Слайд 2
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Lecture Outline
Strategy
Formulation
Competitive Priorities
Operations’ Role in Corporate Strategy
Strategy and the Internet
Strategic
Decisions in Operations
Strategy Deployment
Issues and Trends in Operations
Слайд 3
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Four Steps
for Strategy Formulation
Defining a primary task
What is the firm
in the business of doing?
Assessing core competencies
What does the firm do better than anyone else?
Determining order winners and order qualifiers
What wins the order?
What qualifies an item to be considered for purchase?
Positioning the firm
How will the firm compete?
Слайд 4
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Competitive Priorities
Cost
Quality
Flexibility
Speed
Слайд 5
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Competitive Priorities:
Cost
Lincoln Electric
reduced costs by $10 million a year for
10 years
skilled machine operators save the company millions that would have been spent on automated equipment
Southwest Airlines
one type of airplane facilitates crew changes, record-keeping, maintenance, and inventory costs
direct flights mean no baggage transfers
$30 million annual savings in travel agent commissions by requiring customers to contact the airline directly
Слайд 6
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Competitive Priorities:
Quality
Ritz-Carlton - one customer at a time
Every employee is
empowered to satisfy a guest’s wish
Teams at all levels set objectives and devise quality action plans
Each hotel has a quality leader
Quality reports tracks
guest room preventive maintenance cycles
percentage of check-ins with no waiting
time spent to achieve industry-best clean room appearance
Guest Preference Reports are recorded in a database
Слайд 7
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Competitive Priorities:
Flexibility
Andersen Windows
number of products offered grew from 28,000 to
86,000
number of errors are down to 1 per 200 truckloads
Custom Foot Shoe Store:
customer’s feet are scanned electronically to capture measurements
custom shoes are mailed to the customer’s home in weeks
prices are comparable to off-the-shelf shoes
National Bicycle Industrial Company
offers 11,231,862 variations
delivers within two weeks at costs only 10% above standard models
Слайд 8
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Competitive Priorities:
Speed
Citicorp
advertises a 15-minute mortgage approval
L.L. Bean
ships orders
the day they are received
Wal-Mart
replenishes its stock twice a week
Hewlett-Packard
produces electronic testing equipment in five days
General Electric
reduces time to manufacture circuit-breaker boxes into three days and dishwashers into 18 hours
Dell
ships custom-built computers in two days
Motorola
needs less than 30 minutes to build to order pagers
Слайд 9
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Operations’ Role
in Corporate Strategy
Operations provides support for a differentiated strategy
Operations
serves as a firm’s distinctive competence in executing similar strategies better than competitors
Слайд 10
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Operations Strategy
at Wal-Mart
Слайд 11
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Strategy and
the Internet
Internet can be used to create a distinctive
business strategy
eBay
unlimited capacity and a huge market
all work is done by buyers and sellers and there is no marginal cost
Cisco
integrated value chain is its competitive advantage
Слайд 12
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Strategy and
the Internet (cont.)
Internet can be used to strengthen existing
competitive advantages by integrating new and traditional activities
GE’s Trading Process Network: an automated Web-based purchasing system
cut average purchasing cost in half
enabled a much larger group of suppliers to bid on jobs
customers were able to track their orders through shop in real time
Intel
sells $2 billion a month over the Internet
purchases 80% of its direct materials online
replaced 19,000 sales-order faxes received daily
Слайд 13
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Strategy and
the Internet (cont.)
Lessons from the dot com shakedown
Internet is
the great equalizer
allows innovations to be copied with little investment
companies may reach larger market
customers have more information and can compare prices and features of their products.
These benefits are temporary unless…
Companies provide unique value to customer
Слайд 14
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Strategic Decisions
in Operations
Products
Services
Process
and
Technology
Capacity
Human
Resources
Quality
Facilities
Sourcing
Operating
Systems
Слайд 15
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Operations Strategy:
Products and Services
Make-to-order
products and services are made to customer
specifications after an order has been received
Make-to-stock
products and services are made in anticipation of demand
Assemble-to-order
products and services add options according to customer specifications
Слайд 16
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
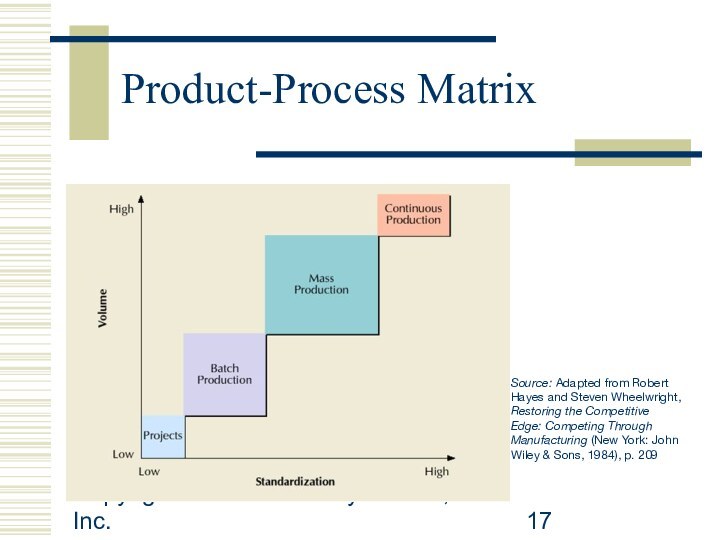
Production Strategy:
Processes
and technology
Project
one-at-a-time production of a product to customer
order
Batch production
systems process many different jobs at the same time in groups (or batches)
Mass production
large volumes of a standard product for a mass market
Continuous production
used for very high volume commodity products
Слайд 17
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Product-Process Matrix
Source:
Adapted from Robert Hayes and Steven Wheelwright, Restoring the
Competitive Edge: Competing Through Manufacturing (New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1984), p. 209
Слайд 18
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Project
Construction of
the aircraft carrier USS Nimitz was a huge project
that took almost 10 years to complete.
Batch Production
At Martin Guitars bindings on the guitar frame are installed by hand and are wrapped with a cloth webbing until glue is dried.
Mass Production
Here in a clean room a worker performs quality checks on a computer assembly line.
Continuous Production
A paper manufacturer produces a continuous sheet paper from wood pulp slurry, which is mixed, pressed, dried, and wound onto reels.
Слайд 19
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
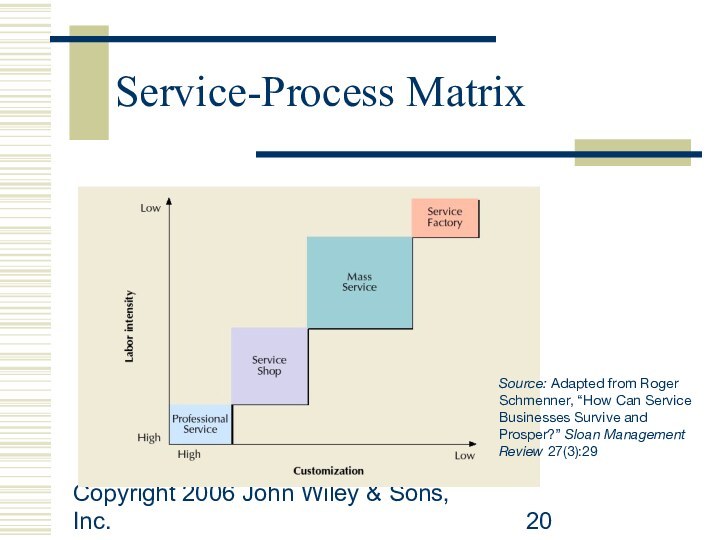
Service Strategy:
Processes
and Technology
Professional service
highly customized and very labor intensive
Service
shop
customized and labor intensive
Mass service
less customized and less labor intensive
Service Factory
least customized and least labor intensive
Слайд 20
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Service-Process Matrix
Source:
Adapted from Roger Schmenner, “How Can Service Businesses Survive
and Prosper?” Sloan Management Review 27(3):29
Слайд 21
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
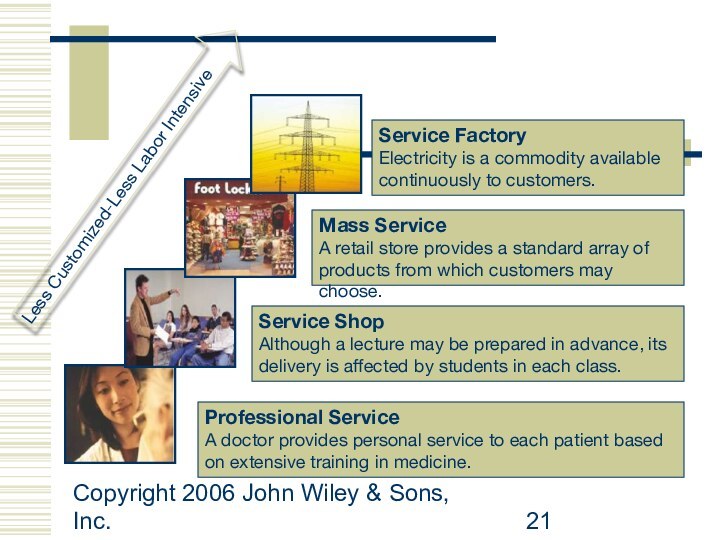
Professional Service
A
doctor provides personal service to each patient based on
extensive training in medicine.
Service Shop
Although a lecture may be prepared in advance, its delivery is affected by students in each class.
Mass Service
A retail store provides a standard array of products from which customers may choose.
Service Factory
Electricity is a commodity available continuously to customers.
Слайд 22
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Operations Strategy:
Capacity
and Facility
Capacity strategic decisions include:
When, how much, and
in what form to alter capacity
Facility strategic decisions include:
whether demand should be met with a few large facilities or with several smaller ones
whether facilities should focus on serving certain geographic regions, product lines, or customers
facility location can also be a strategic decision
Слайд 23
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Operations Strategy:
Human Resources
What is skill levels and degree of autonomy
required to operate production system?
What are training requirements and selection criteria?
What are policies on performance evaluations, compensation, and incentives?
Will workers be salaried, paid an hourly rate, or paid a piece rate?
Will profit sharing be allowed, and if so, on what criteria?
Слайд 24
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Operations Strategy:
Human Resources (cont.)
Will workers perform individual tasks or work
in teams?
Will they have supervisors or work in self-managed work groups?
How many levels of management will be required?
Will extensive worker training be necessary?
Should workforce be cross-trained?
What efforts will be made in terms of retention?
Слайд 25
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Operations Strategy:
Quality
What is target level of quality for our products
and services?
How will it be measured?
How will employees be involved with quality?
What will be the responsibilities of the quality department?
Слайд 26
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Operations Strategy:
Quality (cont.)
What types of systems will be set up
to ensure quality?
How will quality awareness be maintained?
How will quality efforts be evaluated?
How will customer perceptions of quality be determined?
How will decisions in other functional areas affect quality?
Слайд 27
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Operations Strategy:
Sourcing
Vertical integration
degree to which a firm produces parts that
go into its products
Strategic Decisions
How much of work should be done outside the firm?
On what basis should particular items be made in-house?
When should items be outsourced?
How should suppliers be selected?
Слайд 28
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Operations Strategy:
Sourcing (cont.)
What type of relationship should be maintained with
suppliers?
What is expected from suppliers?
How many suppliers should be used?
How can quality and dependability of suppliers be ensured?
How can suppliers be encouraged to collaborate?
Слайд 29
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Operations Strategy:
Operating Systems
How will operating systems execute strategic decisions?
How to
align information technology and operations strategic goals?
How information technology supports both customer and worker demands for rapid access, storage, and retrieval of information?
How information technology support decisions making process related to inventory levels, scheduling priorities, and reward systems?
Слайд 30
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Strategic Planning
Mission
and
Vision
Corporate
Strategy
Operations
Strategy
Marketing
Strategy
Financial
Strategy
Слайд 31
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Policy Deployment
Translating
corporate strategy into measurable objectives
Слайд 32
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
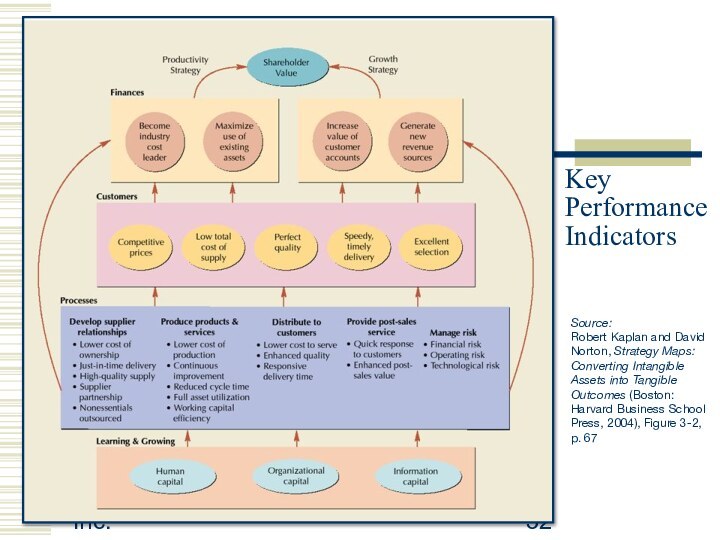
Key Performance
Indicators
Source:
Robert Kaplan and David
Norton, Strategy Maps:
Converting Intangible
Assets into
Tangible
Outcomes (Boston:
Harvard Business School
Press, 2004), Figure 3-2,
p. 67
Слайд 33
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Balanced Scorecard
Radar
Chart
Dashboard
Слайд 34
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Issues and
Trends in Operations
Global markets, global sourcing, and global operations
Virtual
companies
Greater choice, more individualism
Emphasis on service
Speed and flexibility
Слайд 35
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Issues and
Trends in Operations (cont.)
Supply chains
Collaborative commerce
Technological advances
Knowledge and ability
to learn
Environmental and social responsibilities
Слайд 36
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Characteristic
20th-Century
Corporation
21st-Century
Corporation
Changing Corporation
Organization
Focus
Style
Source
of strength
Structure
Resources
Pyramid
Internal
Structures
Stability
Self-sufficiency
Physical assets
Web
External
Flexible
Change
Interdependencies
Information
Source: Reprinted from John Byrne, “Management by
Web,” Business Week (August 28, 2000), p. 87 by special permission, copyright 2000 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Слайд 37
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Characteristic
20th-Century
Corporation
21st-Century
Corporation
Changing Corporation
(cont.)
Operations
Products
Reach
Financials
Inventories
Strategy
Vertical integration
Mass production
Domestic
Quarterly
Months
Top-down
Virtual integration
Mass customization
Global
Real-time
Hours
Bottom-up
Source: Reprinted from John Byrne,
“Management by Web,” Business Week (August 28, 2000), p. 87 by special permission, copyright 2000 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Слайд 38
Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Characteristic
20th-Century
Corporation
21st-Century
Corporation
Changing Corporation
(cont.)
Leadership
Workers
Job expectations
Motivation
Improvements
Quality
Inspirational
Employees, free agents
Personal growth
To build
Revolutionary
No compromise
Source: Reprinted from
John Byrne, “Management by Web,” Business Week (August 28, 2000), p. 87 by special permission, copyright 2000 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Dogmatic
Employees
Security
To compete
Incremental
Affordable best