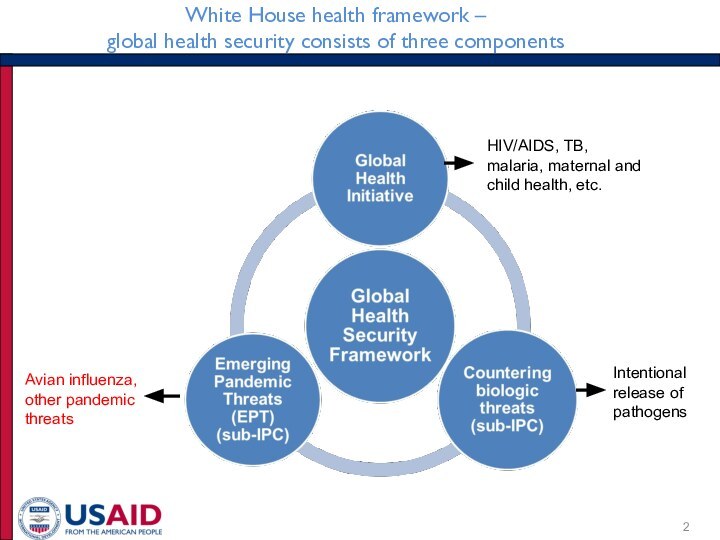
consists of three components
HIV/AIDS, TB, malaria, maternal and child
health, etc.Intentional release of pathogens
Avian influenza, other pandemic threats
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть

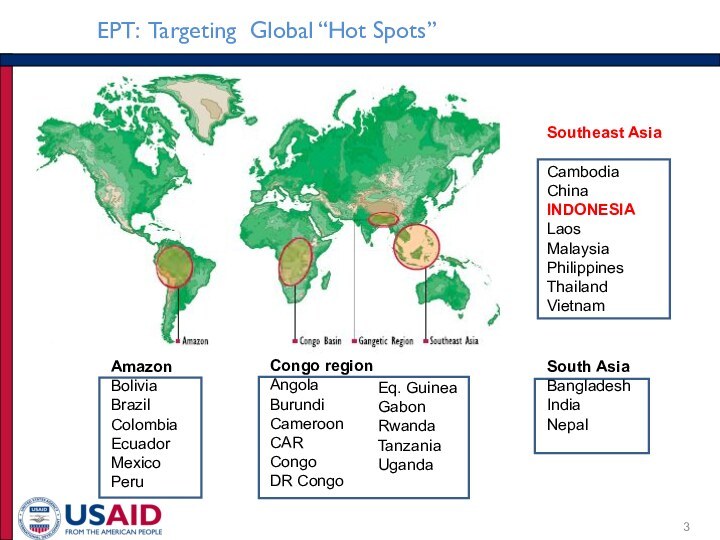





Intentional release of pathogens
Avian influenza, other pandemic threats
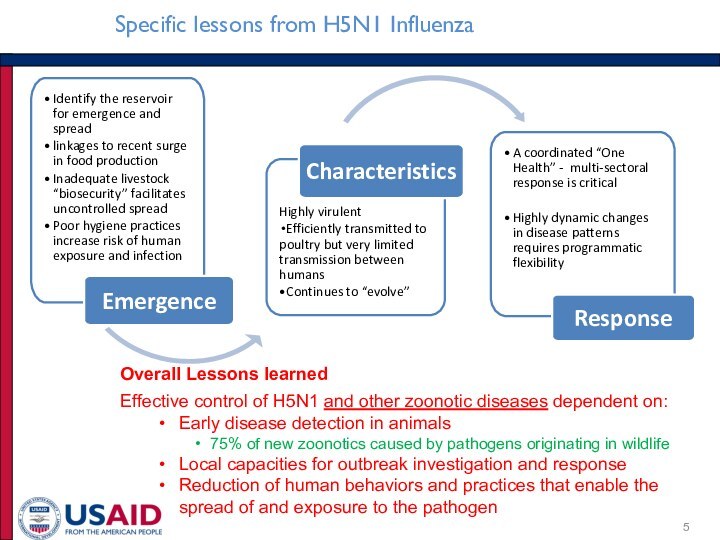
Emergence
Highly virulent
Efficiently transmitted to poultry but very limited transmission between humans
Continues to “evolve”
Characteristics
A coordinated “One Health” - multi-sectoral response is critical
Highly dynamic changes in disease patterns requires programmatic flexibility
Response
Overall Lessons learned
Effective control of H5N1 and other zoonotic diseases dependent on:
Early disease detection in animals
75% of new zoonotics caused by pathogens originating in wildlife
Local capacities for outbreak investigation and response
Reduction of human behaviors and practices that enable the spread of and exposure to the pathogen
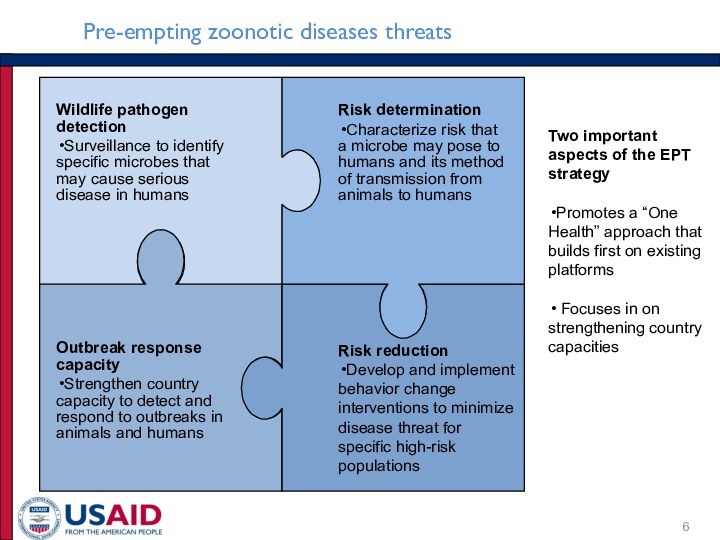
Outbreak response capacity
Strengthen country capacity to detect and respond to outbreaks in animals and humans
Two important aspects of the EPT strategy
Promotes a “One Health” approach that builds first on existing platforms
Focuses in on strengthening country capacities
Risk reduction
Develop and implement behavior change interventions to minimize disease threat for specific high-risk populations
Pre-empting zoonotic diseases threats
Develop models to predict emergence of high-consequence pathogens
Conduct active surveillance for emerging pathogens in animals and humans
Develop and test point-of care diagnostics to rule out endemic diseases
Provide laboratory support to identify new pathogens
Strengthen field epidemiology and laboratory training programs
Collaborate in outbreak investigations
Laboratory support
Strengthening veterinary services
Pathogen discovery
Laboratory strengthening
Laboratory support (through Bio-engagement Program)
Public health diplomacy
*
* CDC USAID provides some funding to CDC for EPT activities.
Pathogen Detection,
Risk (biological) Determination
Outbreak response capacity
Risk (behavioral)
Determination,
Risk Reduction
Strengthen Laboratories
Since officially launched last July 2011