- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Spreadsheets
Содержание
- 2. Spreadsheet A spreadsheet is an interactive
- 3. The program operates on data represented as
- 4. The user of the spreadsheet can make
- 5. In addition to the fundamental operations of
- 6. Spreadsheets have now replaced paper-based systems throughout
- 7. First spreadsheetVisiCalc was the first electronic spreadsheet
- 8. Screenshot of VisiCalc
- 9. MS-DOSLotus 1-2-3 (1983) was the leading spreadsheet
- 10. Lotus 1-2-3
- 11. Other MS-DOS spreadsheetsBorland Quattro that replaced VisiCalc.
- 12. Now Excel now has the largest market
- 13. Microsoft ExcelSince the mid 1990s Excel has been the domineering commercial electronic spreadsheet.
- 14. Open source softwareGnumeric is a free, cross-platform
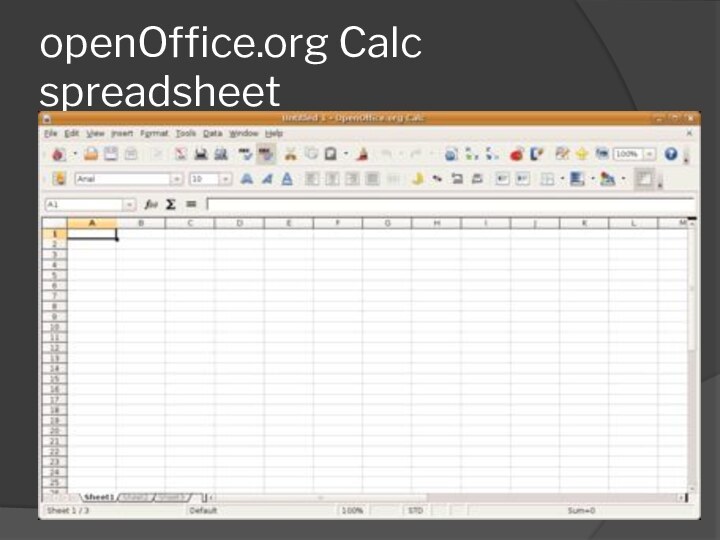
- 15. openOffice.org Calc spreadsheet
- 16. Web-based spreadsheetsOffice Web AppsGoogle SpreadsheetsThey have real-time
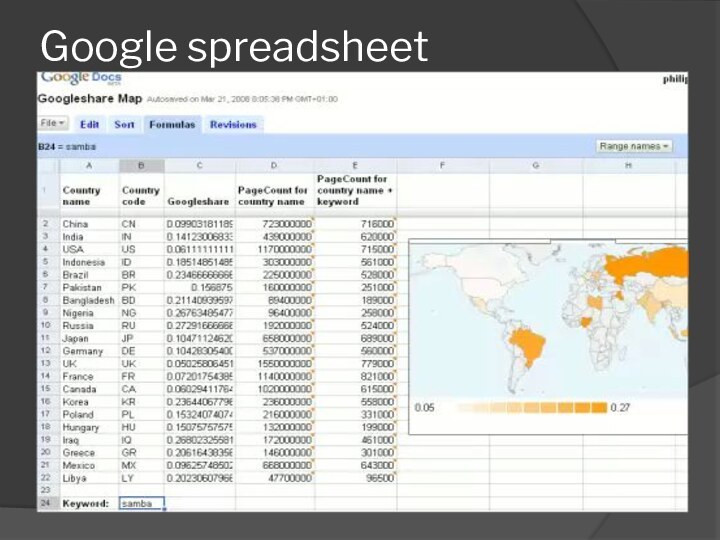
- 17. Google spreadsheet
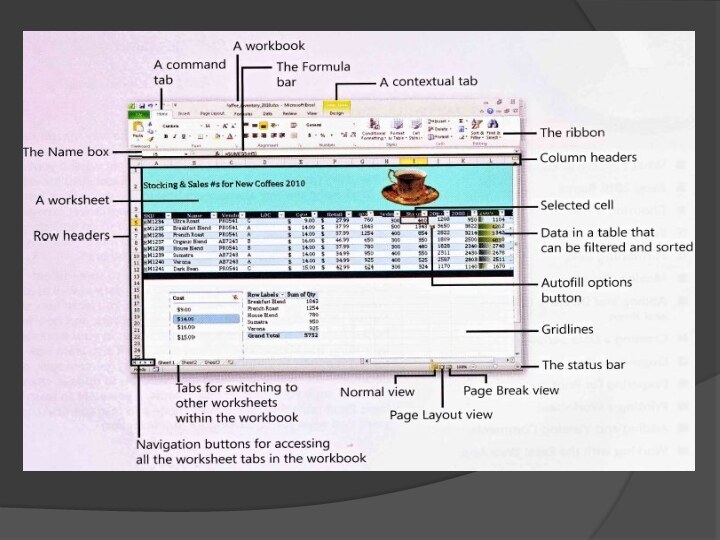
- 18. Excel 2010Organize financial informationPerform calculationsDisplay results in different ways
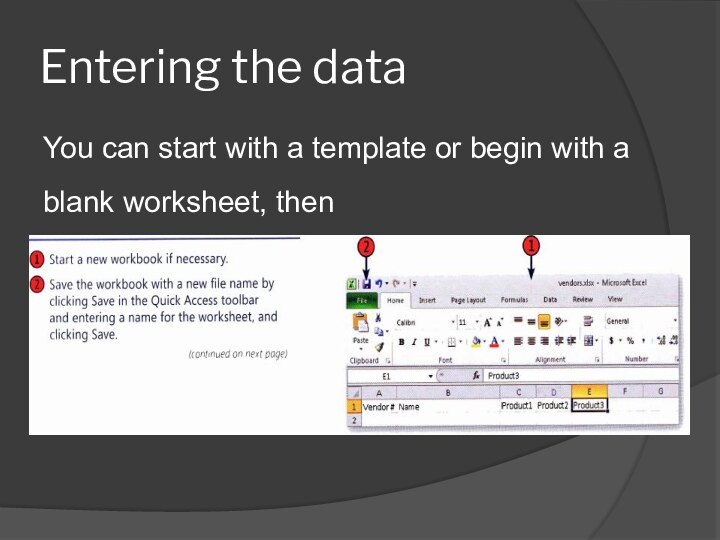
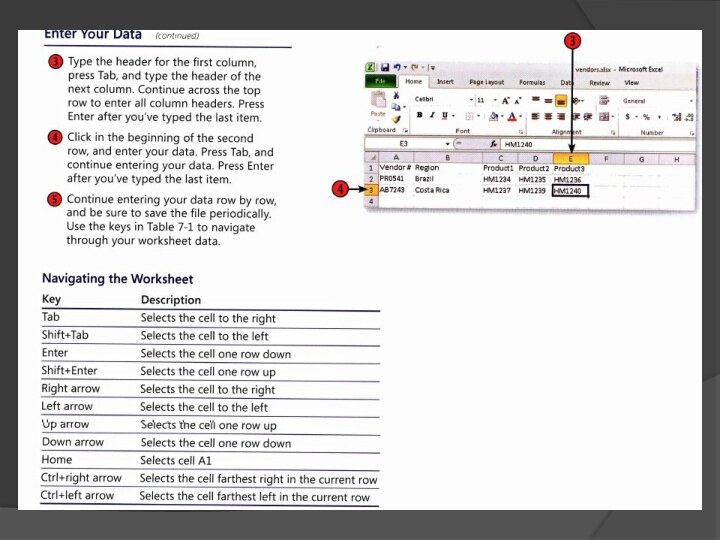
- 21. Entering the dataYou can start with a template or begin with a blank worksheet, then
- 23. More sourcesYou can also import data from
- 24. Some factsNumber of rows 1 048 576Number
- 25. Editing dataOften you need to go back
- 26. Formatting cellsYou can considerably improve the look
- 27. Example of a worksheet with some formatting
- 28. Predefined formatsFor this purpose, you can use
- 29. Formatting numbersWhen you look at columns and
- 30. Moving, copying, pastingMoving, copying and pasting data
- 31. Live PreviewExcel 2010 includes Paste with Live
- 32. Adding and deleting columns and rowsWhen you
- 33. Hiding columns and rowsWhen you create a
- 34. To do this,You select rows or columns
- 35. How?To check for hidden rows or columns,
- 36. Formatting cell dimensionsYou can set the Column
- 37. Formatting Cell Dimensions
- 38. Preparing for PrintingSet page dimensions:On the Page
- 39. Part II
- 40. Creating a Data Series
- 41. Formatting Cell Dimensions
- 42. Organizing Your Worksheets
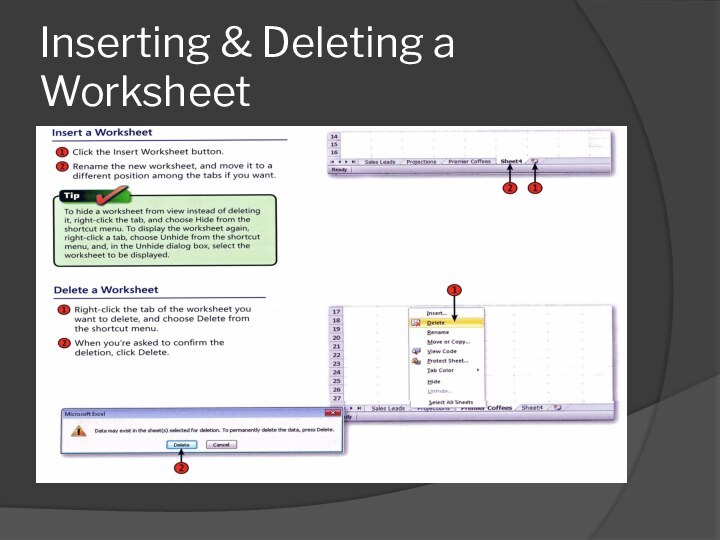
- 43. Inserting & Deleting a Worksheet
- 44. Operations in formulas
- 45. FormulasWhen you scroll the mouse over a
- 46. References RelativeAbsoluteMixed References to other worksheets
- 47. References
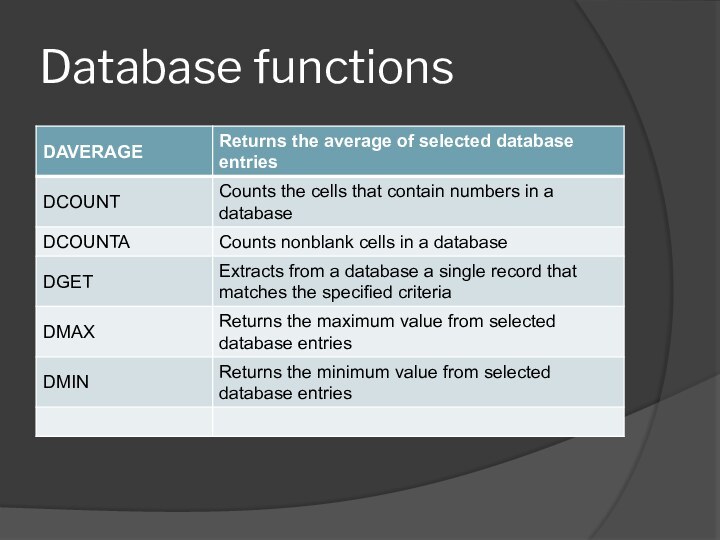
- 48. Database functions
- 49. Date and time functions
- 50. Text functions
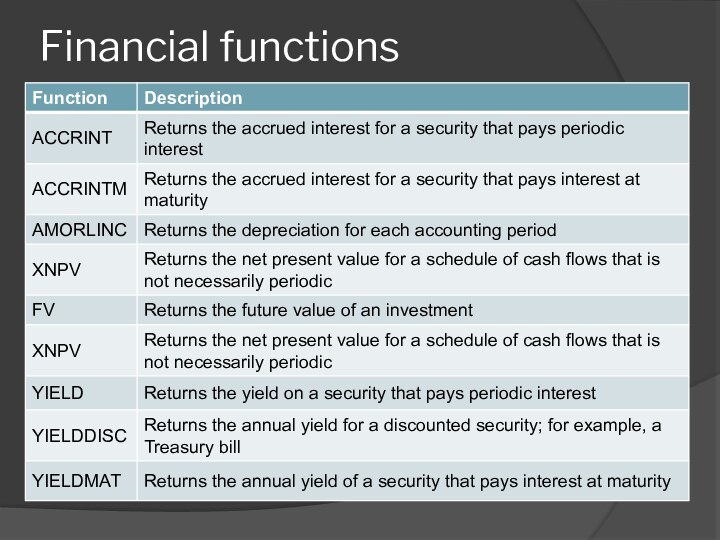
- 51. Financial functions
- 52. Information functions
- 53. Logical functions
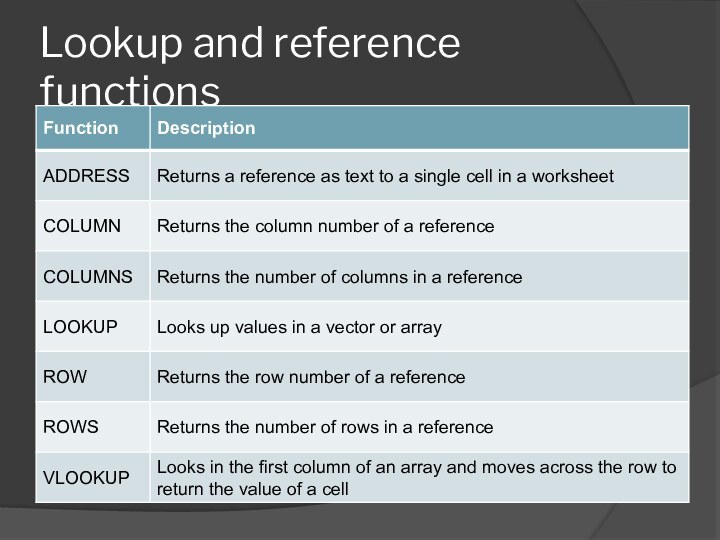
- 54. Lookup and reference functions
- 55. Math and trigonometry functions
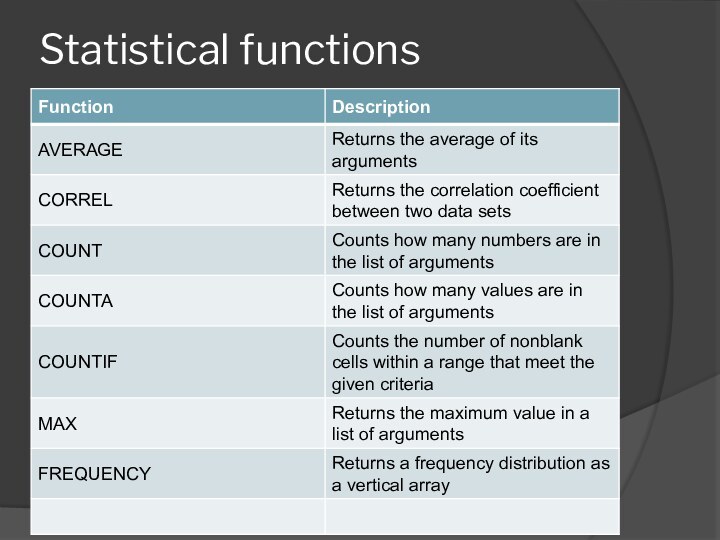
- 56. Statistical functions
- 57. Engineering functionsExternal functions
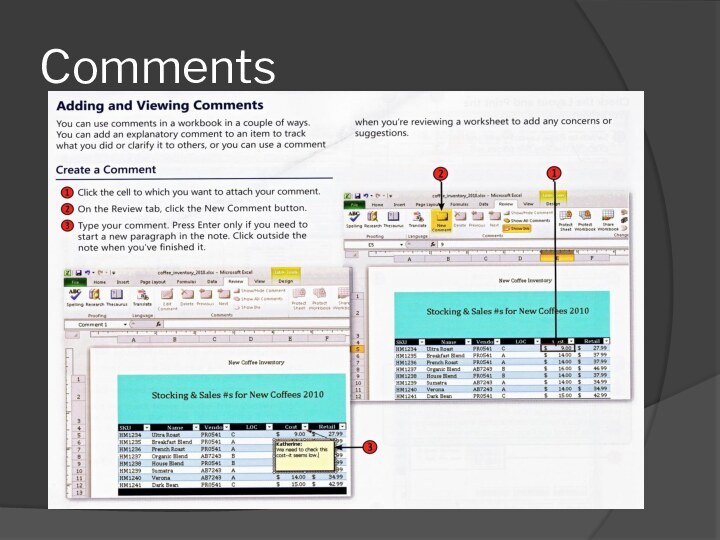
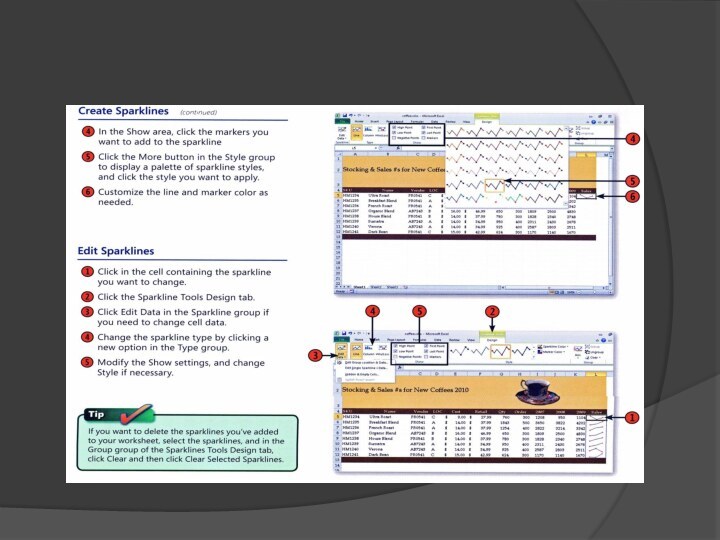
- 58. Comments
- 59. Comments
- 62. Скачать презентацию
- 63. Похожие презентации
Spreadsheet A spreadsheet is an interactive computer application program for organization and analysis of information in tabular form. Spreadsheets developed as computerized simulations of paper accounting worksheets.
















































Слайд 3 The program operates on data represented as cells
of an array, organized in rows and columns. Each
cell of the array is a model–view–controller element that can contain either numeric or text data, or the results of formulas that automatically calculate and display a value based on the contents of other cells.Слайд 4 The user of the spreadsheet can make changes
in any stored value and observe the effects on
calculated values. This makes the spreadsheet useful for "what-if" analysis since many cases can be rapidly investigated without tedious manual recalculation. Modern spreadsheet software can have multiple interacting sheets, and can display data either as text and numerals, or in graphical form.Слайд 5 In addition to the fundamental operations of arithmetic
and mathematical functions, modern spreadsheets provide built-in functions for
common financial and statistical operations. Such calculations as net present value or standard deviation can be applied to tabular data with a pre-programmed function in a formula. Spreadsheet programs also provide conditional expressions, functions to convert between text and numbers, and functions that operate on strings of text.Слайд 6 Spreadsheets have now replaced paper-based systems throughout the
business world. Although they were first developed for accounting
or bookkeeping tasks, they now are used extensively in any context where tabular lists are built, sorted, and shared.
Слайд 7
First spreadsheet
VisiCalc was the first electronic spreadsheet on
a microcomputer, and it helped turn the Apple II
computer into a popular and widely used system (1979). For IBM PC in 1981.
Слайд 9
MS-DOS
Lotus 1-2-3 (1983) was the leading spreadsheet when
DOS was the dominant operating system, was written specially
for IBM PC => good performance. The first “killer application”
Слайд 12
Now
Excel now has the largest market share
on the Windows and Macintosh platforms.
A spreadsheet program
is a standard feature of an office productivity suite; since the advent of web apps, office suites now also exist in web app form.
Слайд 13
Microsoft Excel
Since the mid 1990s Excel has been
the domineering commercial electronic spreadsheet.
Слайд 14
Open source software
Gnumeric is a free, cross-platform spreadsheet
program that is part of the GNOME Free Software
Desktop Project. OpenOffice.org Calc and the very closely related LibreOffice Calc are free and open-source spreadsheets.
Слайд 16
Web-based spreadsheets
Office Web Apps
Google Spreadsheets
They have real-time updates
from remote sources such as stock prices and currency
exchange rates.
Слайд 18
Excel 2010
Organize financial information
Perform calculations
Display results in different
ways
Слайд 23
More sources
You can also import data from
a
text file,
a Web source
MS Access database
In this case
you click the Data tab and click your choice in the Get External Data group, then navigate to the file you want to use and click Open to add your data at the selected cell.
Слайд 24
Some facts
Number of rows 1 048 576
Number of
columns 16 385
Width of column 255 characters
Number of colours 16
mln
Слайд 25
Editing data
Often you need to go back and
make changes to your data after you have entered
it.You can correct and update the data quickly either by replacing the contents of an entire cell or by editing the existing content.
Слайд 26
Formatting cells
You can considerably improve the look of
your worksheet by using Excel’s many formatting features. Formatting
your data serves a number of purposes:Helps others reviewing your data see easily what’s most important on the worksheet;
Helps you organize your data so that you can easily find what you need later.
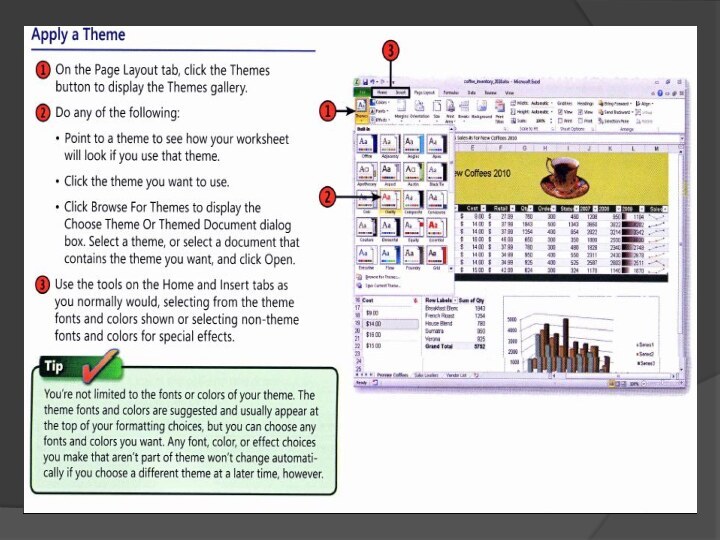
Слайд 28
Predefined formats
For this purpose, you can use Excel’s
predefined formats to choose a look for your cells
that makes the data stand out. The cell styles available in the Styles group of the Home tab are coordinated with the theme you select for the worksheet, so all colors and fonts available are consistent with the overall theme you have chosen.
Слайд 29
Formatting numbers
When you look at columns and rows
full of numbers it might not be clear what
those numbers represent. Are they values showing dollar amount? Are they percentages of something? You can improve the readability of your workbook by using standard numeric formatting to make everything as clear as possible for those viewing your worksheet.
Слайд 30
Moving, copying, pasting
Moving, copying and pasting data is
similar to the same in Word.
However, when you copy
data in Excel, you’ll need to have a blank area ready to receive the data; otherwise, Excel will overwrite any existing data.You can also tell Excel to copy the contents of a cell to a group of adjacent cells.
Слайд 31
Live Preview
Excel 2010 includes Paste with Live Preview
feature to see how your information will look when
pasted using different paste options.You can choose how you want the information to be pasted both before and after you add it to your worksheet.
Слайд 32
Adding and deleting columns and rows
When you add
or delete several rows or columns at one time
or clear all the contents of multiple rows or columns, select them before you right-click. To select nonadjacent rows or columns. Hold down the Ctrl key as you click each row or column header.To quickly clear the content of a selected cell or cells without removing any formatting, press the Delete key.
Слайд 33
Hiding columns and rows
When you create a worksheet,
it sometimes contains columns and rows of data that
aren’t relevant for every review or for every use of the worksheet.You can suppress the display of data you do not want displayed for general view by hiding columns and rows. Late you can reveal the data once again easily to return the data to normal view.
Слайд 34
To do this,
You select rows or columns and
then right-click on the selected headers, and choose Hide
from the shortcut menu.BUT, to make sure that you do not accidentally distribute a worksheet that contains information you do not want to share with others, make sure there are no hidden rows or columns in your final version of the workbook.
Слайд 35
How?
To check for hidden rows or columns, run
the Document Inspector by clicking the File tab, and
then clicking Check For Issues in the Prepare Sharing group.Click Inspect Document in the list.
Слайд 36
Formatting cell dimensions
You can set the
Column width
Row
height
Adjust the Height or Width to fit the content
Слайд 38
Preparing for Printing
Set page dimensions:
On the Page Layout
tab click Margin and set the ones you want
to.Click the Orientation button and click either Portrait or Landscape
Click the Size button, and select the paper size
Specify the scaling to change the size of the printed worksheet
Specify whether you want to display and/or print the gridlines and the headings
Слайд 45
Formulas
When you scroll the mouse over a formula
Excel will have a small dialog box that explains
thepurpose of each formula.





























