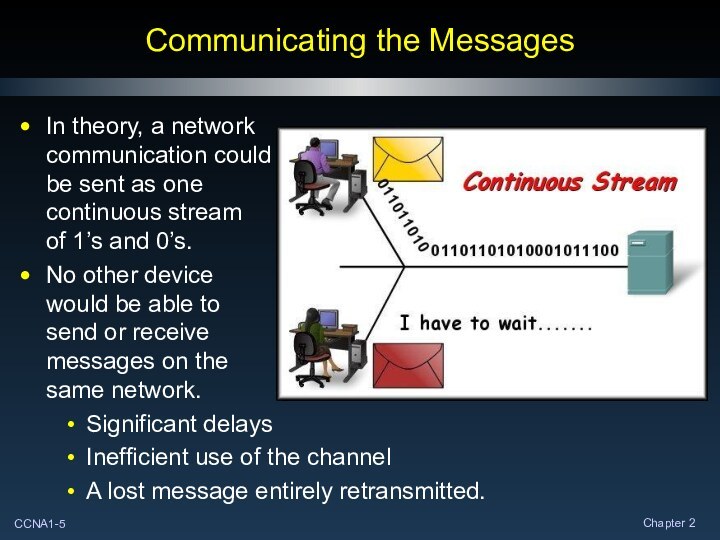
Communicating the Messages
In theory, a network
communication could
be sent
as one
continuous stream
of 1’s and 0’s.
No other device
would be
able to
send or receive
messages on the
same network.
Significant delays
Inefficient use of the channel
A lost message entirely retransmitted.
Слайд 6
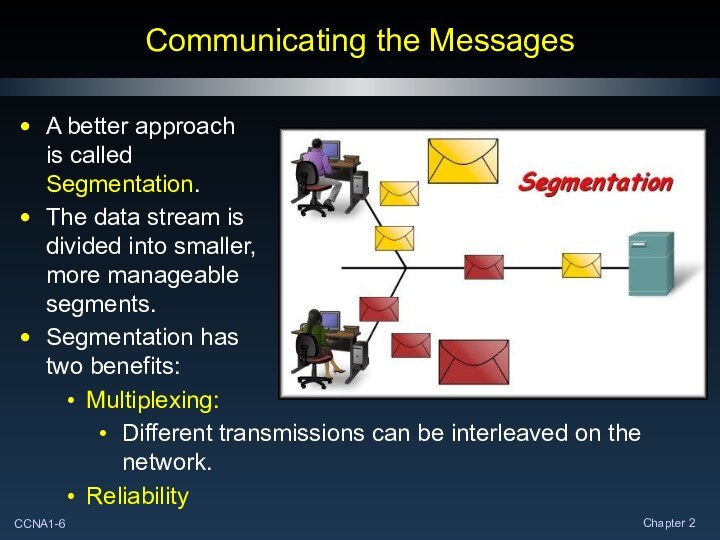
Communicating the Messages
A better approach
is called
Segmentation.
The data stream
is
divided into smaller,
more manageable
segments.
Segmentation has
two benefits:
Multiplexing:
Different transmissions can be
interleaved on the network.
Reliability
Слайд 7
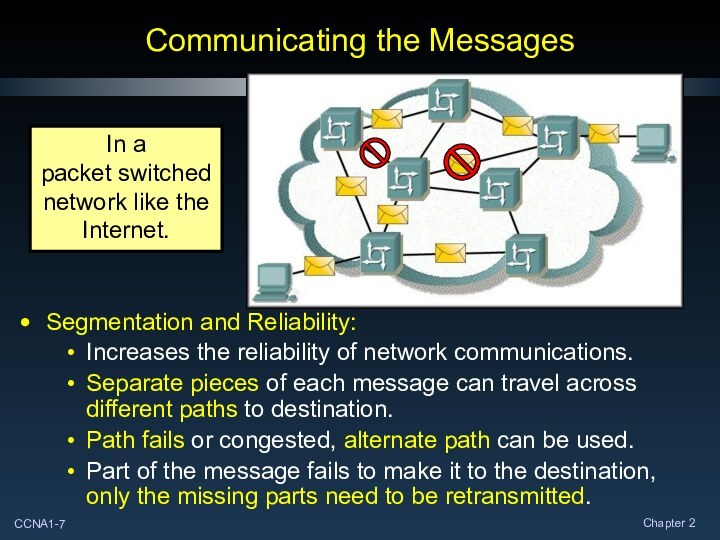
Communicating the Messages
Segmentation and Reliability:
Increases the reliability of
network communications.
Separate pieces of each message can travel
across different paths to destination.
Path fails or congested, alternate path can be used.
Part of the message fails to make it to the destination, only the missing parts need to be retransmitted.
In a
packet switched network like the Internet.
Слайд 8
Communicating the Messages
Segmentation Disadvantage: Added level of complexity.
The
label is a unique sequence number.
Handled by protocols that
format and address the message.
Слайд 10
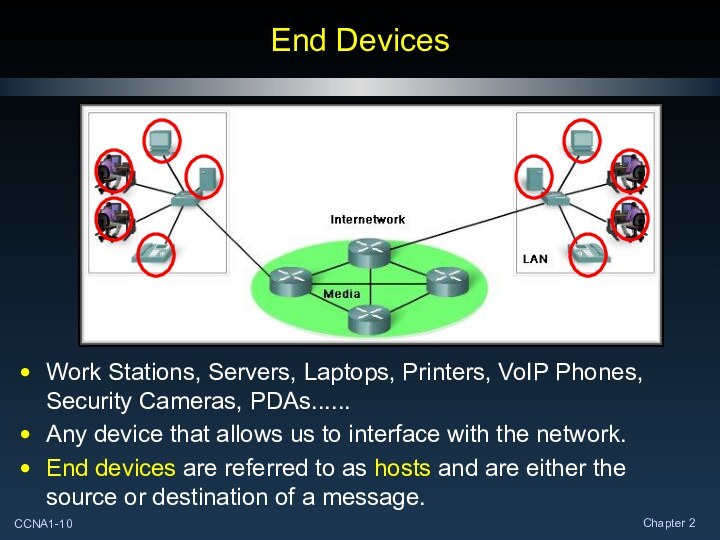
End Devices
Work Stations, Servers, Laptops, Printers, VoIP Phones,
Security Cameras, PDAs......
Any device that allows us to interface
with the network.
End devices are referred to as hosts and are either the source or destination of a message.
Слайд 11
End Devices
End Devices:
A host can be a
client, a
server or
both.
The software
installed on the device determines its role.
Servers:
Software
that enables them to provide information and services (E-mail, Web Pages) to other hosts on the network.
Client:
Software installed that enables them to request and display the information obtained from the server.
Servers
Clients
Слайд 12
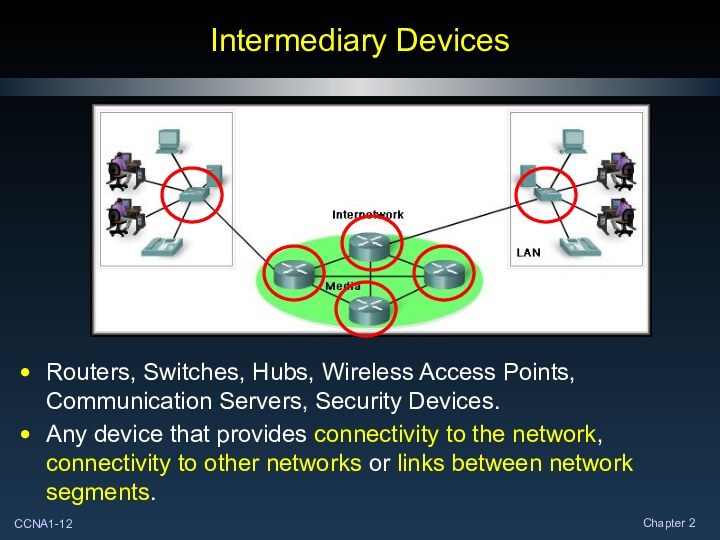
Intermediary Devices
Routers, Switches, Hubs, Wireless Access Points, Communication
Servers, Security Devices.
Any device that provides connectivity to the
network, connectivity to other networks or links between network segments.
Слайд 13
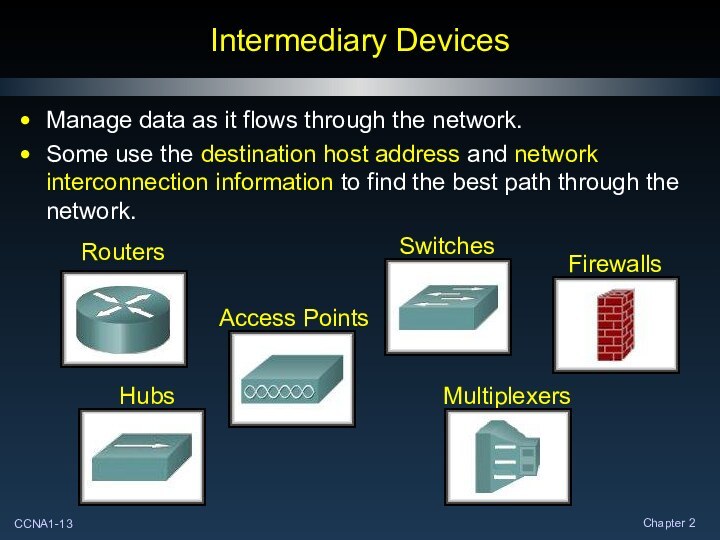
Intermediary Devices
Manage data as it flows through the
network.
Some use the destination host address and network interconnection
information to find the best path through the network.
Слайд 14
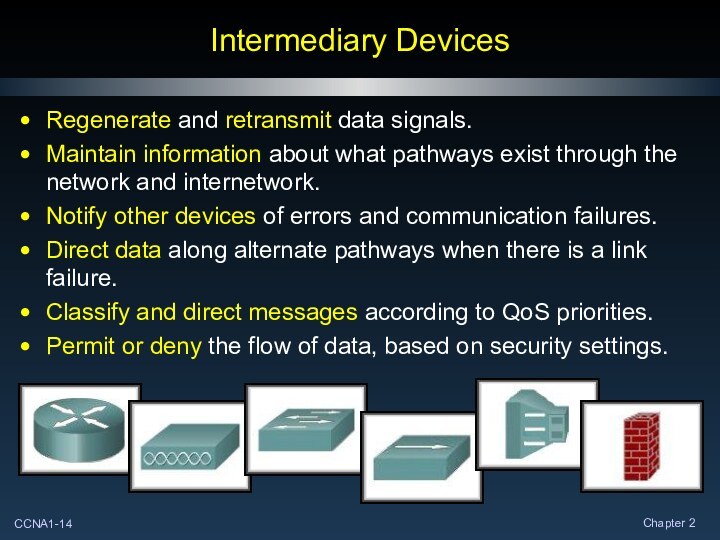
Intermediary Devices
Regenerate and retransmit data signals.
Maintain information about
what pathways exist through the network and internetwork.
Notify other
devices of errors and communication failures.
Direct data along alternate pathways when there is a link failure.
Classify and direct messages according to QoS priorities.
Permit or deny the flow of data, based on security settings.
Слайд 15
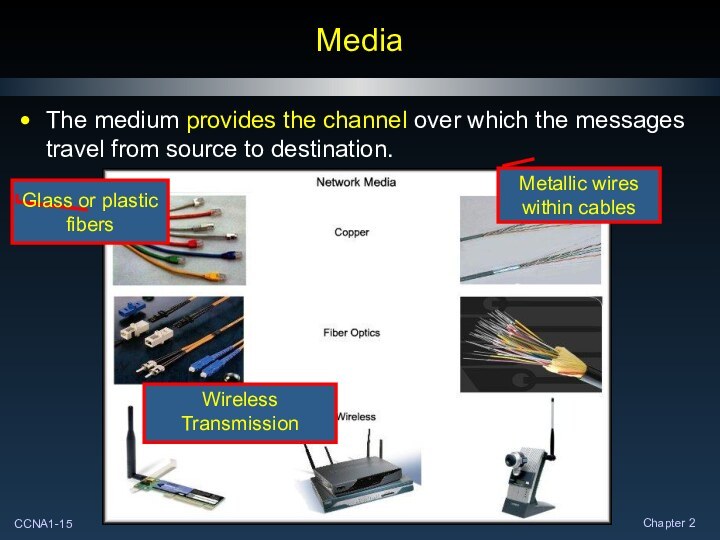
Media
The medium provides the channel over which the
messages travel from source to destination.
Metallic wires within cables
Glass
or plastic fibers
Wireless Transmission
Слайд 16
Media
The signal encoding that must occur is different
for each type of media.
Electrical impulses with specific patterns
Pulses
of light in the infrared or visible ranges
Patterns of electromagnetic waves
Слайд 17
Media
Different network media have different features and benefits.
Not
all network media are appropriate for the same purpose.
You
must make the appropriate choice to provide the proper
channel.
Distance it can carry
the signal
Environment
Bandwidth
Cost of the media
Installation costs
Cost of connectors and devices
Слайд 18
Communicating Over the Network
LANs, WANs and Internetworks
Слайд 19
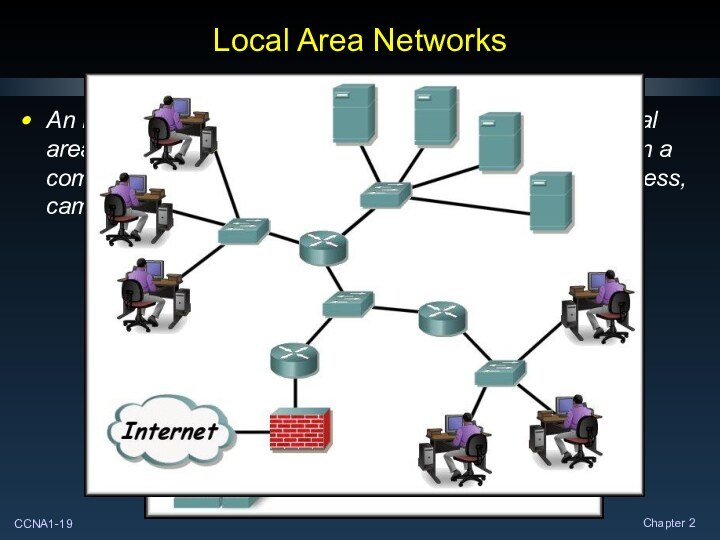
Local Area Networks
An individual network usually spans a
single geographical area, providing services and applications to people
within a common organizational structure, such as a single business, campus or region.
Слайд 20
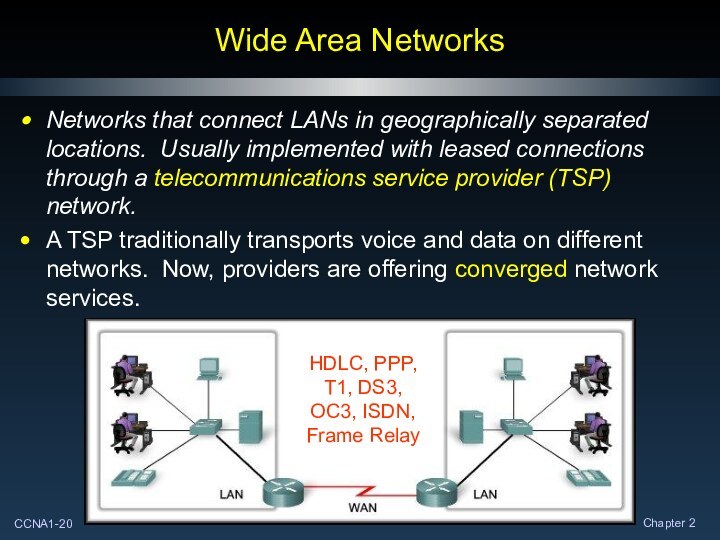
Wide Area Networks
Networks that connect LANs in geographically
separated locations. Usually implemented with leased connections through a
telecommunications service provider (TSP) network.
A TSP traditionally transports voice and data on different networks. Now, providers are offering converged network services.
HDLC, PPP, T1, DS3, OC3, ISDN, Frame Relay
Слайд 21
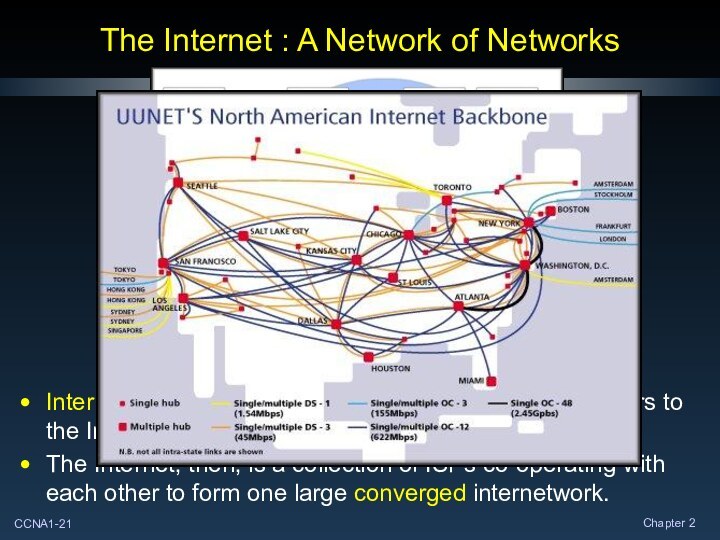
The Internet : A Network of Networks
Internet Service
Providers (ISPs) connect their customers to the Internet through
their network infrastructure.
The Internet, then, is a collection of ISPs co-operating with each other to form one large converged internetwork.
Слайд 22
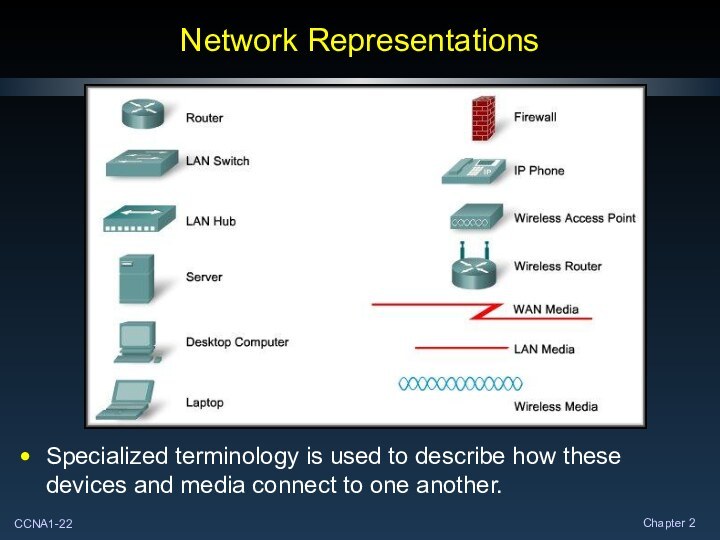
Network Representations
Specialized terminology is used to describe how
these devices and media connect to one another.
Слайд 23
Network Representations
Network Interface Card (NIC):
Provides the physical
connection to
the network
at the PC or other host device.
Physical
Port:
A connector or outlet on a networking device where the media is connected to a host or other networking device.
Слайд 24
Network Representations
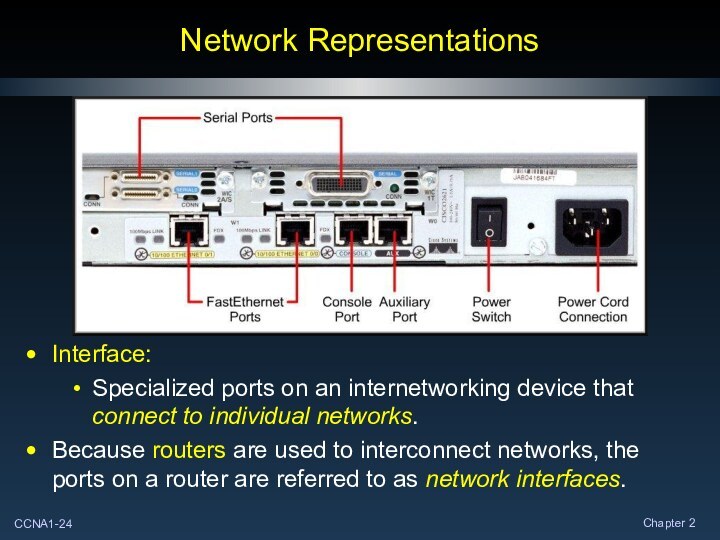
Interface:
Specialized ports on an internetworking device that
connect to individual networks.
Because routers are used to
interconnect networks, the ports on a router are referred to as network interfaces.
Слайд 25
Communicating Over the Network
Protocols
Слайд 26
Rules That Govern Communications
Protocols:
Are the rules that govern
communications.
The format or structure of the message.
How and when
error and system messages are passed between devices.
The setup and termination of data transfer sessions.
The method by which networking devices share information about pathways with other networks.
Слайд 27
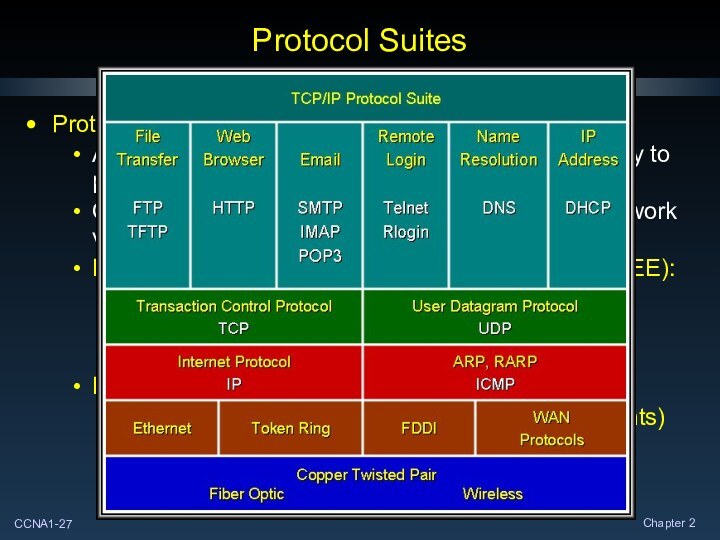
Protocol Suites
Protocol Suite:
A group of inter-related protocols that
are necessary to perform a communication function.
Cannot function without
a set of standards that network vendors can follow.
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE):
Develops standards in telecommunications, information technology and power generation.
Examples: 802.3 (Ethernet), 802.11 (WLAN)
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
Internet standards, RFCs (Request for Comments)
Example: TCP, IP, HTTP, FTP
Слайд 29
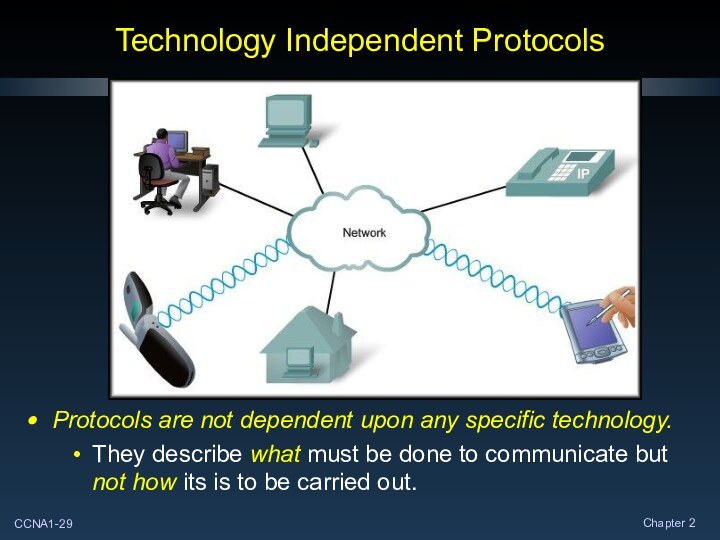
Technology Independent Protocols
Protocols are not dependent upon any
specific technology.
They describe what must be done to communicate
but not how its is to be carried out.
Слайд 30
Communicating Over the Network
Using Layered Models
Слайд 31
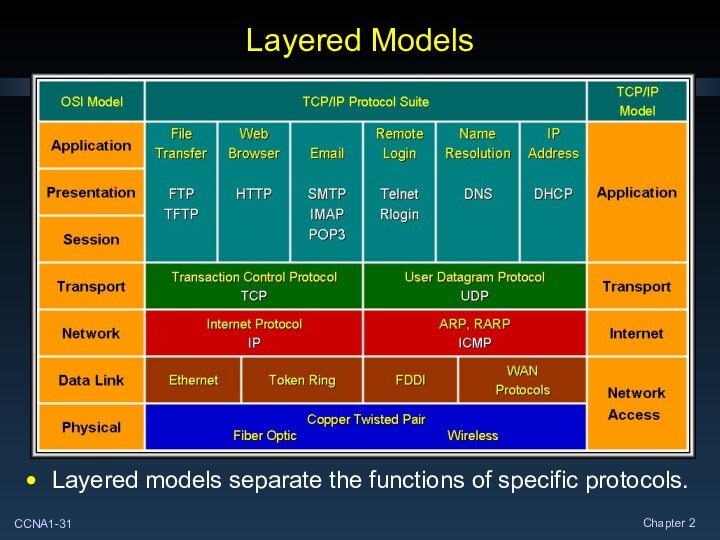
Layered Models
Layered models separate the functions of specific
protocols.
Слайд 32
Benefits of a Layered Model
Benefits of a Layered
Model:
Have defined information that they act upon and a
defined interface to the layers above and below.
Fosters competition because products from different vendors can work together.
Prevents technology or capability changes in one layer from affecting other layers above and below.
Provides a common language to describe networking functions and capabilities.
Слайд 33
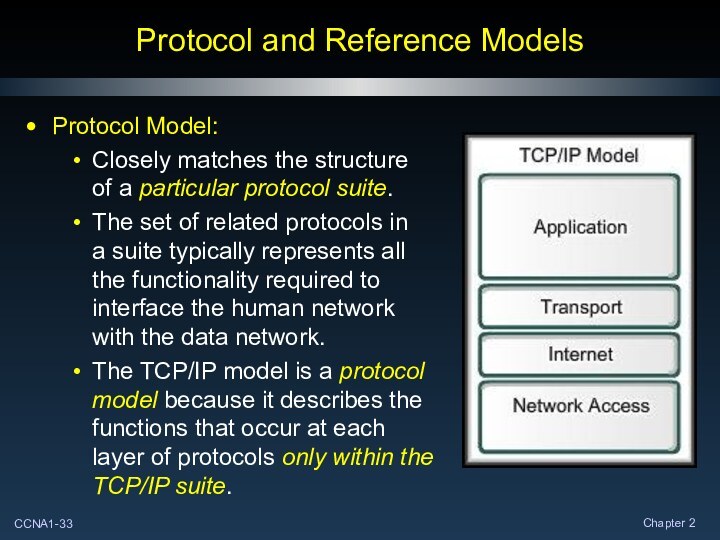
Protocol and Reference Models
Protocol Model:
Closely matches the structure
of
a particular protocol suite.
The set of related protocols in
a
suite typically represents all
the functionality required to
interface the human network
with the data network.
The TCP/IP model is a protocol
model because it describes the
functions that occur at each
layer of protocols only within the
TCP/IP suite.
Слайд 34
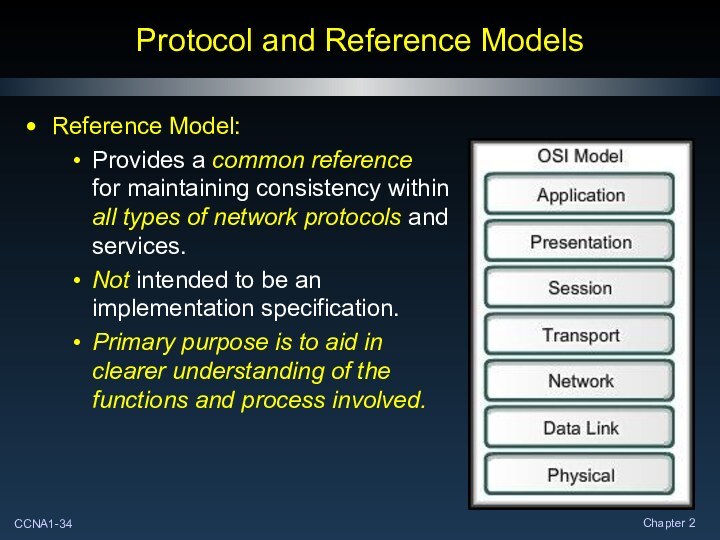
Protocol and Reference Models
Reference Model:
Provides a common reference
for
maintaining consistency within
all types of network protocols and
services.
Not intended
to be an
implementation specification.
Primary purpose is to aid in
clearer understanding of the
functions and process involved.
Слайд 35
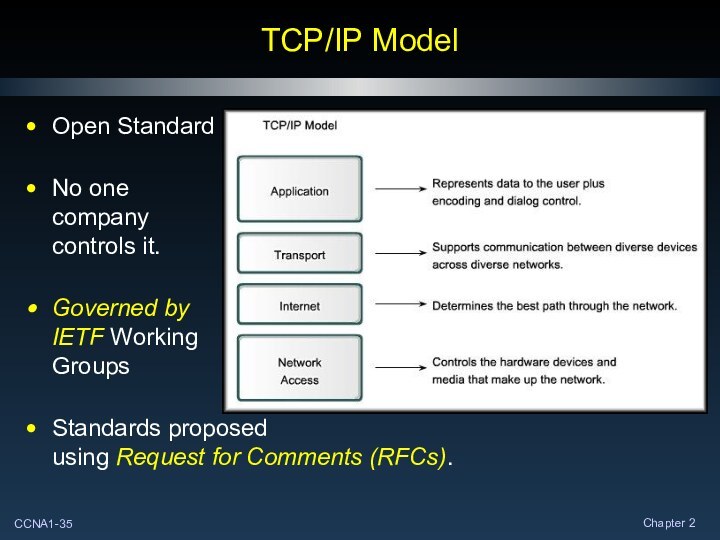
TCP/IP Model
Open Standard
No one
company
controls it.
Governed by
IETF Working
Groups
Standards proposed
using
Request for Comments (RFCs).
Слайд 38
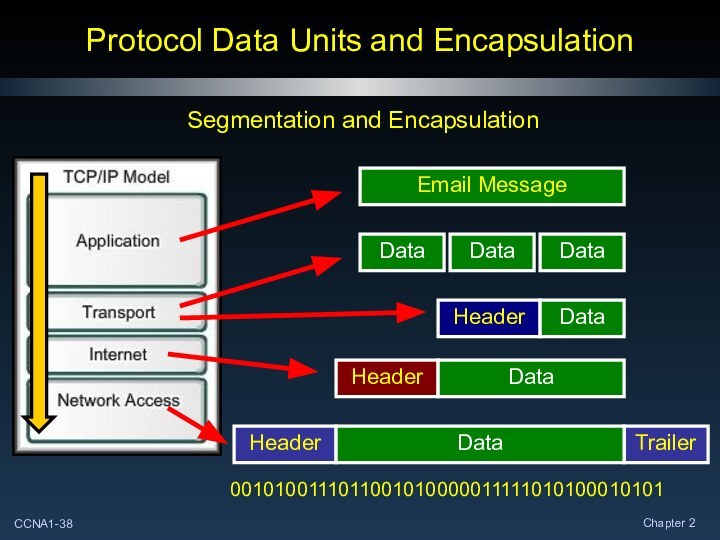
Protocol Data Units and Encapsulation
Header
Header
Data
Header
Trailer
0010100111011001010000011111010100010101
Segmentation and Encapsulation
Слайд 39
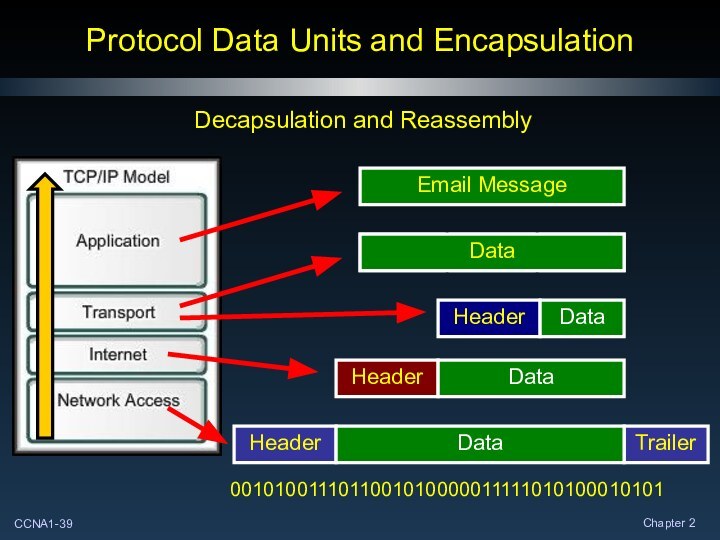
Protocol Data Units and Encapsulation
Header
Header
Header
Trailer
Decapsulation and Reassembly
Data
0010100111011001010000011111010100010101
Слайд 40
Protocol Data Units and Encapsulation
Header
Header
Header
Trailer
Email Message
Data
Data
Data
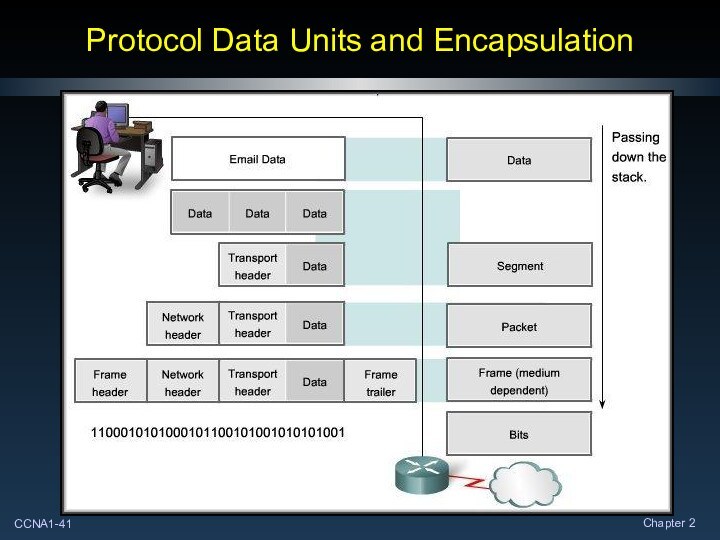
Protocol Data Units
Data
Segment
Packet
Frame
Слайд 41
Protocol Data Units and Encapsulation
Слайд 42
Communicating Over the Network
The OSI Model
Слайд 43
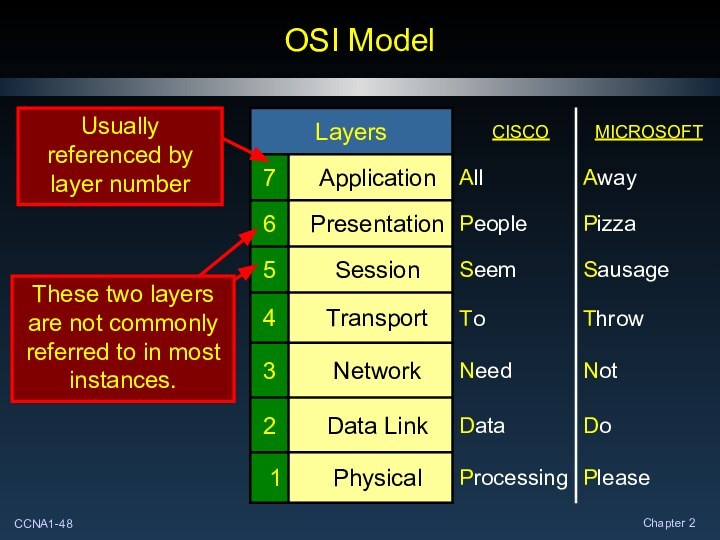
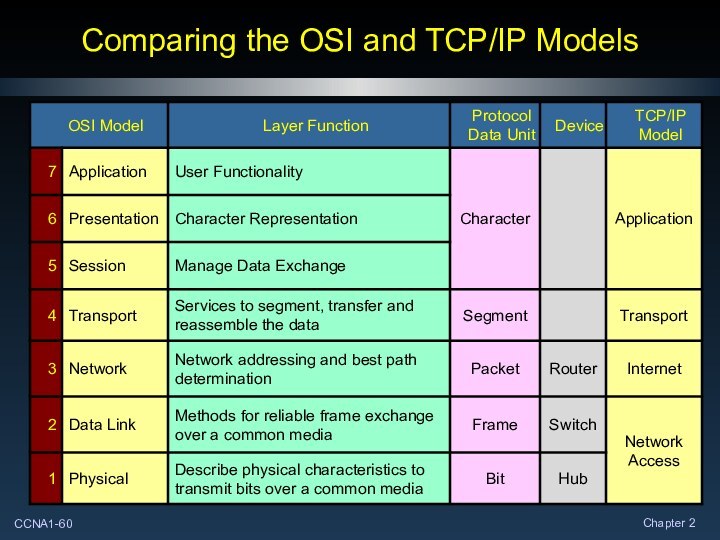
OSI Model
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) released
the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model in 1984.
www.iso.org
for more information
Слайд 44
OSI Model
Breaks network communication into
smaller, more manageable parts.
Makes learning it easier to
understand.
Prevents changes in one layer
from
affecting other layers.
Standardizes network components
to allow multiple vendor development
and support.
Allows different types of network
hardware and software to communicate
with each other.
It is a descriptive scheme.
Слайд 45
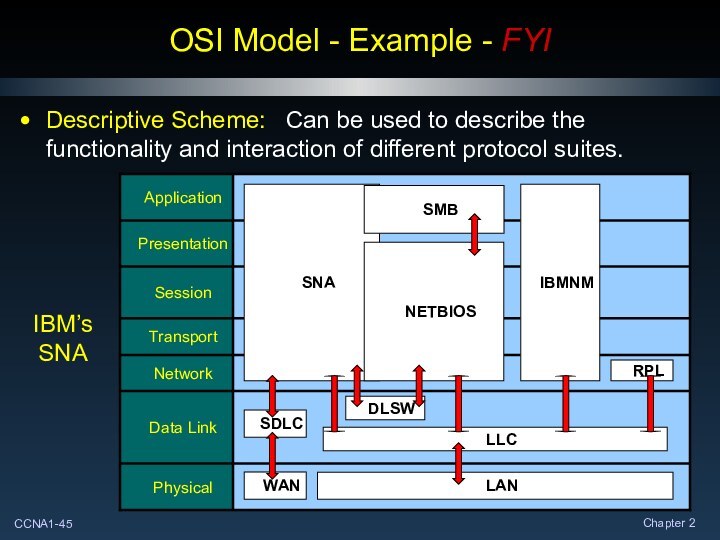
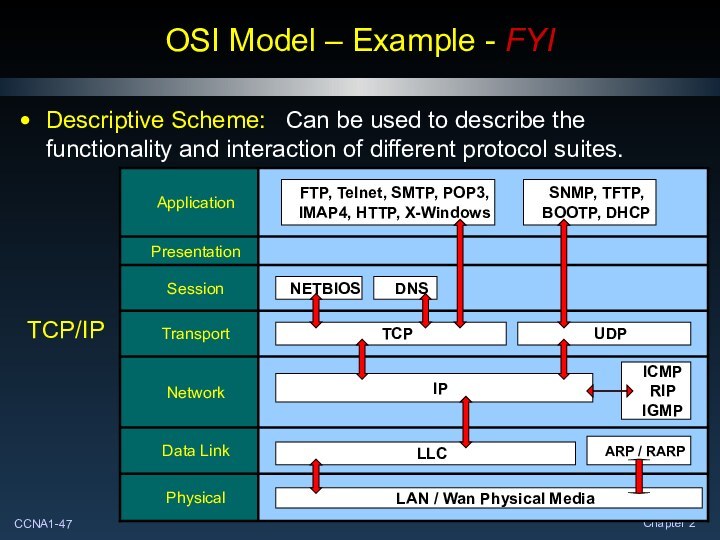
OSI Model - Example - FYI
Descriptive Scheme:
Can be used to describe the functionality and interaction
of different protocol suites.
IBM’s SNA
Слайд 46
OSI Model – Example - FYI
Descriptive Scheme:
Can be used to describe the functionality and interaction
of different protocol suites.
ISO
Слайд 47
OSI Model – Example - FYI
Descriptive Scheme:
Can be used to describe the functionality and interaction
of different protocol suites.
TCP/IP
Слайд 49
OSI Model
Primary concern: Communications between applications
Primary concern: Moving
raw data cross the network
Слайд 50
Communicating Over the Network
Network Addressing
Слайд 52
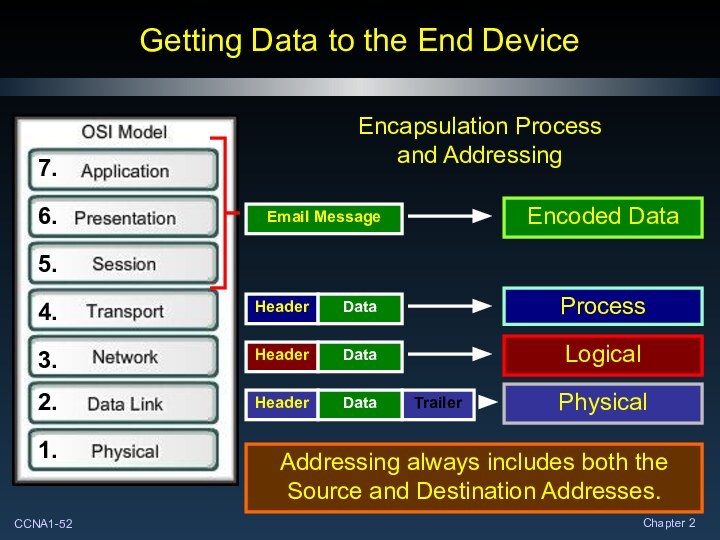
Getting Data to the End Device
Header
Header
Header
Trailer
Email Message
Data
Data
Data
Encoded Data
Process
Logical
Physical
Encapsulation
Process and Addressing
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
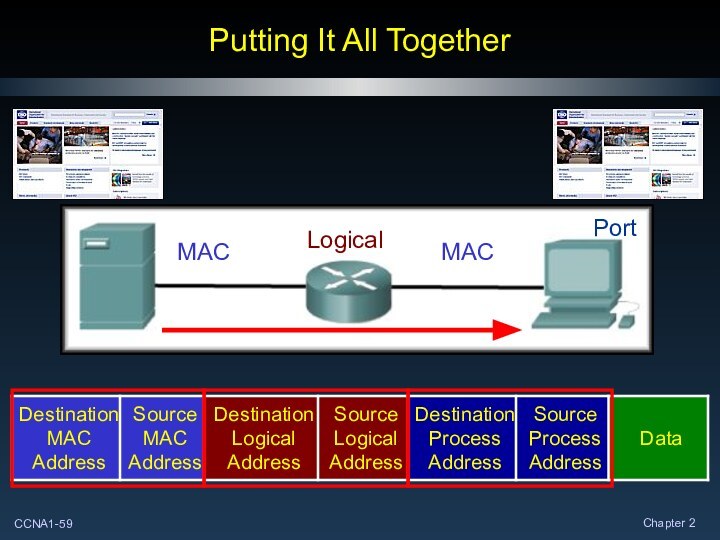
Addressing always includes both the Source and
Destination Addresses.
Слайд 53
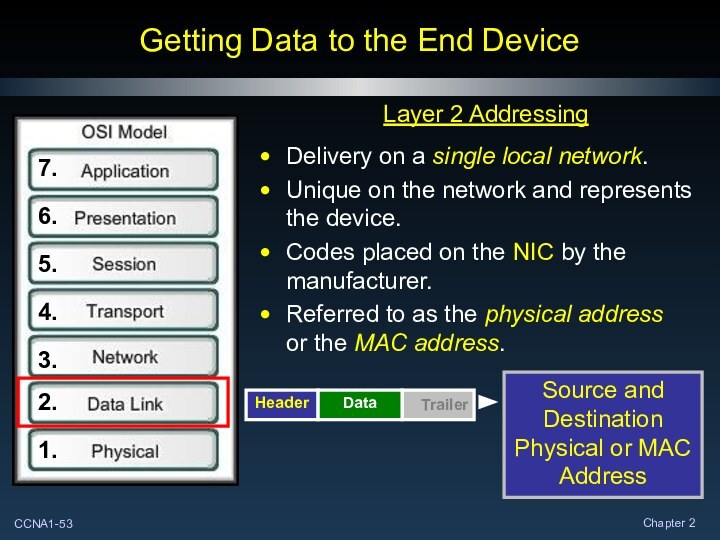
Getting Data to the End Device
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Layer 2 Addressing
Delivery
on a single local network.
Unique on the network and
represents the device.
Codes placed on the NIC by the manufacturer.
Referred to as the physical address
or the MAC address.
Header
Trailer
Data
Source and Destination Physical or MAC Address
Слайд 54
Getting Data to the End Device
Layer 2 Header
Слайд 55
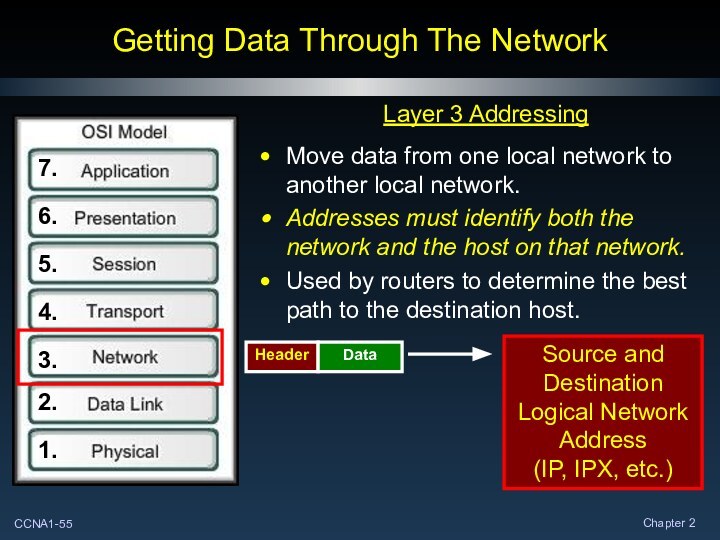
Getting Data Through The Network
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Layer 3 Addressing
Move data
from one local network to another local network.
Addresses must
identify both the network and the host on that network.
Used by routers to determine the best path to the destination host.
Слайд 56
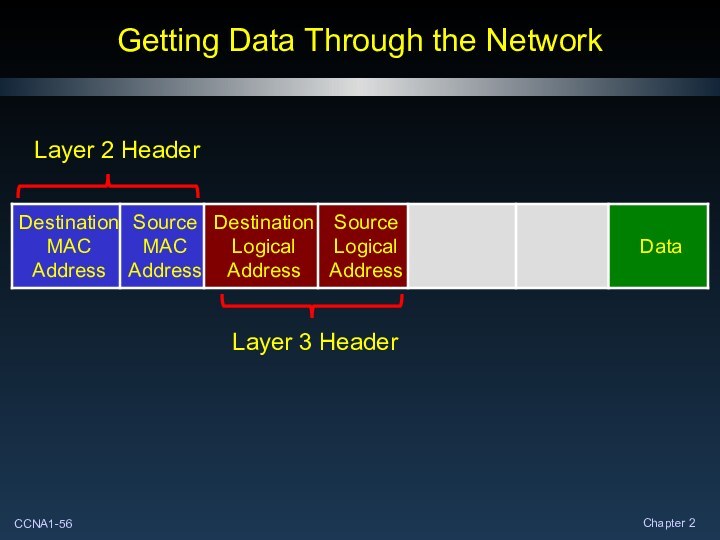
Getting Data Through the Network
Layer 2 Header
Layer 3
Header
Слайд 57
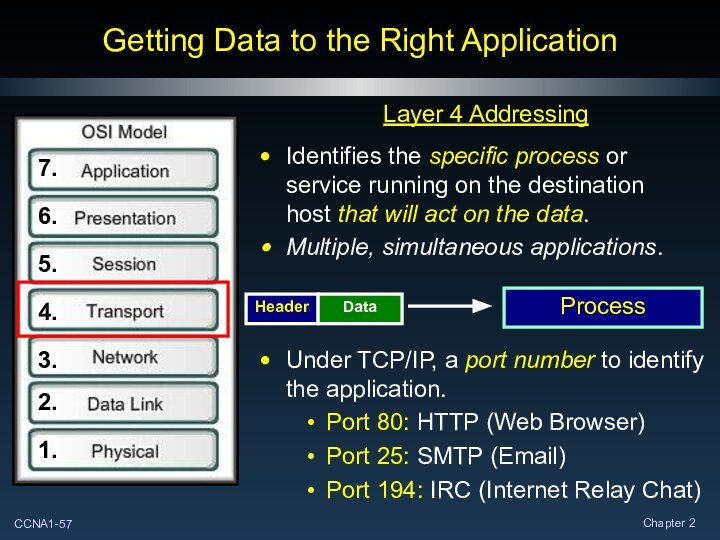
Getting Data to the Right Application
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Layer 4 Addressing
Identifies
the specific process or service running on the destination
host that will act on the data.
Multiple, simultaneous applications.
Слайд 58
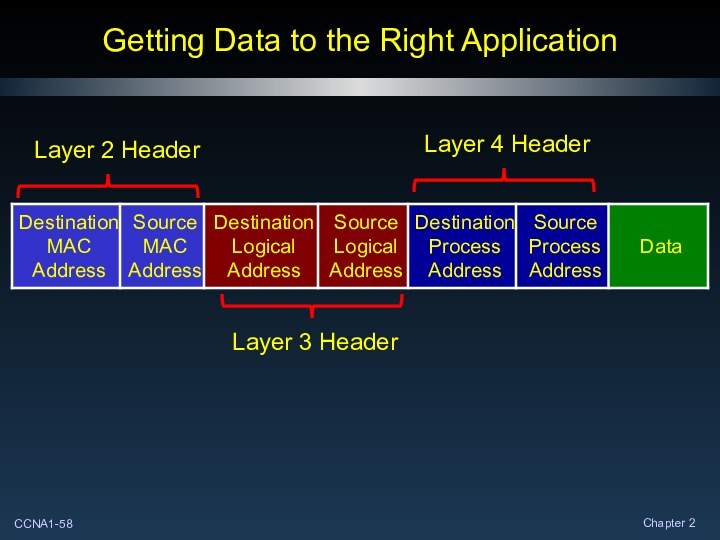
Getting Data to the Right Application
Layer 2 Header
Layer
3 Header
Layer 4 Header
Слайд 59
Putting It All Together
Logical
MAC
Port
MAC
Слайд 60
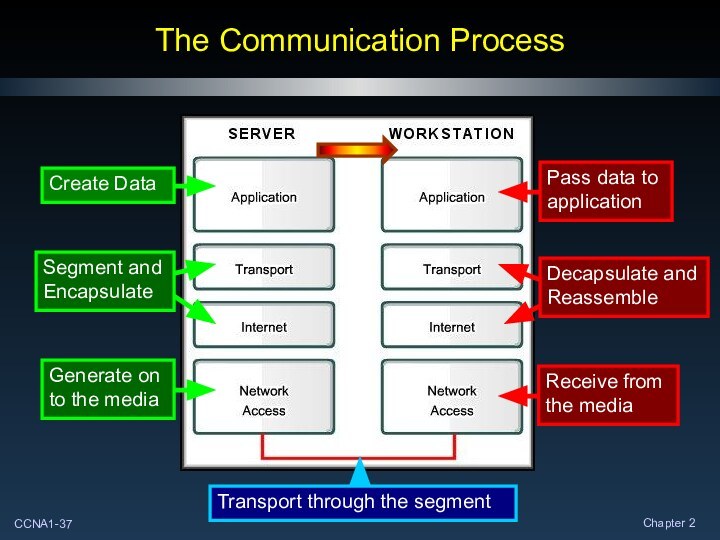
Comparing the OSI and TCP/IP Models