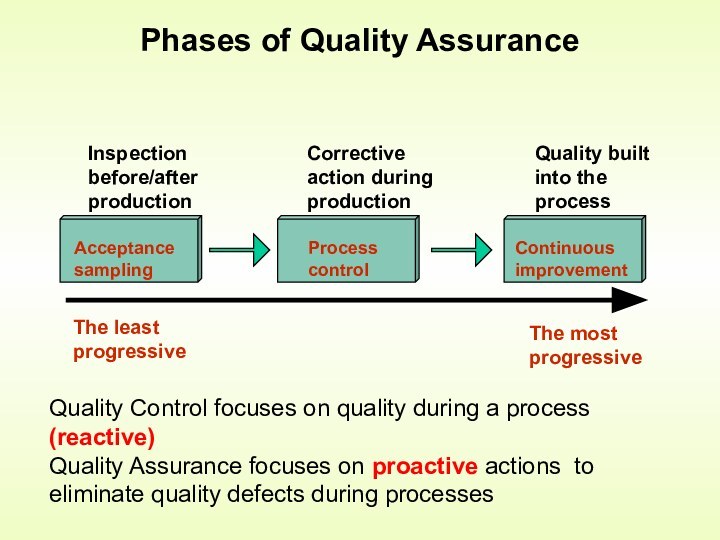
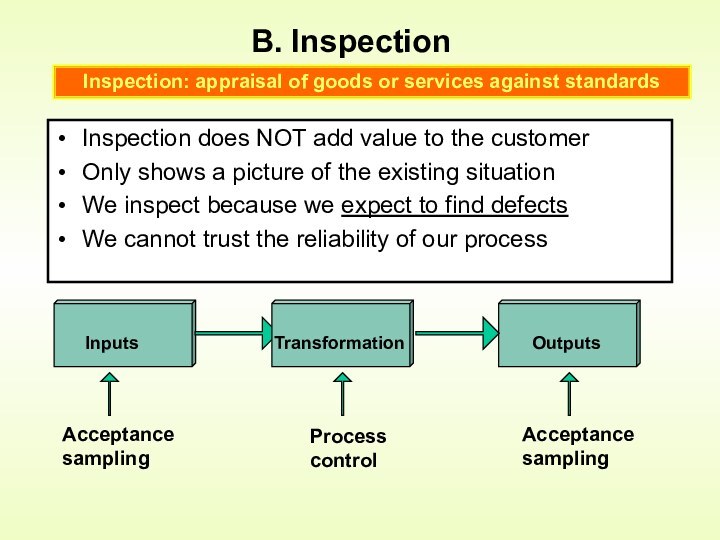
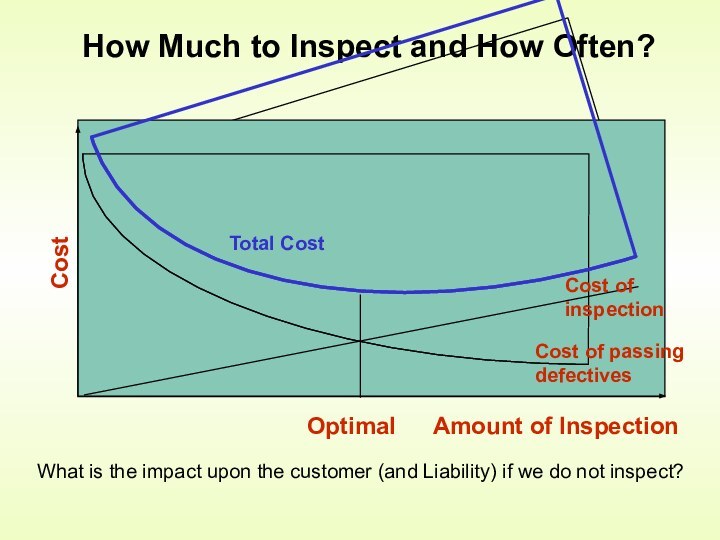
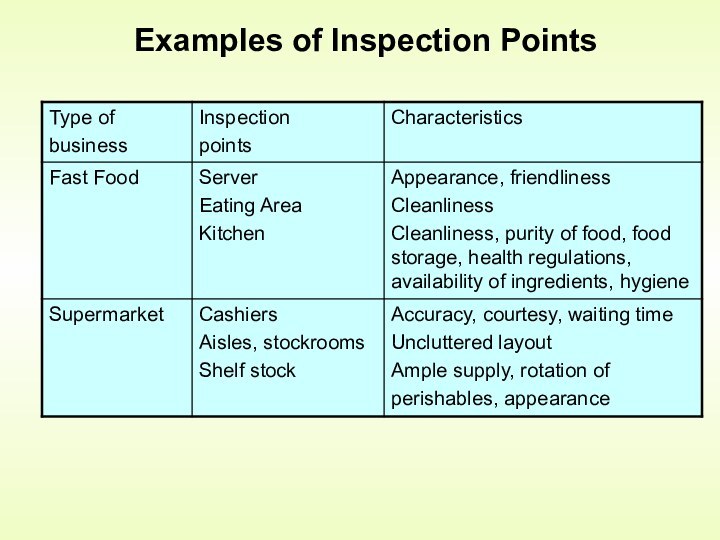
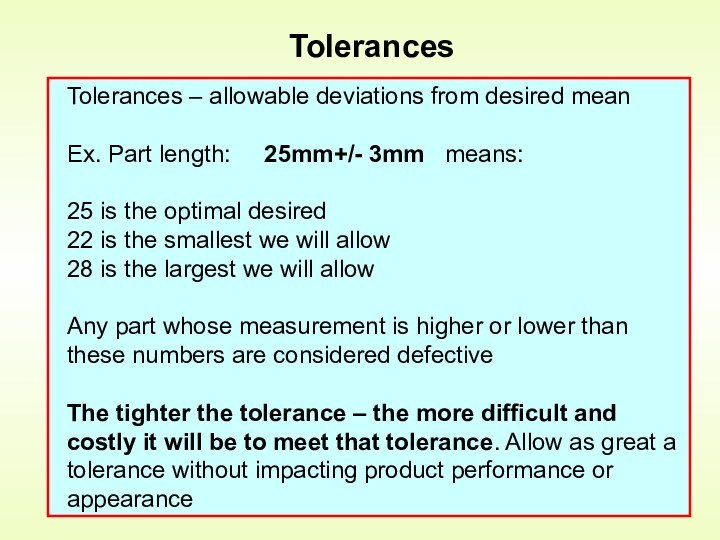
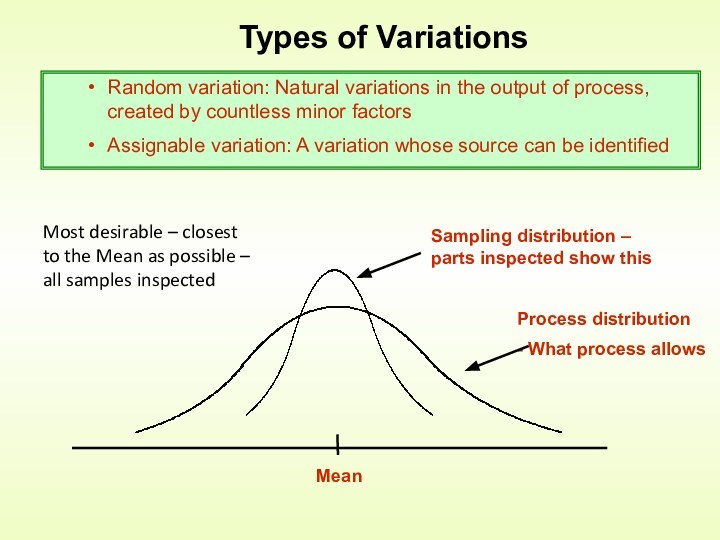
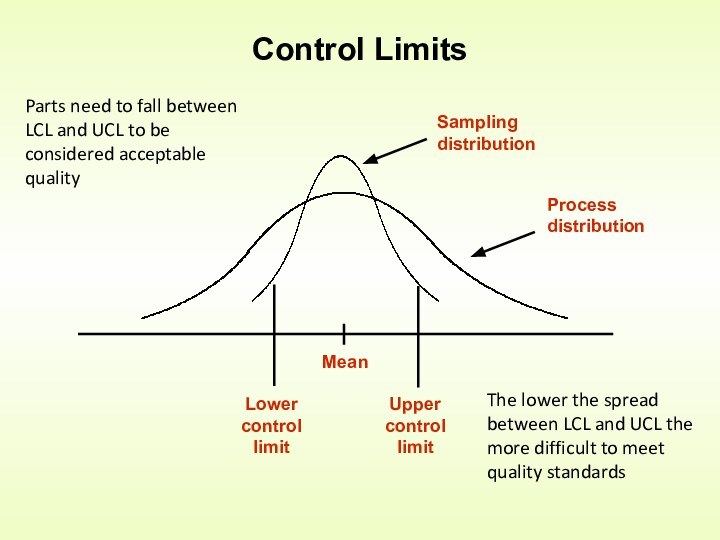
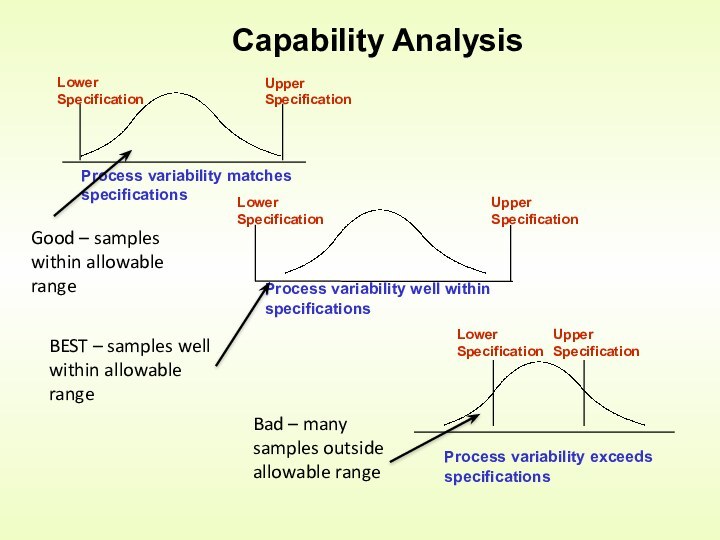
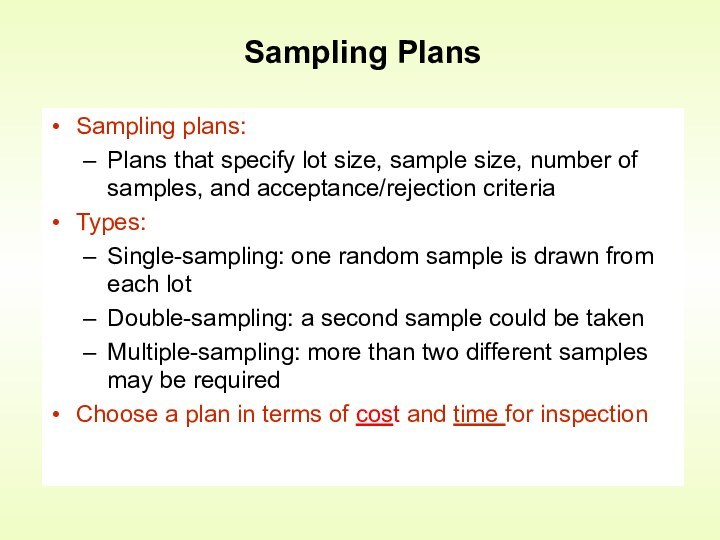
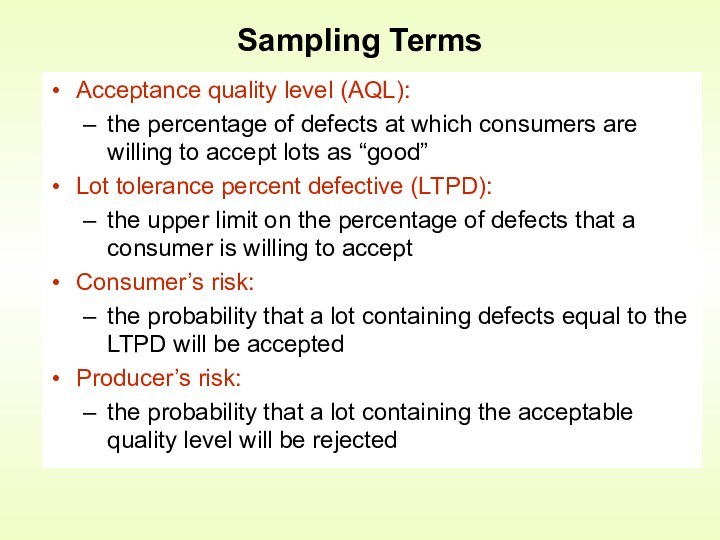
Control is an activity that evaluates quality characteristics relative
to a standard, and takes corrective action when they do not meet standardsHow is quality control accomplished?
by monitoring and inspecting the product during process (but not preventing bad quality from happening)