- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Pathophysiology. (Subject 1)
Содержание
- 2. PATHOPHYSIOLOGYophthalmologyneurologysurgerytherapygynecologystomatologyPHARMACOLOGYPATHOLOGICALANATOMYBiologyMicrobiologyChemistryPhysicsPhilosophyNormal physiologyBiochemistryHistologyImmunologyGeneticsThe interrelations between Pathophysiology and other medical disciplines
- 3. Head of Pathophysiology Department KOLESNIK Yuri MikhailovichRector
- 4. PathophysiologyPATHOS – diseasePHYSIS – essenceLOGOS
- 5. Pathophysiology tasksCreation of the disease general conception
- 6. Experimental therapy Working out of new methods
- 7. The main methods of PathophysiologyExperimental modelling of:pathologic
- 8. Pathophysiological experimentIt includes four stages:Planning the experiment;Carrying
- 9. The main methods of PathophysiologyClinical examination of
- 10. Scientific work of departmentneuro-endocrine mechanisms of endocrine
- 11. Pathogenesis is the study of general mechanisms of diseases onset and development.
- 12. The role of etiologic factor in disease
- 13. The main link of pathogenesis The main
- 14. The role of local and general changes
- 15. The role of pathogenic and adaptive reactions
- 16. The difference between disease and pathological process
- 17. Civilization (lifestyle) diseasesPositive consequences of civilization: resistance
- 18. Causality-effective relations in pathogenesis Direct raw of
- 19. Causality-effective relations in pathogenesisDivaricated type of eventsDilatation
- 20. Causality-effective relations in pathogenesisVicious circleHigh temperature of
- 21. Why disease developREASONSCONDITIONSDISEASEADAPTATIONORGANISM
- 22. Organism responceReactivity - ability to respond to
- 23. Types of reactivityLevels: normal, increased, low, absent
- 24. Types of resistance Passive resistance – barrier
- 25. Скачать презентацию
- 26. Похожие презентации
PATHOPHYSIOLOGYophthalmologyneurologysurgerytherapygynecologystomatologyPHARMACOLOGYPATHOLOGICALANATOMYBiologyMicrobiologyChemistryPhysicsPhilosophyNormal physiologyBiochemistryHistologyImmunologyGeneticsThe interrelations between Pathophysiology and other medical disciplines























Слайд 2
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
ophthalmology
neurology
surgery
therapy
gynecology
stomatology
PHARMACOLOGY
PATHOLOGICAL
ANATOMY
Biology
Microbiology
Chemistry
Physics
Philosophy
Normal physiology
Biochemistry
Histology
Immunology
Genetics
The interrelations between Pathophysiology and other medical
disciplines
Слайд 3
Head of Pathophysiology Department
KOLESNIK Yuri Mikhailovich
Rector of
ZSMU,
M.D., Ph.D., D.Sc., Professor, Honoured Science and Technique Worker
of Ukraine
Слайд 4
Pathophysiology
PATHOS – disease
PHYSIS – essence
LOGOS –
knowledge
Science studying the basic patterns of occurrence, development
and outcome of disease
Слайд 5
Pathophysiology tasks
Creation of the disease general conception (general
nosology)
Study of :
reasons and conditions of disease development (general
etiology)general mechanisms of disease development (general pathogenesis)
typical pathological processes which form the basis of the disease in different combination
Слайд 6
Experimental therapy
Working out of new methods of
diseases treatment and prophylaxis
Sanogenesis – mechanism of recovery
SANOS – health GENESIS – origin sanogenic therapy – type of pathogenetic treatment
(medicines, IR-rays, hypoxia, physical loading, starvation, normalization of mental state).
Слайд 7
The main methods of Pathophysiology
Experimental modelling of:
pathologic processes
on animals;
protective and adaptive reactions on animals and humans;
Types
of experiments:acute (vivisection) – collapse, shock, renal failure
chronic – atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension
Слайд 8
Pathophysiological experiment
It includes four stages:
Planning the experiment;
Carrying out
of experiment (modelling and obtaining results);
Statistic analysis of observations;
Formulating
the conclusions.
Слайд 9
The main methods of Pathophysiology
Clinical examination of various
diseases with different tests (clinical pathophysiology)
to reveal specific
features
of a disease in a certain patientto increase effectiveness of treatment
Physical and mathematical modelling
Слайд 10
Scientific work of department
neuro-endocrine mechanisms of endocrine pancreas
regulation
the role of hypothalamic neuro-hormones in diabetes mellitus
pathogenesis new methods of treatment and prophylaxis of diabetes mellitus and prevention of its complications
pathogenesis of arterial hypertension
Слайд 12
The role of etiologic factor in disease development
Etiologic
factor can “switch” some diseases (radiation sickness, myocardial infarction).
Etiologic
factor can be constantly present in the organism (insulin deficiency in diabetes mellitus).The role of etiologic factor in chronic infectious diseases changes according to the stage of disease
Слайд 13
The main link of pathogenesis
The main link
of pathogenesis is that process that is absolutely important
and underlies disease development.Allergy – release of biologically active substances and their influence on tissues (histamine and others)
Atherosclerosis – accumulation of lipids inside the vessel wall
Слайд 14 The role of local and general changes in
the organism
Local changes may start the disease (trauma,
burns) and then become the part of organism’s general reaction to injury.Local changes may appear after the development of disease’s general signs and symptoms.
Слайд 15 The role of pathogenic and adaptive reactions during
disease development
Pathogenesis of all the diseases and pathological processes
includes both pathological and adaptive reactions.Their combination, importance and the level of expression widely vary even in the patients with the same pathology.
Слайд 17
Civilization (lifestyle) diseases
Positive consequences of civilization: resistance to
infections, increased life duration.
Negative consequences: ↑ amount of meat
and lipids in food, hypodynamia, smoking, stresses. Civilization diseases: circulatory and respiratory system diseases, atherosclerosis, malignant neoplasms, diabetes, allergy etc.
Слайд 18
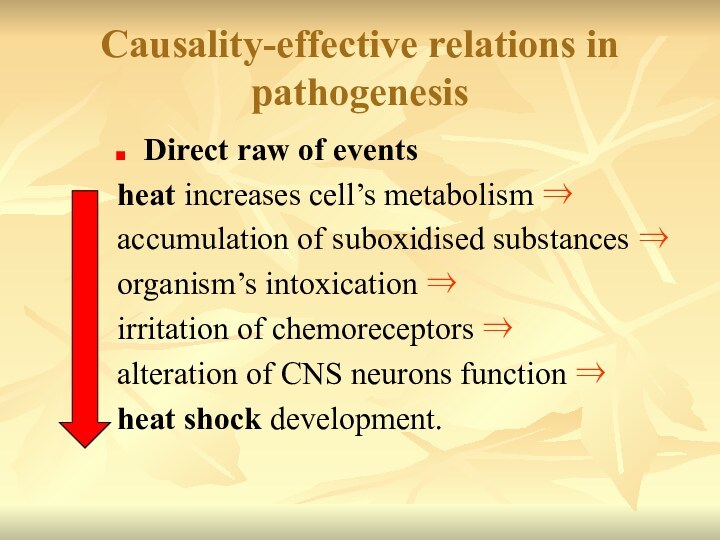
Causality-effective relations in pathogenesis
Direct raw of events
heat increases cell’s metabolism ⇒
accumulation of suboxidised substances
⇒organism’s intoxication ⇒
irritation of chemoreceptors ⇒
alteration of CNS neurons function ⇒
heat shock development.
Слайд 19
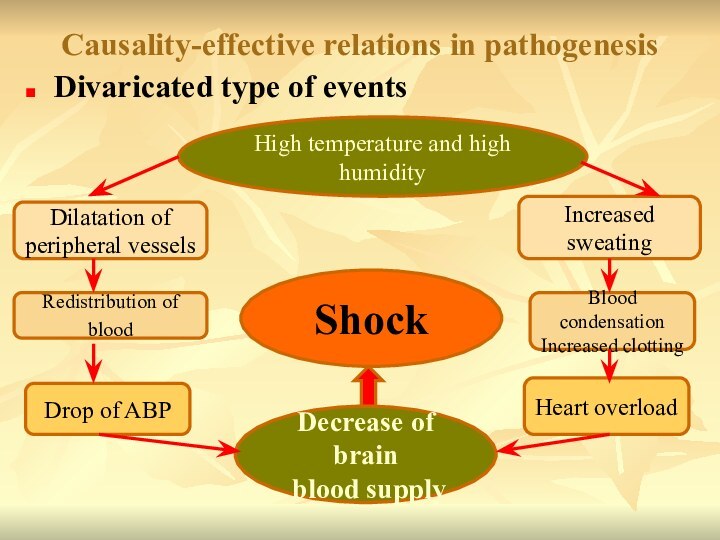
Causality-effective relations in pathogenesis
Divaricated type of events
Dilatation of
peripheral vessels
Drop of ABP
Increased sweating
Blood condensation
Increased clotting
Heart overload
Redistribution
of blood High temperature and high humidity
Decrease of brain
blood supply
Shock
Слайд 20
Causality-effective relations in pathogenesis
Vicious circle
High temperature of the
air
High body
temperature
Increased neuro-muscular
excitability
Convulsions
Increase of
retractive
thermogenesis
Слайд 22
Organism responce
Reactivity - ability to respond to internal
and external factors.
Resistance - stability of the organism to
the action of unfavorable factors. Relationship
Normally - direct dependence
irregular dependence:
? reactivity ? resistance – allergy
? reactivity ? resistance – in hibernating animals
Слайд 23
Types of reactivity
Levels: normal, increased, low, absent (anergy)
Species reactivity (fish, bird, rat, dog, human)
Group reactivity
Age-related
(newborns, children, old people)Sex-related
Constitution-related (asthenic, hyperstenic)
Individual reactivity
Слайд 24
Types of resistance
Passive resistance – barrier systems,
bactericidial agents, inborn immunity.
Active resistance – adaptative and compensatory
mechanisms.Compensatory reaction – to restore the homeostasis and decrease the injury
Adaptation –organism is adapted to environment
Cross-resistance: the development of resistance to one factor is accompanied with the stability to another factors (conditioning to cold, hypoxia)





























