Слайд 2
Process Basics
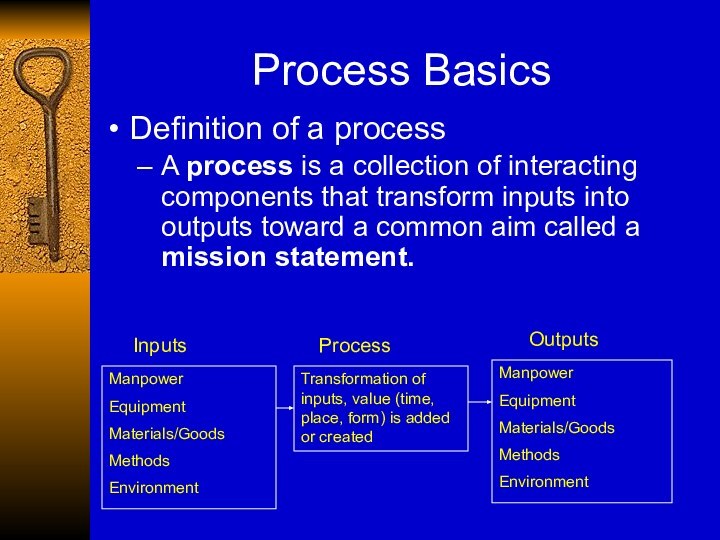
Definition of a process
A process is
a collection of interacting components that transform inputs into
outputs toward a common aim called a mission statement.
Manpower
Equipment
Materials/Goods
Methods
Environment
Inputs
Transformation of inputs, value (time, place, form) is added or created
Process
Manpower
Equipment
Materials/Goods
Methods
Environment
Outputs
Слайд 3
Definition of a process
It is management’s job to
optimize (improve) the entire process toward its aim.
This may
require the sub-optimization of selected components of the process.
Слайд 4
Definition of a Process
Processes exist in all facets
of organizations and our understanding of them is crucial:
Administration
Sales
and service
Human resources
Maintenance
Communication
Production
Relationships between people are processes
All processes can be studied, documented, defined, improved, and innovated.
Слайд 5
Definition of a process
An organization is a multiplicity
(great number) of micro sub-processes, all synergistically (robust) building
to the macro process of that firm.
All processes have customers and suppliers; these customers and suppliers can be internal or external to the organization.
Слайд 6
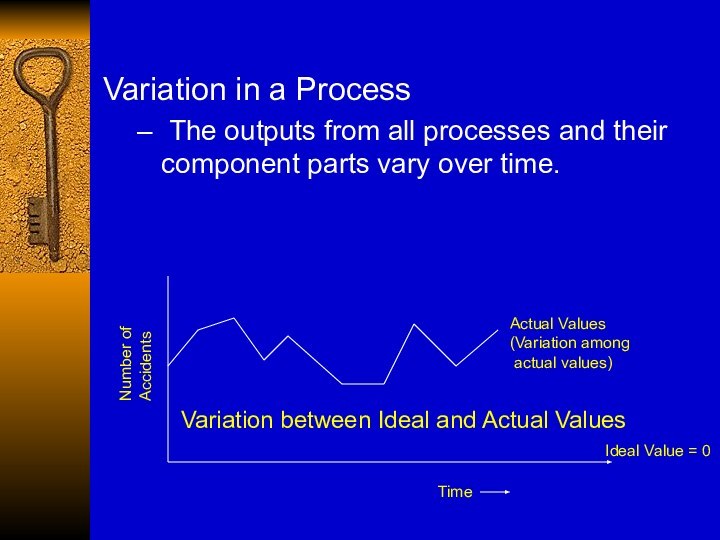
Variation in a Process
The outputs from all
processes and their component parts vary over time.
Time
Number of
Accidents
Actual
Values
(Variation among
actual values)
Ideal Value = 0
Variation between Ideal and Actual Values
Слайд 7
Variation in a process
Special causes of variation are
due to events external to the usual functioning of
a system.
Examples could include (if they are not part of the system):
New raw materials
New employee
A new operator
Слайд 8
Variation in a process
Common causes of variation are
due to the process itself.
Process capability is determined by
inherent (deeply come) common causes of variation.
Examples of common causes of variation include:
Hiring, training and supervisory practices
Lighting
Stress
Management style
Policies and procedures
Design of products or services
Слайд 9
Variation in a process
Employees cannot control a common
cause of variation.
Managers must realize that unless a
change is made in the process (which only they can make) the process’s capability will remain the same.
Слайд 11
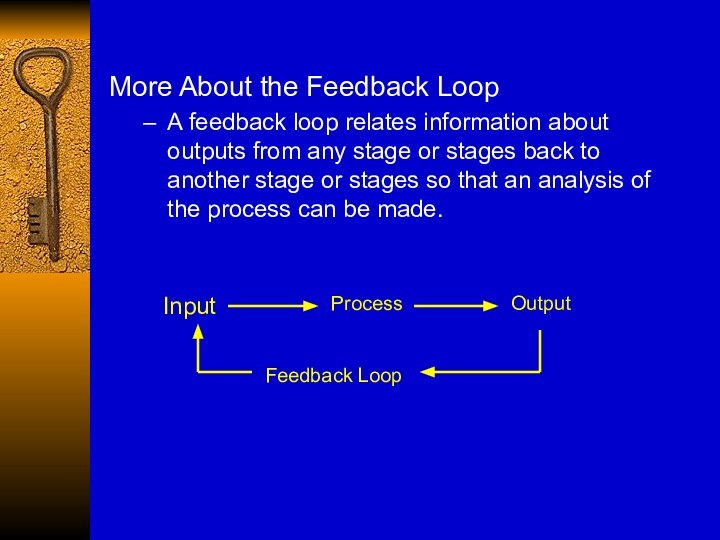
More About the Feedback Loop
A feedback loop relates
information about outputs from any stage or stages back
to another stage or stages so that an analysis of the process can be made.
Input
Process
Output
Feedback Loop
Слайд 12
More About the Feedback Loop
There are three feedback
loop situations
no feedback loop
special cause only feedback
loop
special and common cause feedback loop
Слайд 13
The Quality Environment
The pursuit (follow up) of quality
requires that organizations globally optimize (develop) their system of
interdependent (correlation) stakeholders.
This system includes employees, customers, investors, suppliers and subcontractors, regulators, the environment, and the community.
Слайд 14
Employees are the most critical stakeholders of an
organization.
According to quality expert Kaoru Ishikawa: “In management,
the first concern of the company is the happiness of people who are connected with it. If the people do not feel happy and cannot be made happy, that company does not deserve to exist. . . The first order of business is to let the employees have adequate income. Their humanity must be respected, and they must be given an opportunity to enjoy their work and lead a happy life.”
Слайд 15
Types of Quality
There are three types of quality:
Quality
of design / redesign
Quality of conformance
Quality of performance
The above
types of quality create the never ending spiral (cycle) of continuous improvement of products, services or processes
Слайд 16
Quality of design
Quality of design / redesign
focuses on determining the quality characteristics of products that
are suited to the needs and wants of a market, at a given cost; that is, quality of design develops products from a customer orientation.
Слайд 17
Quality of design / redesign
Quality of design studies
begin with consumer research, service call analysis, and sales
call analysis, and lead to the determination of a product concept that meets the consumer’s needs and wants.
Next, specifications are prepared for the product concept.
Слайд 18
Quality of conformance
Quality of conformance is the extent
to which a firm and its suppliers can produce
products with a predictable degree of uniformity (symmetry) and dependability (confidence and accreditation), at a cost that is in keeping with the quality characteristics determined in a quality-of-design study.
The ultimate (main) goal of process improvement and innovation efforts is to create products and services whose quality is so high that consumers (both external and internal) extol (celebrate, achieve) them.
Слайд 19
Quality-of-performance
Quality of performance studies focus on determining how
the quality characteristics determined in quality-of-design studies, and improved
and innovated in quality-of-conformance studies, are performing in the marketplace.
The major tools of quality-of-performance studies are consumer research and sales/service call analysis.
These tools are used to study after-sales service, maintenance, reliability, and logistical support, as well as to determine why consumers do not purchase the company’s products.
Слайд 20
Relationship between
Quality and Cost
Features and Price
Features and
price determine whether a consumer will initially enter a
market segment; hence features and price determine market size.
Dependability (confidence) and uniformity (organizing) determine a product’s success, and therefore its market share, within a market segment.
Слайд 21
Generally, products or services with more features have
higher costs to the manufacturer and higher prices to
the consumer than products or services with fewer or simpler features.
Слайд 23
Dependability and Uniformity:
Accreditation and standards
Uniformity and dependability
create an inverse relationship between quality and cost. When
the degree of uniformity and dependability of a product is high, the quality of the product is high, and the overall cost to both the manufacture and the consumer is less.
Слайд 24
Conclusion
Managers must balance the cost of having
many market segments with the benefits of high consumer
satisfaction caused by small deviations between an individual consumer’s needs and the product characteristic package for his market segment. Also, managers must continually strive to reduce variation in product characteristics for all market segments.
Слайд 25
Stressing productivity often has the opposite effect of
what management desires
Management’s ability to improve the process results
in a decrease in defectives, yielding an increase in good units, quality, and productivity