Слайд 2
Chapter Goals
Explain packet switching
Describe the basic roles of
various network protocols
Explain the role of a firewall
Compare and
contrast network hostnames and IP addresses
Explain the domain name system
Describe cloud computing and its benefits
Слайд 3
Networking
Computer network
A collection of computing devices
connected in order to communicate and share resources
Connections between
computing devices can be physical using wires or cables or wireless using radio waves or infrared signals
Can you name some of the devices in a computer network?
Слайд 4
Networking
Node (host)
Any device on a network
Data transfer
rate (bandwidth)
The speed with which data is moved from
one place to another on a network
Why is bandwidth so key?
Слайд 5
Networking
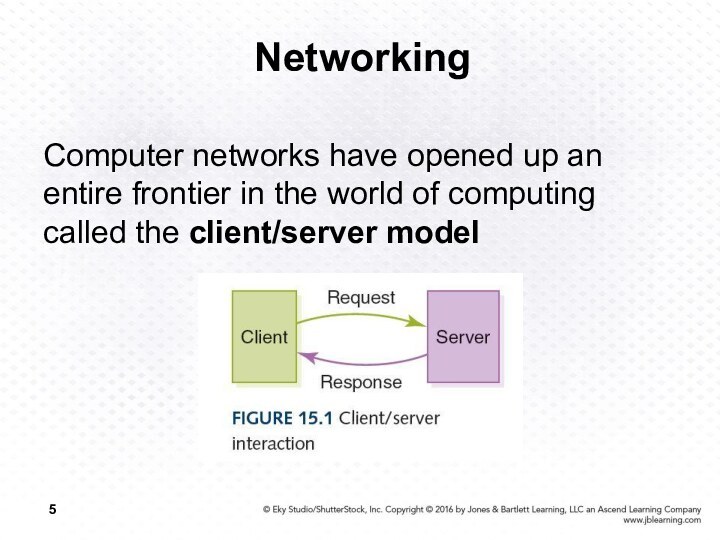
Computer networks have opened up an entire frontier
in the world of computing called the client/server model
Слайд 6
Networking
Protocol
A set of rules that defines how data
is formatted and processed on a network
File server
A
computer dedicated to storing and managing files for network users
Web server
A computer dedicated to responding to requests for web pages
P2P model
A decentralized approach that shares resources and responsibilities among many “peer” computers
Слайд 7
Types of Networks
Local-area network (LAN)
A network
that connects a relatively small number of machines in
a relatively close geographical area
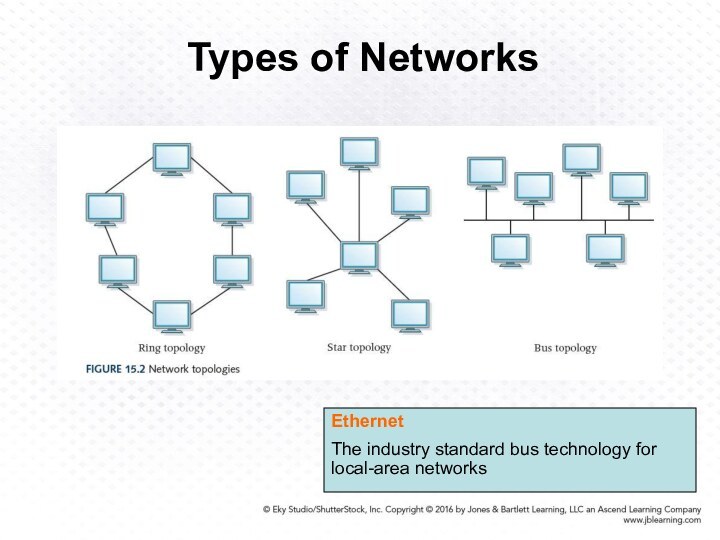
Ring topology connects all nodes in a closed loop on which messages travel in one direction
Star topology centers around one node to which all others are connected and through which all messages are sent
Bus topology nodes are connected to a single communication line that carries messages in both directions
Слайд 8
Types of Networks
Ethernet
The industry standard bus technology
for local-area networks
Слайд 9
Types of Networks
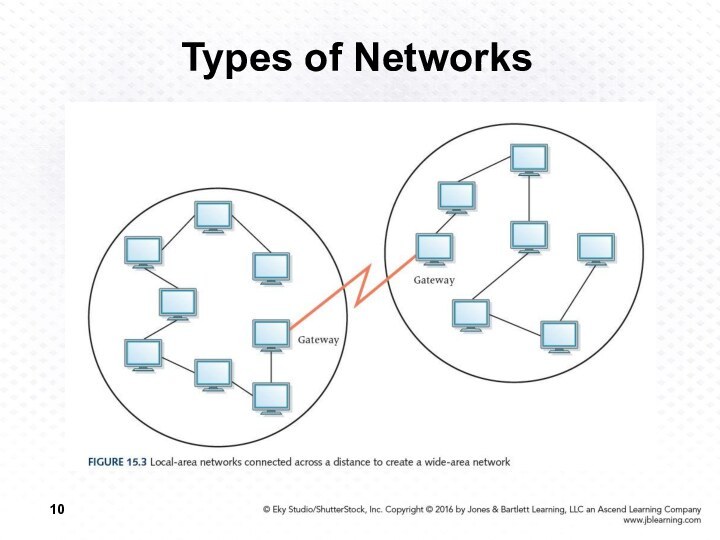
Wide-area network (WAN)
A network
that connects local-area networks over a potentially large geographic
distance
Metropolitan-area network (MAN)
The communication infrastructures that have been developed in and around large cities
Gateway
One particular set up to handle all communication going between that LAN and other networks
Слайд 11
Types of Networks
Internet
A wide area network that spans
the planet
So, who owns the Internet?
Слайд 12
Internet Connections
Wireless network
A network in which devices
communicate with other nodes through a wireless access point
Bluetooth
A
technology used for wireless communication over short distances
Слайд 13
Internet Connections
Internet backbone
A set of high-speed networks
that carry Internet traffic, provided by companies such as
AT&T, Verizon, GTE, British Telecom, and IBM
Internet service provider (ISP)
An organization providing access to the Internet
Слайд 14
Internet Connections
Various technologies available to connect a home
computer to the Internet
Phone modem converts computer data into
an analog audio signal for transfer over a telephone line, and then a modem at the destination converts it back again into data
Digital subscriber line (DSL) uses regular copper phone lines to transfer digital data to and from the phone company’s central office
Cable modem uses the same line that your cable TV signals come in on to transfer the data back and forth
Слайд 15
Internet Connections
Broadband
A connection in which transfer speeds
are faster than 768 kilobits per second
DSL connections and
cable modems are broadband connections
The speed for downloads (getting data from the Internet to your home computer) may not be the same as uploads (sending data from your home computer to the Internet)
Слайд 16
Packet Switching
Packet
A unit of data sent across a
network
Router
A network device that directs a packet between
networks toward its final destination
Packet switching
Messages are divided into fixed-sized, numbered packets; packets are individually routed to their destination, then reassembled
Слайд 17
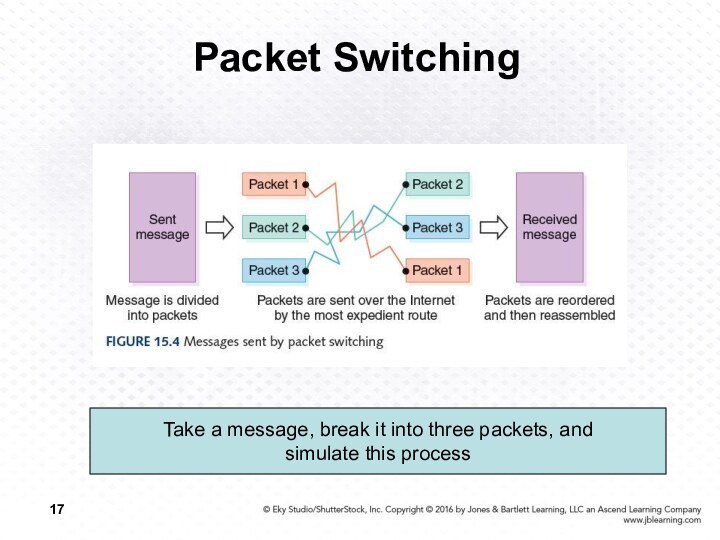
Packet Switching
Take a message, break it into three
packets, and
simulate this process
Слайд 18
Open Systems
A logical progression...
Proprietary system
A system that
uses technologies kept private by a particular commercial vendor
Interoperability
The ability of software and hardware on multiple machines and from multiple commercial vendors to communicate
Open systems
Systems based on a common model of network architecture and a suite of protocols used in its implementation
Слайд 19
Open Systems
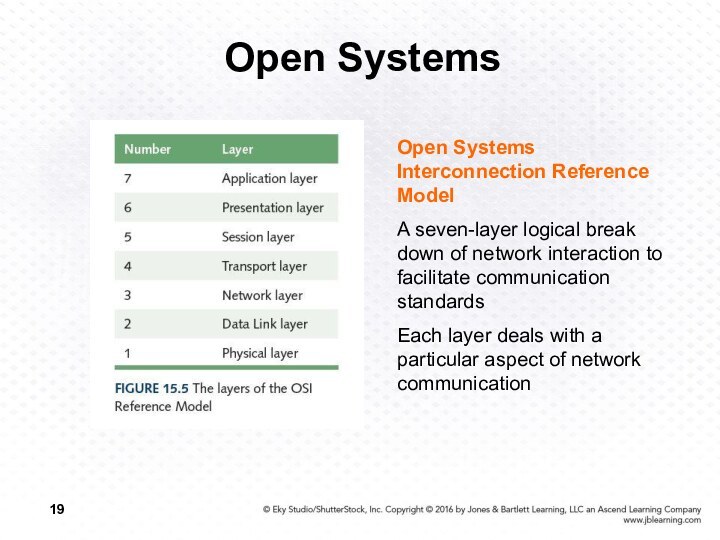
Open Systems Interconnection Reference Model
A seven-layer logical
break down of network interaction to facilitate communication standards
Each
layer deals with a particular aspect of network communication
Слайд 20
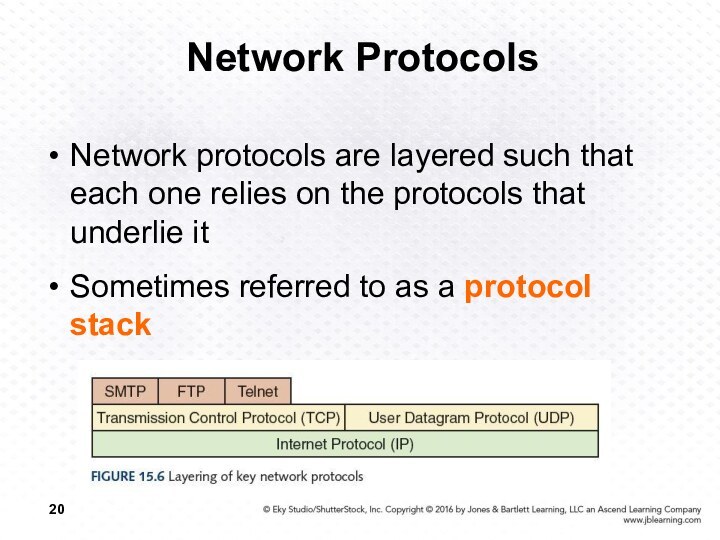
Network Protocols
Network protocols are layered such that each
one relies on the protocols that underlie it
Sometimes referred
to as a protocol stack
Слайд 21
TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
Software that breaks messages into
packets, hands them off to the IP software for
delivery, and then orders and reassembles the packets at their destination
Internet Protocol (IP)
Software that deals with the routing of packets through the maze of interconnected networks to their final destination
Слайд 22
TCP/IP
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
An alternative to TCP that
is faster but less reliable
Ping
A program used to test
whether a particular network computer is active and reachable
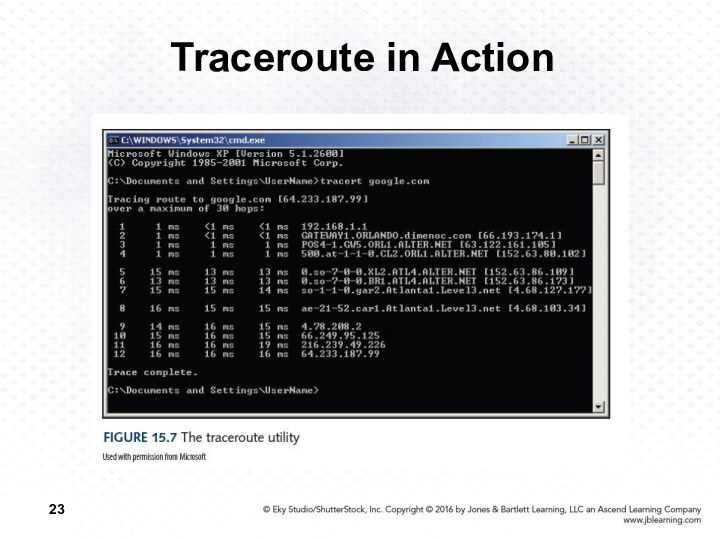
Traceroute
A program that shows the route a packet takes across the Internet
Слайд 24
High-Level Protocols
Other protocols build on TCP/IP protocol suite
Simple
Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) used to specify transfer of
electronic mail
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) allows a user to transfer files to and from another computer
Telnet used to log onto one computer from another
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (http) allows exchange of Web documents
Which of these have you used?
Слайд 25
High-Level Protocols
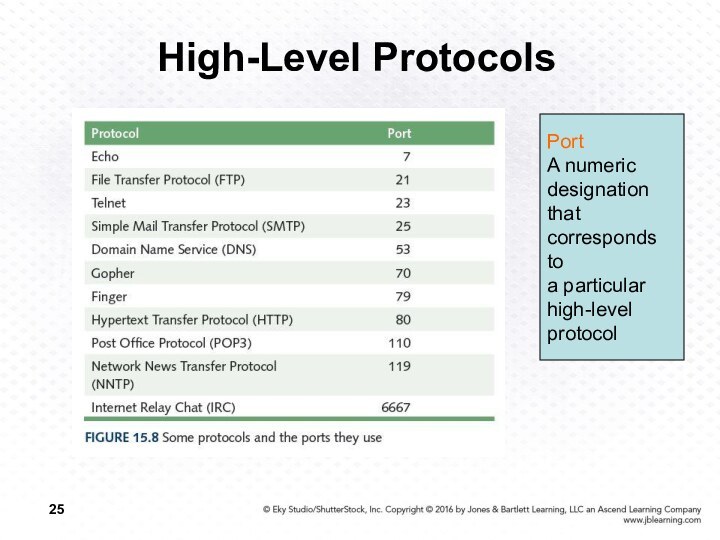
Port
A numeric
designation
that
corresponds to
a particular
high-level
protocol
Слайд 26
MIME Types
MIME type
A standard for defining the format
of files that are included as email attachments or
on websites
What does MIME stand for?
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension
Слайд 27
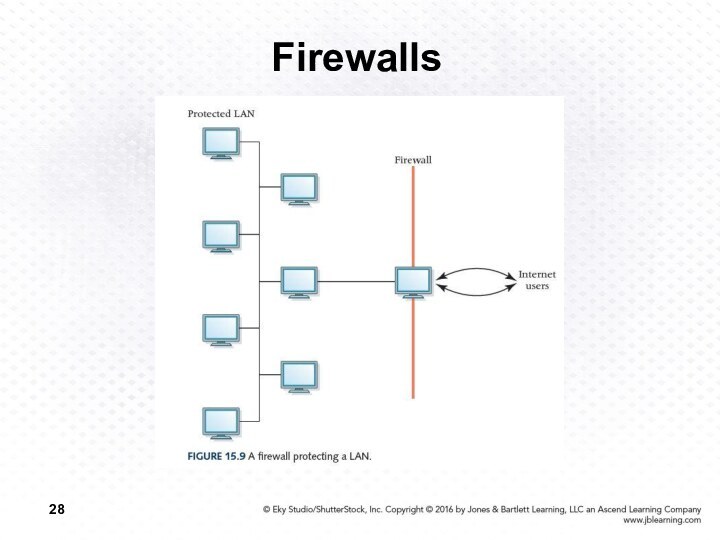
Firewalls
Firewall
A gateway machine and its software that
protects a network by filtering the traffic it allows
Access
control policy
A set of rules established by an organization that specifies what types of network communication are permitted and denied
Have your messages ever been
returned undelivered, blocked by a firewall?
Слайд 29
Network Addresses
Hostname
A name made up of words
separated by dots that uniquely identifies a computer on
the Internet
IP address
An address made up of four one-byte numeric values separated by dots that uniquely identifies a computer on the Internet
Is there a correspondence between the parts of a hostname and an IP address?
Слайд 30
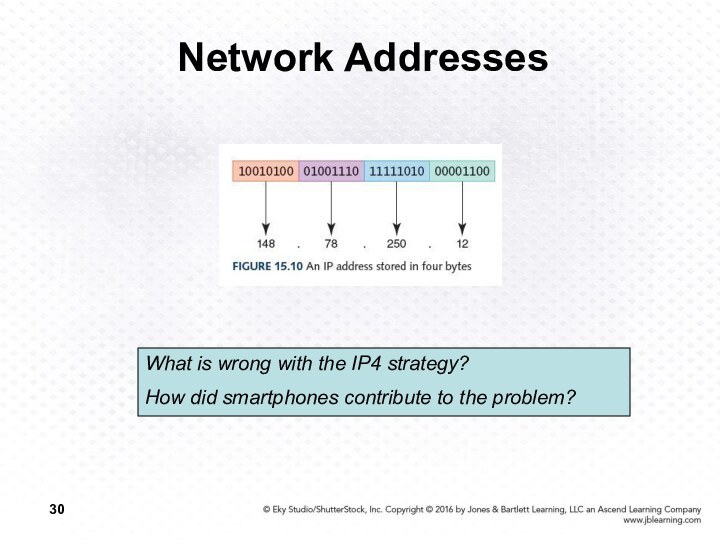
Network Addresses
What is wrong with the IP4 strategy?
How
did smartphones contribute to the problem?
Слайд 31
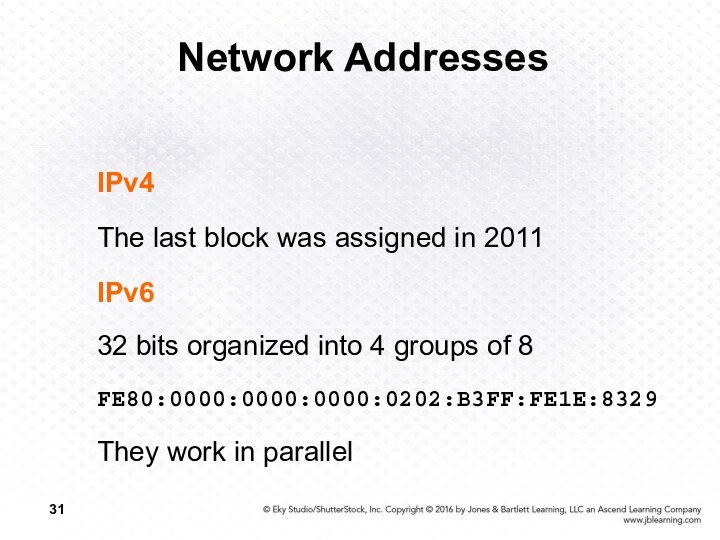
Network Addresses
IPv4
The last block was assigned in
2011
IPv6
32 bits organized into 4 groups of 8
FE80:0000:0000:0000:0202:B3FF:FE1E:8329
They work
in parallel
Слайд 32
Domain Name System
Host number
The part of the IP
address that specifies a particular host (machine) on the
network Yes, but what is it?
Domain name
The part of a hostname that specifies a specific organization or group
Top-level domain (TLD)
The last section of a domain name that specifies the type of organization or its country of origin
Слайд 33
Domain Name System
Domain name system (DNS)
A distributed
system for managing hostname resolution
Domain name server
A computer that
attempts to translate a hostname into an IP address
Domain Squatting
Ransoming domain names
Should the tables containing hostname/IP mappings be sorted or unsorted? Why?
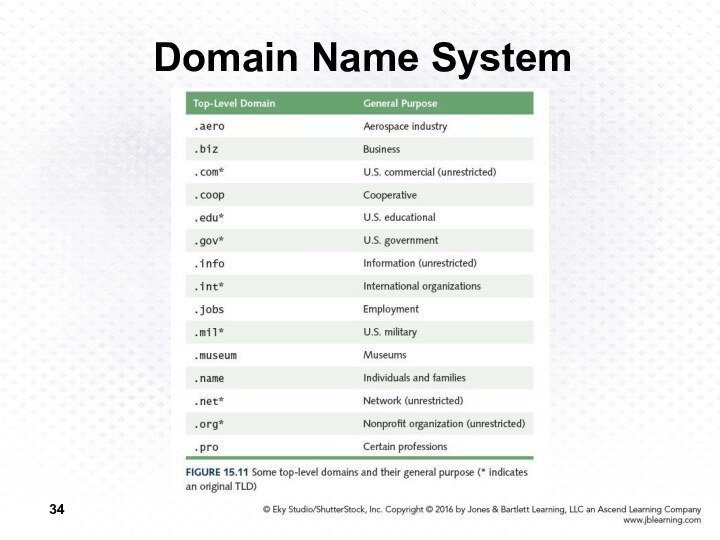
Слайд 35
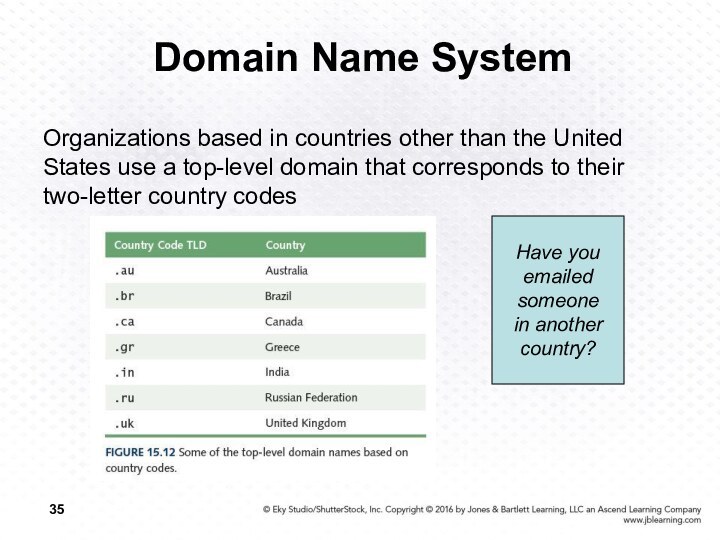
Domain Name System
Organizations based in countries other than
the United States use a top-level domain that corresponds
to their two-letter country codes
Have you
emailed
someone
in another
country?
Слайд 36
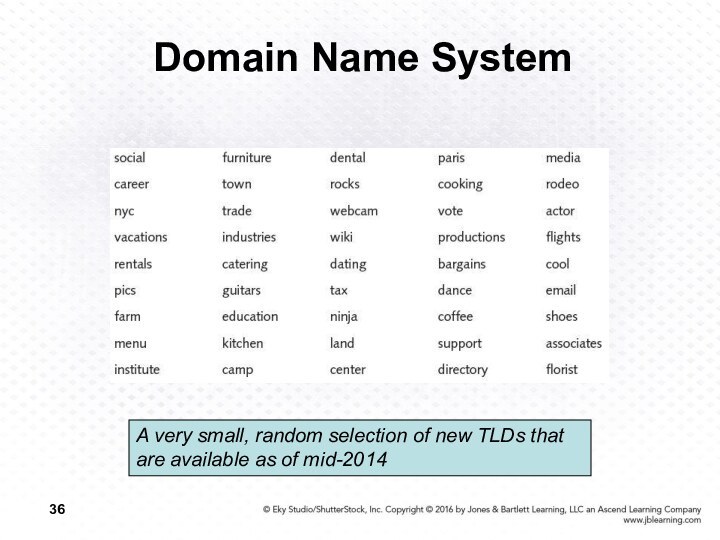
Domain Name System
A very small, random selection of
new TLDs that are available as of mid-2014
Слайд 37
Who Controls the Internet?
Control of IP addresses and
domain names
Internet began as ARPANET, a project of the
US Dept. of Defense
Control subcontracted to ICANN in 1998
US gov’t to further reduce role as early as 2015
FCC proposal
Would allow ISPs to provide “premium” access to certain customers, perhaps by deliberately slowing down data transfer for others
Net neutrality - The principle that ISPs should deliver data to everyone equally, as fast as the technology allows
Слайд 38
Cloud Computing
Public clouds are accessible by any subscriber
Private
clouds are established for a specific group or organization
Community
clouds are shared among two or more organizations with the same needs
Hybrid clouds are some combination of the others
Слайд 39
Ethical Issues
Effects of Social Networking
What are some examples
of popular social networking sites?
Who uses social networking?
What are
the benefits and the disadvantages of using these social networking sites?
Do the benefits of social networking out weigh the potential costs?
Слайд 40
Who am I?
What two major
awards did
I win?
For
what
were they
given?