- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Factors influencing human interaction. Managing technical people
Содержание
- 2. 9 week: Communication10 week: Decision Making11 week: Negotiation12 week: Conflict Management13 week: Managing Relationships14 week: LeadershipFUTHERMORE
- 3. Skills of Effective ManagersFactors of Human InteractionProcess
- 4. Understand the complexity of software developmentBe aware
- 5. A multidisciplinary approach combining:Management ScienceBehavioral ScienceDecision ScienceLeadership ScienceWhat Is This Course About?
- 6. You interact with the world around youVarious
- 7. “Today’s business graduates have an abundance of
- 8. “In 360-degree surveys, managers typically rate themselves
- 9. WHAT SKILLS MUST AN EFFECTIVE MANAGER HAVE?Setting
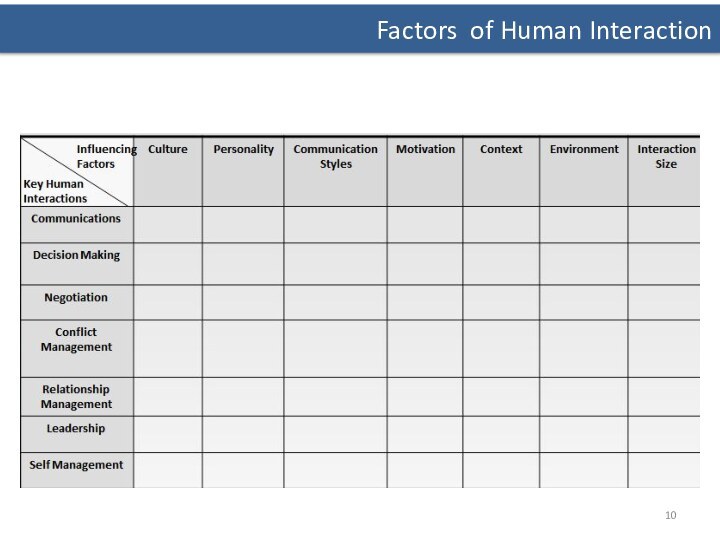
- 10. Factors of Human Interaction
- 11. Factors of Human Interaction
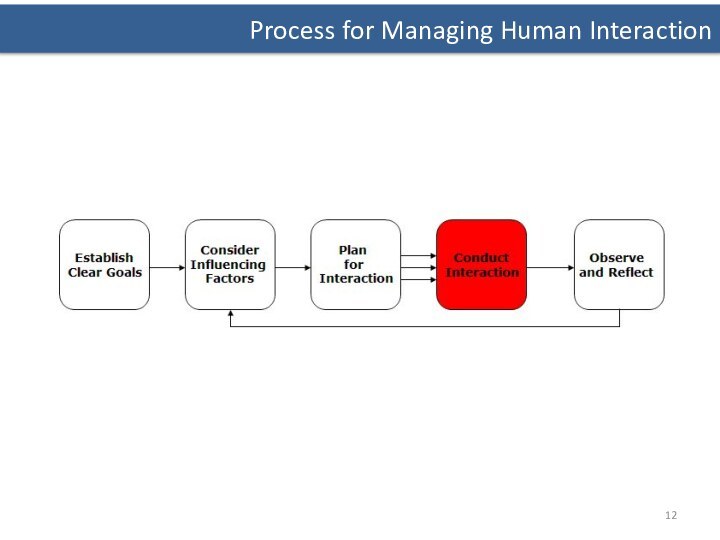
- 12. Process for Managing Human Interaction
- 13. Process for Managing Human Interaction (Scenario) Think
- 14. What is Culture?“Patterns of thinking, feeling and acting learned throughout a lifetime.”Geert Hofstede Dutch Social Psychologist
- 15. What is Culture?Culture is comprised of our:Social
- 16. Why should we care?Today’s workplace is globalRecognizing cultural differences helps foster mutual understanding
- 17. Cultural Differences
- 18. Cultural Differences“For a German and a Finn,
- 19. Hofstede’s Cultural DimensionsPower Distance Index (PDI) Focuses
- 20. Examples: Culture’s Consequences
- 21. Culture and Software DevelopmentHow do Hofstede’s cultural dimensions apply to software development?
- 22. A ScenarioYour phone rings. One of your
- 23. Stereotypes about Software DevelopersSoftware Developers:Are lonersLike to
- 24. Personality Types Stereotypes exist as a result of
- 25. Personality Types Back in the days of the
- 26. Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)Myers-Briggs Type Inventory
- 27. Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)Main application areas
- 28. Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)
- 29. Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)
- 30. Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)Thinking Make decisions
- 31. Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)Thinking Make decisions
- 32. Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)
- 33. Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)
- 34. Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)http://www.myersbriggs.org/my-mbti-personality-type/mbti-basics/
- 35. Platinum Rule Behavior Styles
- 36. SocializersRelationship-oriented“Big Picture” people Prefer a faster-paced atmosphereGather
- 37. Directors:Driven, task-oriented and like to be in
- 38. Thinkers:Analytic problem-solversFocus on logic and content Detailed
- 39. Relaters:Relationship-oriented Loyal, supportive and reliable Foster sincere,
- 40. Скачать презентацию
- 41. Похожие презентации

































Слайд 2
9 week: Communication
10 week: Decision Making
11 week: Negotiation
12
week: Conflict Management
Слайд 3
Skills of Effective Managers
Factors of Human Interaction
Process for
Managing Human Interaction
What is Culture?
Cultural Dimensions & Cultural Differences
Personality
Types Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)
“Platinum Rule” Behavior Styles
Topics & Agenda
Слайд 4
Understand the complexity of software development
Be aware of
the issues surrounding human aspects of software development
Improve skills
in:Communication
Conflict resolution
Leadership
Negotiations
Teamwork
Situation analysis and decision making
What Is This Course About?
Слайд 5
A multidisciplinary approach combining:
Management Science
Behavioral Science
Decision Science
Leadership Science
What
Is This Course About?
Слайд 6
You interact with the world around you
Various factors
influence human interactions
Managing people is challenging
There is no single
solution Key Principles
Слайд 7 “Today’s business graduates have an abundance of technical
knowledge. They can do linear programming problems, calculate a
discounted rate of return, develop a sophisticated marketing plan and crunch numbers on an excel spreadsheet.They’re technically solid, but most lack the interpersonal and social skills necessary to manage people. If there is an area where business schools need to improve, it’s in developing the “people skills” of their graduates.”
- A Corporate Recruiter
Skills of Effective Managers
Слайд 8 “In 360-degree surveys, managers typically rate themselves higher
than their colleagues do on most measures of performance.
This well-established pattern holds both for ratings of specific behaviors such as ‘Keeps people up-to-date with information’ and for broader performance measures such as ‘Is an effective manager overall.’ ”
“So You Think You’re a Good Listener” - Patrick Barwise and Sean Meehan, Harvard Business Review
Skills of Effective Managers
Слайд 9
WHAT SKILLS MUST AN EFFECTIVE MANAGER HAVE?
Setting goals
Decision making
Working with teams
Communicating information
Listening
Providing feedback
Leading
Managing
changeSelf awareness
Persuading
Running meetings
Resolving conflicts
Negotiating
Working with diverse groups of people
Creative problem solving
Skills of Effective Managers
Слайд 13
Process for Managing Human Interaction (Scenario)
Think about:
Goals
for the interaction
Potential influencing factors
Your plan for the interaction
Слайд 14
What is Culture?
“Patterns of thinking, feeling and acting
learned throughout a lifetime.”
Geert Hofstede
Dutch Social Psychologist
Слайд 15
What is Culture?
Culture is comprised of our:
Social Environment
Life
Experiences & Context
Family, Friends, Education
Civilization (Art, Education, etc.) vs.
Social Anthropology
Слайд 16
Why should we care?
Today’s workplace is global
Recognizing cultural
differences helps foster mutual understanding
Слайд 18
Cultural Differences
“For a German and a Finn, the
truth is the truth. In Japan and Britain, it
is all right if it doesn’t rock the boat. In China there is no absolute truth. In Italy, it is negotiable.”- Richard D. Lewis
Слайд 19
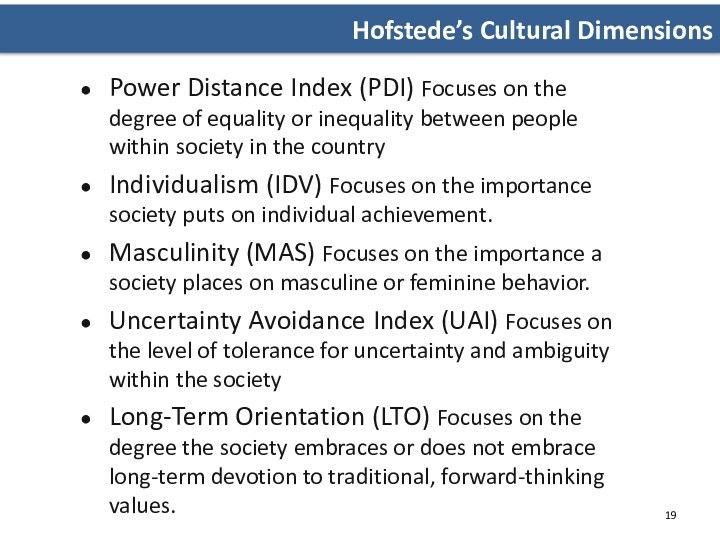
Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions
Power Distance Index (PDI) Focuses on
the degree of equality or inequality between people within
society in the countryIndividualism (IDV) Focuses on the importance society puts on individual achievement.
Masculinity (MAS) Focuses on the importance a society places on masculine or feminine behavior.
Uncertainty Avoidance Index (UAI) Focuses on the level of tolerance for uncertainty and ambiguity within the society
Long-Term Orientation (LTO) Focuses on the degree the society embraces or does not embrace long-term devotion to traditional, forward-thinking values.
Слайд 21
Culture and Software Development
How do Hofstede’s cultural dimensions
apply to software development?
Слайд 22
A Scenario
Your phone rings. One of your department
heads says he’s coming right over with a problem
that’s “urgent!”. He sounds so upset you feel he might be on the verge of an emotional meltdown.Before he arrives, you ask yourself, “What are the ways I might handle this…?”
Слайд 23
Stereotypes about Software Developers
Software Developers:
Are loners
Like to work
in isolation
Are usually quiet and talk in jargon
Have difficulty
explaining thingsDo not like to be told what to do
Слайд 24
Personality Types
Stereotypes exist as a result of someone
attempting to categorize personality characteristics and related behavior into
discrete types; and associating people with particular personality or behavior types.Some names of personality categories or characteristics you might be familiar with include:
Extroverted versus introverted
Outgoing versus shy
High key versus low key
Quick tempered versus slow to anger
Active (assertive or aggressive) versus passive
Sensing versus intuitive
Thinking versus feeling
Judging versus perceiving
Слайд 25
Personality Types
Back in the days of the ancient
Greeks, Hippocrates and Galen theorized four categories or personality
types which included:Choleric (irritable)
Melancholic (depressed)
Sanguine (optimistic)
Phlegmatic (calm)
Слайд 26
Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)
Myers-Briggs Type Inventory :
Based
on Carl Jung’s research
Developed by Katherine Briggs & Isabel
Briggs MyersFour Basic Personality Areas:
Extroverted or Introverted
Sensing or Intuitive
Thinking or Feeling
Judging or Perceiving
Слайд 27
Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)
Main application areas use
the Myers-Briggs typology:
self-knowledge and personal growth;
career and vocational guidance;
development
organizations;management and leadership training;
problem solving;
family counseling;
education and curriculum development;
scientific work;
training interpersonal interaction
Слайд 30
Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)
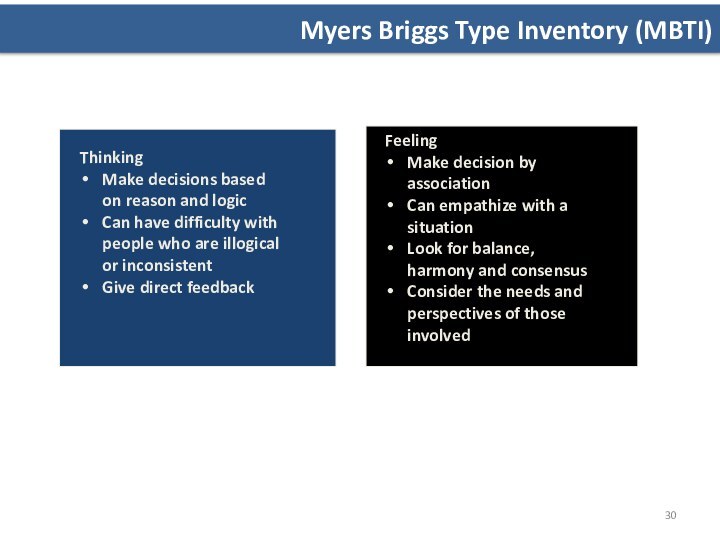
Thinking
Make decisions based
on reason and logic
Can have difficulty with people who
are illogical or inconsistentGive direct feedback
Feeling
Make decision by association
Can empathize with a situation
Look for balance, harmony and consensus
Consider the needs and perspectives of those involved
Слайд 31
Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)
Thinking
Make decisions based
on reason and logic
Can have difficulty with people who
are illogical or inconsistentGive direct feedback
Feeling
Make decision by association
Can empathize with a situation
Look for balance, harmony and consensus
Consider the needs and perspectives of those involved
Judging
Like things to be settled and organized
Task-oriented and goal focused
Prefers to make decisions instead of remaining open to new possibilities
Perceiving
Like to keep options open
Prefer to consider a wide range of options and information
Deal well with change and respond to situation as needed
Appears to be flexible and spontaneous
Слайд 34
Myers Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)
http://www.myersbriggs.org/my-mbti-personality-type/mbti-basics/
Слайд 36
Socializers
Relationship-oriented
“Big Picture” people
Prefer a faster-paced atmosphere
Gather information
verbally
Like to brainstorm and collaborate
Are persuasive
May be impatient
Can be frustrating for others to work with
Socializer
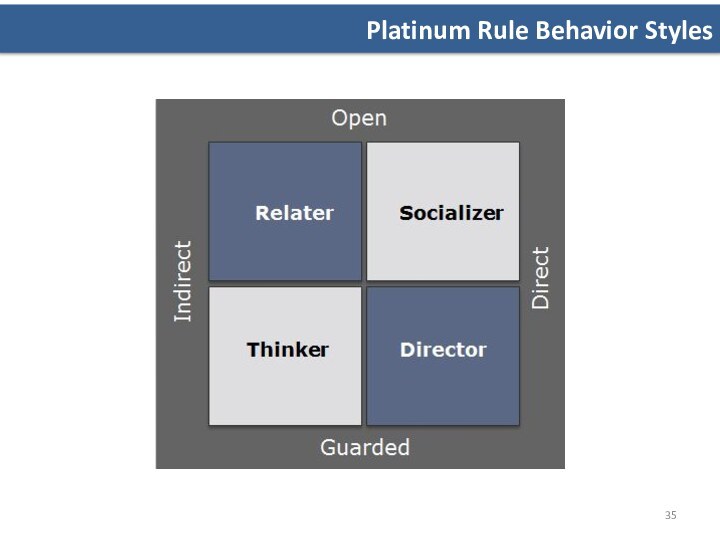
Platinum Rule Behavior Styles
Слайд 37
Directors:
Driven, task-oriented and like to be in control
Focus on change, growth and goals
Appear confident
Enjoy challenges
and risks Good problem solvers and leaders
Like fast-paced environments
Can be abrasive
May neglect personal life
Director
Platinum Rule Behavior Styles
Слайд 38
Thinkers:
Analytic problem-solvers
Focus on logic and content
Detailed oriented
Like process and structure
Avoid risk, compensate by planning
Make
decisions slowly Don’t like surprises
Can be perfectionists
Thinker
Platinum Rule Behavior Styles
Слайд 39
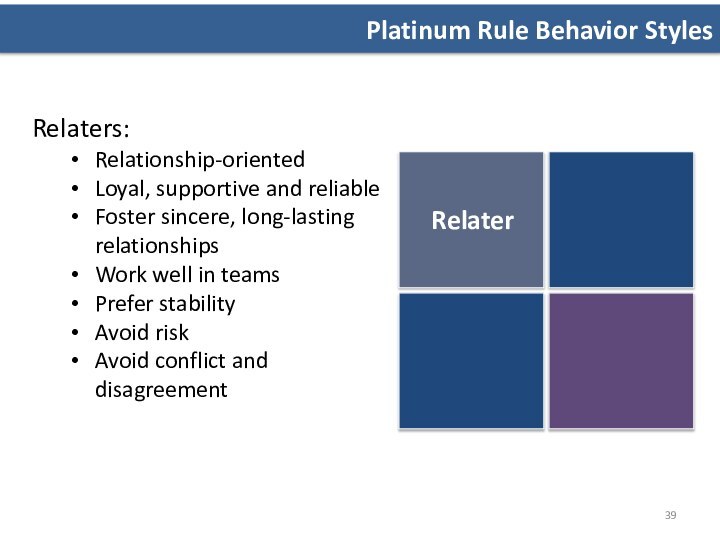
Relaters:
Relationship-oriented
Loyal, supportive and reliable
Foster sincere, long-lasting
relationships
Work well in teams
Prefer stability
Avoid risk
Avoid
conflict and disagreementRelater
Platinum Rule Behavior Styles





























